Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and dimensional strength compared to polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for high-performance packaging films. Polyethylene provides excellent flexibility and moisture resistance, which are essential for cost-effective, everyday food packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
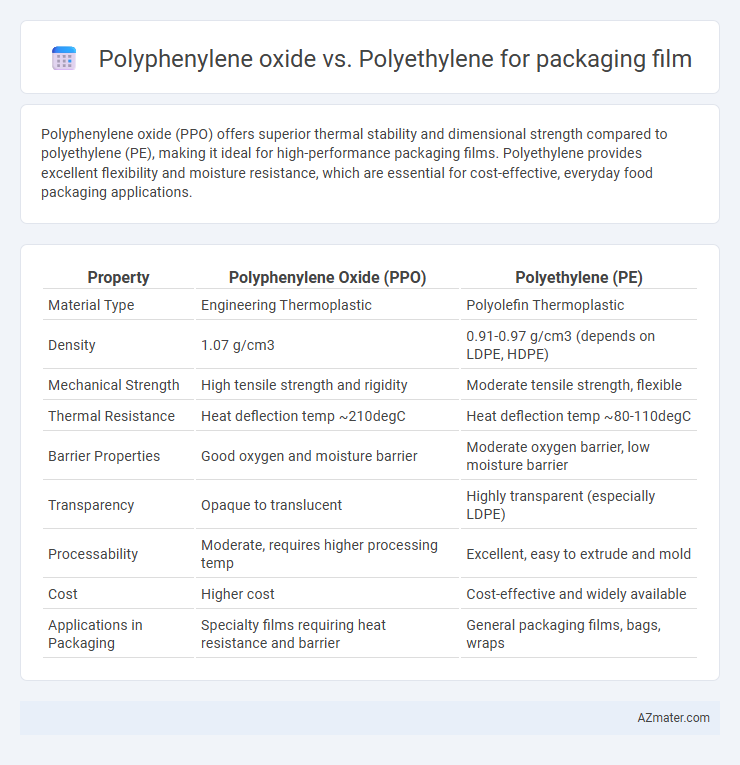
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Engineering Thermoplastic | Polyolefin Thermoplastic |
| Density | 1.07 g/cm3 | 0.91-0.97 g/cm3 (depends on LDPE, HDPE) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Moderate tensile strength, flexible |
| Thermal Resistance | Heat deflection temp ~210degC | Heat deflection temp ~80-110degC |
| Barrier Properties | Good oxygen and moisture barrier | Moderate oxygen barrier, low moisture barrier |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent (especially LDPE) |
| Processability | Moderate, requires higher processing temp | Excellent, easy to extrude and mold |
| Cost | Higher cost | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Applications in Packaging | Specialty films requiring heat resistance and barrier | General packaging films, bags, wraps |
Introduction to Packaging Films: Polyphenylene Oxide vs Polyethylene
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and excellent moisture barrier properties compared to polyethylene (PE), making it suitable for high-performance packaging films. Polyethylene is favored for its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of processing in packaging film applications. Both materials serve distinct roles based on product protection requirements and environmental exposure in packaging industries.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic backbone with oxygen linkages, providing high thermal stability and excellent dimensional stability, while polyethylene (PE) consists of long, flexible aliphatic carbon chains that lend it high flexibility and impact resistance. PPO exhibits superior barrier properties against gases and moisture due to its polar ether groups and densely packed structure, making it suitable for preserving product freshness. In contrast, polyethylene's nonpolar, semicrystalline structure offers lower gas barrier performance but ensures cost-effective production and versatility in packaging film applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polyethylene (PE) in packaging films, offering higher tensile strength and stiffness that enhance resistance to deformation under stress. PPO's excellent thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation contribute to its prolonged performance in harsh environments, making it ideal for packaging applications requiring long-term durability. In contrast, polyethylene films provide good flexibility but generally exhibit lower mechanical strength and are more susceptible to environmental stress cracking and wear over time.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Gas, and Aroma Retention
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior barrier properties compared to polyethylene (PE), offering enhanced resistance to moisture, oxygen, and aromatic compounds, which is critical for preserving food freshness and extending shelf life. PPO's molecular structure creates a dense, non-polar matrix that effectively limits gas permeability and aroma loss, outperforming the relatively permeable, linear chains of PE. This makes PPO an ideal choice for high-performance packaging films that require stringent control over moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) and oxygen transmission rate (OTR).
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polyethylene, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 200degC, whereas polyethylene typically withstands up to 120degC before deformation. PPO's high glass transition temperature around 210degC ensures excellent temperature resistance, making it suitable for packaging applications requiring heat exposure. In contrast, polyethylene's lower melting point restricts its use in high-temperature packaging environments, limiting its thermal performance.
Processability and Manufacturing Techniques
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent thermal stability and high dimensional accuracy during processing, making it suitable for advanced manufacturing techniques like injection molding and extrusion in packaging films. Polyethylene (PE), dominated by its low cost and ease of processing, excels in film blowing and cast film processes, allowing rapid production and flexible film gauges. While PPO demands precise temperature control and specialized equipment, PE benefits from widespread availability of manufacturing technologies and scalability in high-volume packaging film production.
Optical Clarity and Surface Finish
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior optical clarity compared to polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for packaging films that require transparent and high-gloss finishes. PPO's inherent rigidity and high glass transition temperature contribute to a smooth surface finish, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and barrier properties of packaging films. In contrast, polyethylene typically exhibits lower gloss and clarity due to its semi-crystalline structure, which can scatter light and result in a more matte surface texture.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene (PE), making it less prone to degradation during recycling processes, which enhances its recyclability in packaging film applications. PE, widely used in packaging, has established recycling streams but often contributes to environmental pollution due to its slower degradation rate and lower mechanical recycling efficiency in mixed plastic waste. The environmental impact of PPO is generally lower in long-term use due to its durability and potential for repeated recycling without significant loss of properties, whereas PE's large-scale waste accumulation poses significant challenges for sustainable packaging solutions.
Cost Analysis and Commercial Availability
Polyethylene offers a significantly lower cost per kilogram compared to polyphenylene oxide, making it more economical for large-scale packaging film production. Polyethylene is widely available globally with extensive commercial supply chains, ensuring consistent availability for various packaging applications. Polyphenylene oxide, although providing superior thermal and barrier properties, faces limited commercial availability and higher price points, restricting its use primarily to niche or high-performance packaging films.
Application Suitability in Packaging Films
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and excellent oxygen barrier properties, making it highly suitable for packaging films requiring extended shelf life and protection against oxidation. Polyethylene (PE), particularly low-density polyethylene (LDPE), excels in flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, ideal for everyday packaging applications like food wraps and bags. PPO is preferred for high-performance packaging where durability and barrier properties are critical, whereas PE dominates in applications prioritizing flexibility and affordability.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyethylene for Packaging film
 azmater.com
azmater.com