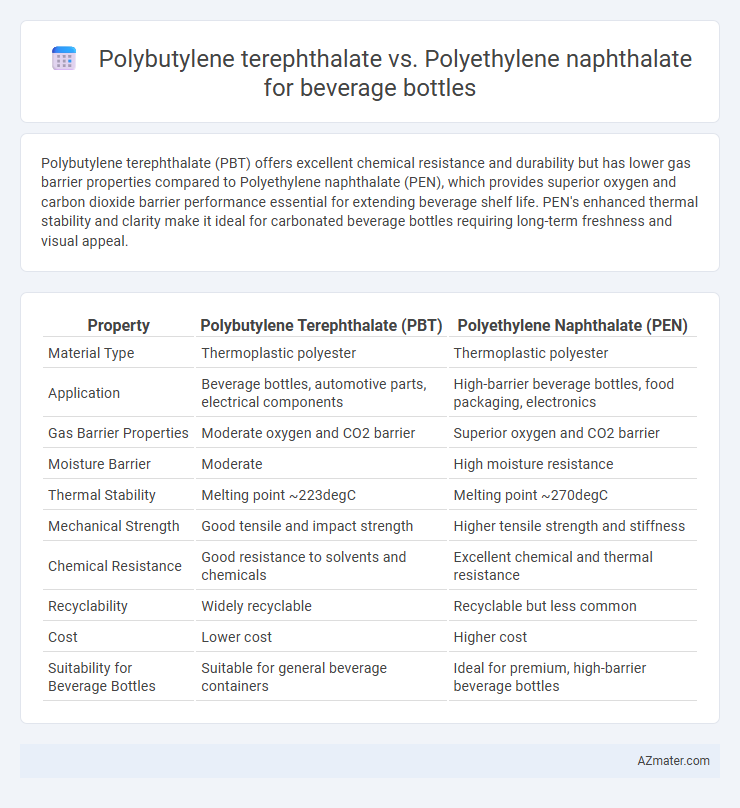
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance and durability but has lower gas barrier properties compared to Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), which provides superior oxygen and carbon dioxide barrier performance essential for extending beverage shelf life. PEN's enhanced thermal stability and clarity make it ideal for carbonated beverage bottles requiring long-term freshness and visual appeal.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Thermoplastic polyester |
| Application | Beverage bottles, automotive parts, electrical components | High-barrier beverage bottles, food packaging, electronics |
| Gas Barrier Properties | Moderate oxygen and CO2 barrier | Superior oxygen and CO2 barrier |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate | High moisture resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Melting point ~223degC | Melting point ~270degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile and impact strength | Higher tensile strength and stiffness |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and chemicals | Excellent chemical and thermal resistance |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable | Recyclable but less common |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Suitability for Beverage Bottles | Suitable for general beverage containers | Ideal for premium, high-barrier beverage bottles |
Introduction to Beverage Bottle Polymers
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) are two advanced polymers commonly used in beverage bottle manufacturing due to their exceptional barrier properties and mechanical strength. PEN offers superior gas and moisture barrier performance compared to PBT, making it ideal for preserving carbonation and extending shelf life in carbonated beverages. PBT provides excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, suitable for non-carbonated drinks, but PEN's higher thermal stability and reduced permeability give it a competitive edge in premium beverage packaging.
Overview of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it suitable for beverage bottle applications. PBT offers good barrier properties against moisture and gases, although it is generally less effective than polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) in blocking oxygen and carbon dioxide. Its rapid crystallization kinetics enable efficient processing, contributing to cost-effective production of durable beverage containers.
Overview of Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN)
Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) is a high-performance polyester known for its superior gas barrier properties, thermal stability, and mechanical strength compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT). PEN's enhanced oxygen and carbon dioxide barrier capabilities make it ideal for carbonated beverage bottles, extending product shelf life and maintaining freshness. Its excellent clarity and resistance to heat and chemicals ensure durability during processing and consumer use, positioning PEN as a premium material in beverage packaging applications.
Key Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance, high dimensional stability, and a melting point around 223degC, making it suitable for durable beverage bottles requiring resistance to heat and impact. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) features superior barrier properties against oxygen and CO2, higher glass transition temperature (~123degC), and enhanced UV resistance due to its rigid aromatic naphthalene rings, improving shelf life for carbonated drinks. PEN's improved chemical stability and lower gas permeability compared to PBT result in better preservation of beverage quality, though PEN typically exhibits higher production costs.
Barrier Performance: Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) exhibits superior oxygen and carbon dioxide barrier properties compared to Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), making it more suitable for beverage bottles requiring extended shelf life. PEN's enhanced barrier performance reduces gas permeation rates, effectively preserving carbonation and flavor integrity in carbonated drinks. Conversely, PBT offers moderate barrier protection but is less effective in preventing oxygen and CO2 transmission, limiting its use in high-barrier packaging applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers moderate mechanical strength with good impact resistance suitable for lightweight beverage bottles, but Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) exhibits superior tensile strength and enhanced thermal stability, providing increased durability under high-stress conditions. PEN's higher glass transition temperature (around 120degC) compared to PBT (approximately 22-45degC) ensures better shape retention and resistance to deformation during hot-fill processes common in beverage packaging. The superior oxygen and moisture barrier properties of PEN contribute to extended shelf life, making it a more durable choice for beverage bottles requiring enhanced mechanical robustness.
Impact on Beverage Shelf Life
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers moderate barrier properties against oxygen and moisture, which can result in a shorter beverage shelf life compared to Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN). PEN exhibits superior gas barrier performance, significantly reducing oxygen permeability and thereby enhancing the preservation of flavor and carbonation in beverages. This improved barrier capacity of PEN extends the shelf life of beverages by minimizing oxidation and maintaining product quality over time.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers moderate recyclability and is derived from petrochemical sources, leading to a relatively higher carbon footprint compared to bio-based options. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) demonstrates superior barrier properties that extend beverage shelf life, reducing waste and improving sustainability in packaging. PEN's enhanced thermal stability allows for repeated recycling cycles with minimal degradation, making it a more environmentally favorable choice for long-term beverage bottle applications.
Cost Implications and Manufacturing Processes
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers lower material costs and easier injection molding, making it economically attractive for beverage bottle production compared to polyethyrene naphthalate (PEN), which incurs higher raw material expenses and requires specialized extrusion techniques due to its higher melting point. PEN provides superior barrier properties and thermal stability, but its complex manufacturing processes translate into increased production costs and longer cycle times. Cost implications heavily influence material selection, with PBT favored for budget-sensitive applications, while PEN suits premium beverages demanding enhanced shelf life and clarity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Polymer for Bottling
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for durable beverage bottles; however, Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) provides superior gas barrier properties and thermal stability, which are critical for preserving beverage freshness and extending shelf life. PEN's higher oxygen barrier and UV resistance outperform PBT, essential for sensitive beverages like juices and carbonated drinks. Selecting PEN for beverage bottles is optimal when prioritizing product longevity and quality, while PBT is preferable for cost-sensitive applications requiring robustness.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyethylene naphthalate for Beverage bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com