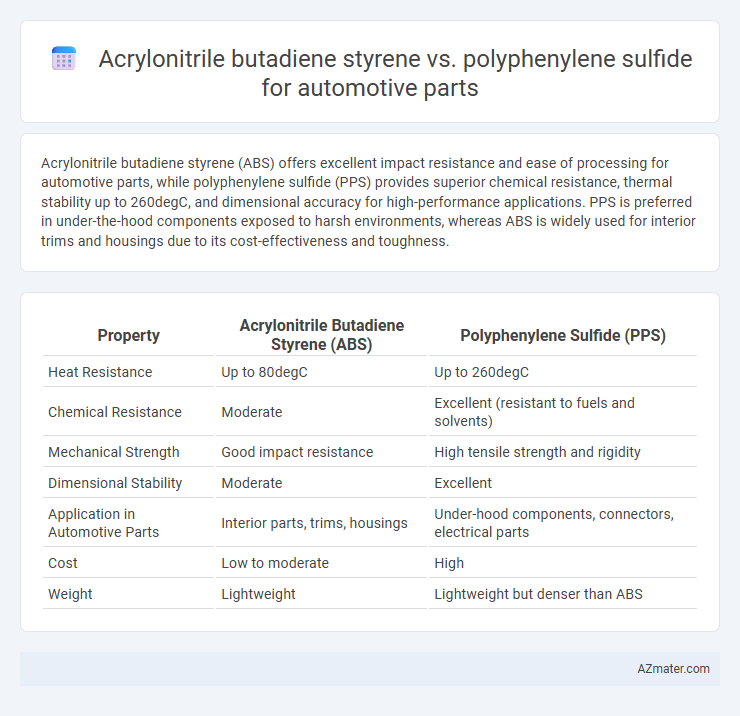
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and ease of processing for automotive parts, while polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) provides superior chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 260degC, and dimensional accuracy for high-performance applications. PPS is preferred in under-the-hood components exposed to harsh environments, whereas ABS is widely used for interior trims and housings due to its cost-effectiveness and toughness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80degC | Up to 260degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Excellent (resistant to fuels and solvents) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good impact resistance | High tensile strength and rigidity |
| Dimensional Stability | Moderate | Excellent |
| Application in Automotive Parts | Interior parts, trims, housings | Under-hood components, connectors, electrical parts |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but denser than ABS |
Overview of Engineering Plastics in Automotive Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) are prominent engineering plastics used in automotive applications due to their distinct mechanical and thermal properties. ABS offers excellent impact resistance, surface finish, and ease of processing, making it ideal for interior components such as dashboards and trims. PPS provides superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and dimensional stability, which suits under-the-hood parts requiring long-term exposure to harsh environments and elevated temperatures.
Introduction to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer in automotive parts due to its excellent impact resistance, toughness, and ease of machining. Compared to Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS), ABS offers better affordability and superior surface finish, making it ideal for interior components and housings. Its high strength-to-weight ratio and good dimensional stability allow it to meet demanding automotive industry standards for durability and performance.
Introduction to Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS)
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 260degC, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), PPS offers superior mechanical strength and resistance to fuels and lubricants, contributing to enhanced durability and longevity in under-the-hood applications. Its low moisture absorption and excellent electrical insulating properties further ensure reliable performance in critical automotive components like connectors, sensors, and housings.
Mechanical Properties: ABS vs PPS
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and good toughness, making it suitable for automotive parts subjected to moderate mechanical stress. In contrast, Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) exhibits superior tensile strength, higher dimensional stability, and outstanding resistance to fatigue and wear under high-temperature conditions. PPS is often preferred in under-the-hood automotive components where enhanced mechanical performance and chemical resistance are critical.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate thermal resistance with a heat deflection temperature around 80-100degC, making it suitable for interior automotive parts but limited in high-heat environments. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) boasts superior thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at continuous use temperatures up to 220-260degC, ideal for under-the-hood automotive components. The high thermal stability of PPS outperforms ABS in applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures and aggressive chemicals.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate chemical resistance, performing well against acids, alkalis, and oils but showing vulnerability to strong solvents and UV degradation, which can affect its long-term durability in automotive applications. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) offers superior chemical resistance, maintaining stability when exposed to aggressive chemicals such as fuels, brake fluids, and high-temperature hydrocarbons, ensuring enhanced durability and performance under harsh under-the-hood conditions. PPS's inherently high thermal stability and resistance to oxidative degradation make it a preferred choice for automotive parts requiring long-lasting durability and reliable chemical resistance in demanding environments.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers ease of injection molding with lower processing temperatures around 220-250degC, allowing faster cycle times and cost-effective manufacturing for complex automotive parts. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) requires higher processing temperatures near 280-320degC and specialized equipment to ensure thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for high-performance, under-the-hood components. ABS has better dimensional stability and surface finish flexibility, whereas PPS excels in long-term heat resistance and chemical durability, impacting tooling design and molding conditions significantly.
Cost Analysis: ABS vs PPS for Automotive Parts
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a lower initial material cost than Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS), making it a more budget-friendly choice for automotive parts requiring moderate mechanical strength and surface finish. PPS, while more expensive, delivers superior thermal resistance, chemical stability, and long-term durability, justifying its higher cost for high-performance automotive components exposed to harsh environments. The cost analysis must consider lifecycle expenses, where PPS parts often provide cost savings through enhanced longevity and reduced maintenance compared to ABS alternatives.
Typical Automotive Applications for ABS and PPS
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is widely used in automotive interiors, including dashboards, trim components, and housing for electronic modules due to its excellent impact resistance, ease of processing, and good surface finish. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is favored for under-the-hood applications such as fuel system components, engine covers, and electrical connectors because of its high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability in harsh conditions. The choice between ABS and PPS in automotive parts depends on the specific performance requirements like temperature exposure and mechanical stress.
Summary: Choosing the Right Material for Automotive Parts
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for interior automotive components like dashboards and trims. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) provides superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, well-suited for under-the-hood applications exposed to high temperatures and harsh environments. Selecting the right material depends on balancing mechanical performance, thermal endurance, and environmental exposure specific to the automotive part's function.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyphenylene sulfide for Automotive part
 azmater.com
azmater.com