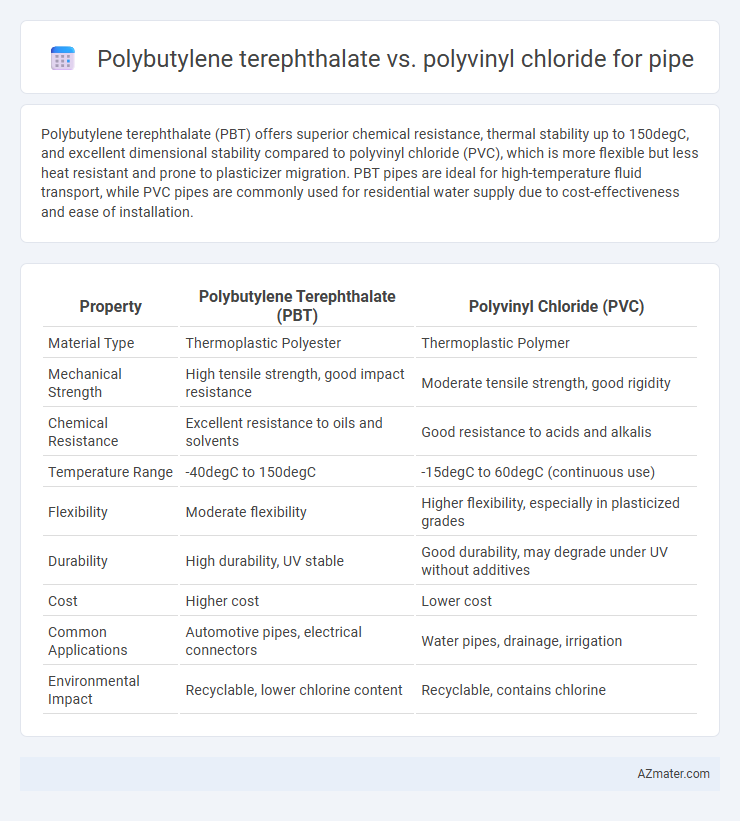
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 150degC, and excellent dimensional stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is more flexible but less heat resistant and prone to plasticizer migration. PBT pipes are ideal for high-temperature fluid transport, while PVC pipes are commonly used for residential water supply due to cost-effectiveness and ease of installation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good impact resistance | Moderate tensile strength, good rigidity |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils and solvents | Good resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -15degC to 60degC (continuous use) |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Higher flexibility, especially in plasticized grades |
| Durability | High durability, UV stable | Good durability, may degrade under UV without additives |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Common Applications | Automotive pipes, electrical connectors | Water pipes, drainage, irrigation |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, lower chlorine content | Recyclable, contains chlorine |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipes
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) pipes offer excellent chemical resistance, high mechanical strength, and superior thermal stability, making them suitable for demanding industrial and automotive applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are widely used in residential and commercial plumbing due to their affordability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation. Both materials provide durable piping solutions, but PBT generally excels in high-temperature and high-pressure environments, whereas PVC is preferred for standard water distribution and drainage systems.
Material Composition and Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its high chemical resistance, excellent dimensional stability, and superior mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-pressure pipe applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used plastic characterized by good chemical resistance, high rigidity, and cost-effectiveness, but it has lower impact resistance and thermal stability compared to PBT. The key material composition difference is that PBT is a polyester formed by polymerizing terephthalic acid and butanediol, providing enhanced thermal properties, while PVC is a vinyl polymer containing chlorine atoms, contributing to its flame retardancy but limiting high-temperature performance.
Mechanical Strength and Structural Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior mechanical strength compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with higher tensile strength and better impact resistance, making it ideal for high-stress pipe applications. PBT demonstrates enhanced structural performance due to its excellent resistance to creep and fatigue, ensuring long-term durability under dynamic loads. In contrast, PVC pipes, while cost-effective and chemically resistant, have lower mechanical strength and can become brittle over time under mechanical stress.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), particularly against hydrocarbons, oils, and various solvents used in industrial piping applications. PVC exhibits good resistance to acids, alkalis, and salts but can degrade when exposed to certain organic solvents and high temperatures, limiting its environmental suitability in harsh chemical environments. PBT's enhanced durability under thermal cycling and resistance to environmental stress cracking make it a preferable choice for long-term use in chemically aggressive conditions and environmentally demanding installations.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Tolerance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 150degC, while PVC generally withstands temperatures only up to 60degC. PBT's high melting point and resistance to thermal degradation make it ideal for applications requiring elevated temperature tolerance and long-term durability. PVC, although cost-effective and chemically resistant, is prone to deformation and softening under prolonged heat exposure, limiting its use in high-temperature piping systems.
Installation Processes and Flexibility
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) pipes offer superior flexibility and ease of installation compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, requiring fewer fittings and allowing for continuous runs that reduce leak points. PBT's heat resistance enables faster and more reliable thermal fusion joining methods, while PVC typically relies on solvent welding or mechanical joints, which can be more time-consuming and less adaptable to complex layouts. The enhanced flexibility of PBT pipes makes them ideal for installations in confined spaces or areas prone to vibration, whereas PVC's rigidity often necessitates additional supports and careful alignment during installation.
Longevity, Durability, and Maintenance Needs
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior longevity and chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), withstanding higher temperatures and UV exposure without significant degradation. PBT's enhanced durability reduces the risk of cracking and corrosion, making it ideal for industrial pipe applications where consistent structural integrity is critical. Maintenance needs for PBT pipes are minimal due to their robust resistance to wear and biofouling, whereas PVC pipes often require more frequent inspections and repairs to address brittleness and potential chlorine-induced deterioration.
Cost Analysis: PBT vs PVC Pipes
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) pipes generally have higher upfront costs compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes due to advanced material properties and manufacturing processes. PVC pipes are often favored for their cost-effectiveness in large-scale installations, offering lower material and installation expenses. Long-term cost considerations for PBT include improved chemical resistance and durability, which can reduce maintenance and replacement costs compared to PVC.
Common Applications in Plumbing and Industry
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is widely used in plumbing for its excellent chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for hot and cold water pipe systems and industrial fluid transport. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) remains dominant in plumbing due to its affordability, ease of installation, and strong resistance to corrosion and abrasion, commonly found in residential sewage and drainage systems as well as industrial waste management. PBT's superior mechanical properties make it preferable for precision-fit components in automotive and electrical conduits, while PVC's versatility supports a broad range of standard piping applications in both construction and industrial sectors.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature and aggressive chemical piping applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are widely favored for their cost-effectiveness, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation in residential and commercial plumbing. Key factors to consider when choosing between PBT and PVC include temperature range, chemical exposure, mechanical strength requirements, and long-term durability in the intended environment.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyvinyl chloride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com