Polyethylene offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and affordability for plumbing pipes compared to polybutylene, which is more prone to oxidation and failure. Polyethylene's enhanced durability and ease of installation make it the preferred material in modern plumbing systems.
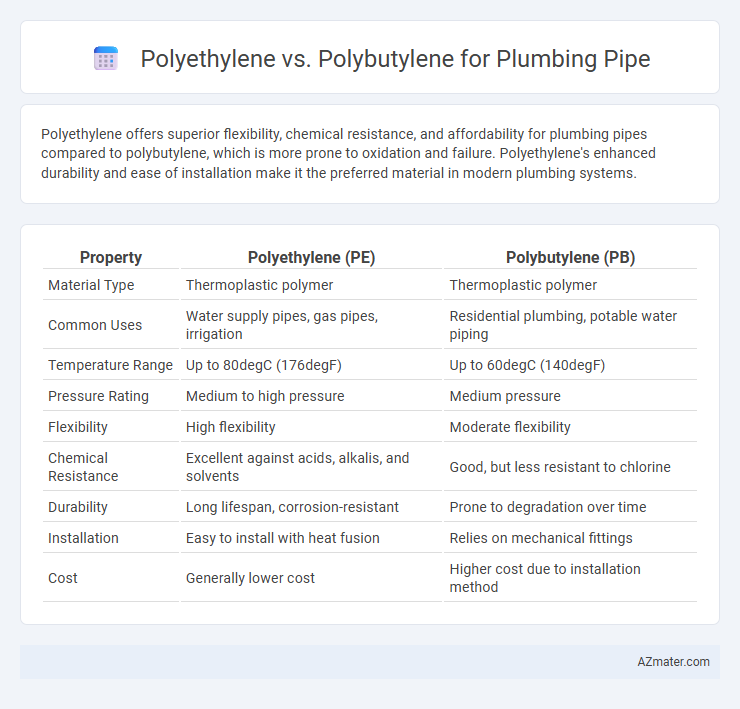
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polybutylene (PB) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Common Uses | Water supply pipes, gas pipes, irrigation | Residential plumbing, potable water piping |
| Temperature Range | Up to 80degC (176degF) | Up to 60degC (140degF) |
| Pressure Rating | Medium to high pressure | Medium pressure |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Moderate flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, alkalis, and solvents | Good, but less resistant to chlorine |
| Durability | Long lifespan, corrosion-resistant | Prone to degradation over time |
| Installation | Easy to install with heat fusion | Relies on mechanical fittings |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to installation method |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polybutylene Pipes
Polyethylene pipes, known for high corrosion resistance and flexibility, are widely used in plumbing for water distribution and gas lines due to their durability and ease of installation. Polybutylene pipes, made from a polymer similar to polyethylene but with different chemical structure, gained popularity for their cost-effectiveness and flexibility before being largely replaced due to issues with long-term reliability and susceptibility to chemical degradation. Both materials offer advantages in specific plumbing applications, with polyethylene currently favored for its proven longevity and chemical resistance in residential and commercial piping systems.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Polyethylene (PE) and Polybutylene (PB) differ significantly in chemical composition, with polyethylene composed of long chains of ethylene monomers, providing excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, while polybutylene consists of butylene monomers, offering greater toughness and impact resistance. PE pipes exhibit superior resistance to chlorine and other chemicals commonly found in water systems, making them highly durable for plumbing applications, whereas PB pipes demonstrate enhanced resilience under thermal stress and flexibility under pressure variations. The molecular structure of PE contributes to lower water absorption and enhanced longevity, while PB's polymer chain branching results in higher elasticity and resistance to crack propagation in dynamic environments.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Polyethylene (PE) pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making them highly resistant to corrosion, cracking, and environmental stress over time. Polybutylene (PB) pipes, while flexible and cost-effective, have a history of premature failures due to material degradation and susceptibility to chlorine in water, reducing their overall longevity. Industry studies show that polyethylene pipes typically last over 50 years under normal conditions, whereas polybutylene pipes often face replacement well before this timeframe.
Installation Process and Ease of Use
Polyethylene (PE) pipes for plumbing are highly flexible, lightweight, and compatible with heat fusion techniques, allowing seamless joints that reduce leak risks and simplify installation in tight spaces. Polybutylene (PB) pipes are softer and more pliable but require specialized crimp or clamp fittings, which can complicate installation compared to PE's solvent-free fusion process. Overall, polyethylene pipes offer greater ease of use and faster installation times, making them a preferred choice for modern plumbing systems.
Resistance to Corrosion and Chemical Degradation
Polyethylene plumbing pipes exhibit superior resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation, making them highly durable in harsh environments and suitable for potable water systems. Polybutylene pipes, while flexible and cost-effective, tend to degrade over time when exposed to chlorine and other chemicals, leading to increased risk of leaks and failures. The chemical stability of polyethylene ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance compared to polybutylene in plumbing applications.
Temperature and Pressure Tolerance
Polyethylene pipes typically offer temperature resistance up to 140degF (60degC) and pressure ratings around 200 psi, making them suitable for cold and warm water plumbing applications. Polybutylene pipes withstand higher temperatures, up to 180degF (82degC), and maintain pressure tolerance near 250 psi, providing enhanced durability under hot water conditions. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate material to ensure long-term performance and safety in plumbing systems.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polyethylene (PE) plumbing pipes offer high chemical resistance and low risk of leaching harmful substances, making them safe for potable water applications and compliance with NSF/ANSI 61 health standards. Polybutylene (PB) pipes have faced concerns due to their susceptibility to oxidative degradation and potential contaminants leaching, which has led to recalls and reduced usage in potable water systems. Choosing polyethylene pipes ensures durability and health safety with minimal risk of chemical contamination in residential and commercial plumbing installations.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Polyethylene plumbing pipes generally offer a lower initial cost compared to polybutylene, making them a budget-friendly choice for many residential applications. Polybutylene pipes, while more expensive upfront, provide enhanced flexibility and durability that can reduce maintenance costs and potential replacement expenses over time. Evaluating the long-term value, polyethylene's resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation often results in extended service life, ensuring cost savings through fewer repairs and longevity in plumbing systems.
Industry Standards and Building Code Compliance
Polyethylene (PE) plumbing pipes comply with NSF/ANSI 61 and ASTM F876 standards, ensuring safety for potable water systems and widespread approval under International Plumbing Code (IPC) and Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC) regulations. Polybutylene (PB) pipes, once popular in the 1980s and 1990s, often fail current ASTM F877 and ASTM D2846 standards due to durability concerns and lack endorsement in most modern building codes. Industry standards emphasize PE's superior chemical resistance and longevity, making it the preferred choice for code-compliant plumbing installations in residential and commercial buildings.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Plumbing Pipe
Polyethylene pipes offer superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and UV stability, making them ideal for outdoor and underground plumbing applications. Polybutylene pipes provide cost-effective installation but have been linked to higher failure rates and potential leakage issues over time. Selecting the right plumbing pipe depends on durability requirements, exposure conditions, and long-term performance expectations to ensure a reliable water supply system.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polybutylene for Plumbing Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com