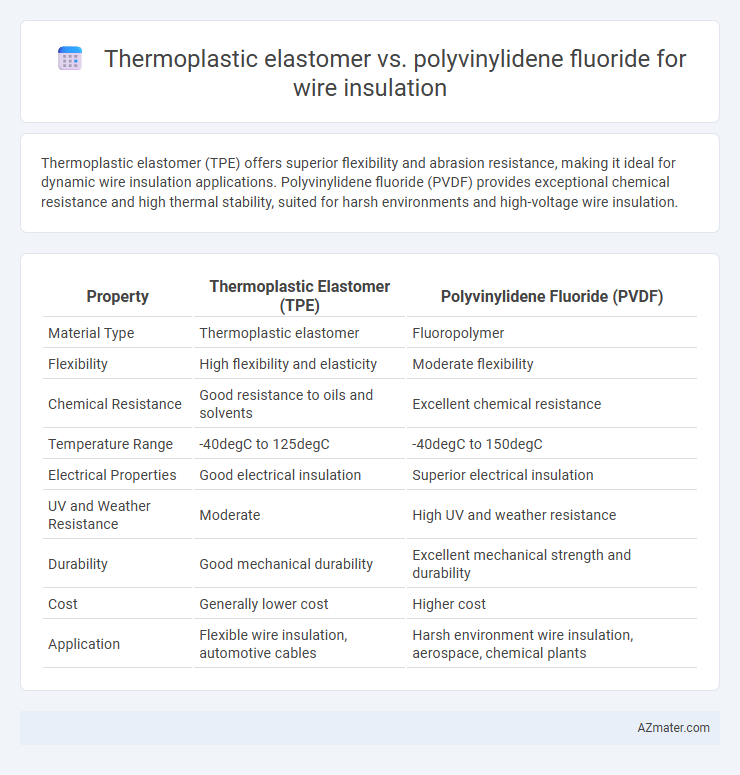
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) offers superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for dynamic wire insulation applications. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides exceptional chemical resistance and high thermal stability, suited for harsh environments and high-voltage wire insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic elastomer | Fluoropolymer |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Moderate flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 125degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Electrical Properties | Good electrical insulation | Superior electrical insulation |
| UV and Weather Resistance | Moderate | High UV and weather resistance |
| Durability | Good mechanical durability | Excellent mechanical strength and durability |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost |
| Application | Flexible wire insulation, automotive cables | Harsh environment wire insulation, aerospace, chemical plants |
Introduction: Importance of Wire Insulation Materials
Wire insulation materials are crucial for ensuring electrical safety, durability, and performance under varying environmental conditions. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer flexibility, chemical resistance, and excellent elasticity, making them suitable for dynamic wire applications. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior thermal stability, high dielectric strength, and exceptional resistance to UV radiation and chemicals, ideal for harsh industrial environments.
Overview of Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer exceptional flexibility and high abrasion resistance, making them ideal for wire insulation in dynamic environments. Their ability to combine the elastic properties of rubber with the processability of plastics allows for efficient manufacturing and recyclability. TPE materials provide excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, ensuring durable performance in various electrical applications.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 150degC, and excellent electrical insulating properties, making it ideal for wire insulation in harsh environments. PVDF offers superior mechanical strength, UV resistance, and flame retardancy compared to thermoplastic elastomers, ensuring long-lasting durability and safety in industrial and aerospace applications. Its low dielectric constant and high dielectric strength provide reliable signal integrity for high-frequency wiring.
Thermal Performance: TPE vs PVDF
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer moderate thermal resistance, typically with continuous use temperatures up to 125degC, making them suitable for flexible wire insulation in everyday applications. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) excels with a higher thermal stability, sustaining continuous exposure up to 150-170degC and superior resistance to thermal degradation and chemical exposure. PVDF's enhanced thermal performance ensures greater longevity and reliability in high-temperature environments compared to TPE.
Electrical Properties Comparison
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer excellent flexibility and good dielectric strength, typically ranging from 15 to 25 kV/mm, making them suitable for moderate voltage wire insulation applications. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior electrical properties, including high dielectric strength of approximately 35 kV/mm, low dielectric constant, and exceptional resistance to electrical degradation under harsh conditions. PVDF's outstanding electrical insulation performance ensures better long-term reliability in high-voltage and high-frequency environments compared to TPE.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) exhibit excellent chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and some solvents but have moderate durability under prolonged exposure to harsh environments. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance to a broader range of aggressive chemicals, including acids and solvents, along with exceptional durability in extreme temperatures and UV radiation. PVDF's enhanced resistance and long-term performance make it a preferred choice for wire insulation in highly corrosive or demanding industrial applications.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) provide superior flexibility for wire insulation, allowing cables to bend and stretch without compromising the insulation's integrity. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) excels in mechanical strength, offering excellent abrasion resistance and durability under harsh environmental conditions. Choosing between TPE and PVDF depends on the balance between the need for flexibility in dynamic applications and the requirement for robust mechanical protection in demanding environments.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior recyclability in wire insulation due to their ability to be remelted and reshaped, reducing waste and environmental burden compared to thermoset plastics. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), while chemically resistant and durable, presents challenges in recycling due to its fluoropolymer structure, leading to longer degradation times and potential environmental persistence. Selecting TPE enhances sustainability in wire insulation by facilitating circular material use and minimizing ecological impact through easier processing and lower emissions during recycling.
Cost Analysis and Application Suitability
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer cost-effective wire insulation due to their lower raw material and processing expenses compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), which commands a premium pricing driven by its superior chemical resistance and thermal stability. TPE's flexibility and ease of extrusion make it suitable for general-purpose electrical wiring, whereas PVDF is preferred in specialized applications requiring high-performance insulation, such as aerospace, chemical processing, and harsh environmental conditions. Evaluating total cost of ownership should consider both material costs and the application's demand for durability, temperature resistance, and chemical exposure to ensure optimal insulation performance.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Material for Wire Insulation
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and ease of processing, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent bending and dynamic stress. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior thermal stability, UV resistance, and chemical inertness, suitable for harsh environments with high temperature and exposure to corrosive substances. Selecting the right material depends on application-specific needs, balancing flexibility and environmental resistance, where TPE suits dynamic mechanical demands and PVDF excels in extreme durability and longevity.
Infographic: Thermoplastic elastomer vs Polyvinylidene fluoride for Wire insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com