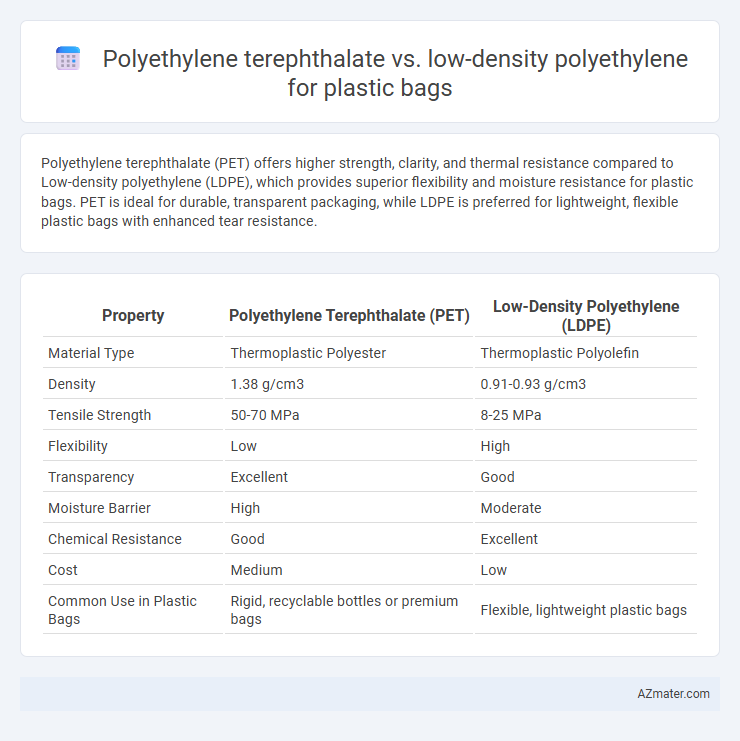
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers higher strength, clarity, and thermal resistance compared to Low-density polyethylene (LDPE), which provides superior flexibility and moisture resistance for plastic bags. PET is ideal for durable, transparent packaging, while LDPE is preferred for lightweight, flexible plastic bags with enhanced tear resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Thermoplastic Polyolefin |
| Density | 1.38 g/cm3 | 0.91-0.93 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 50-70 MPa | 8-25 MPa |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Transparency | Excellent | Good |
| Moisture Barrier | High | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Medium | Low |
| Common Use in Plastic Bags | Rigid, recyclable bottles or premium bags | Flexible, lightweight plastic bags |
Introduction to Polyethylene Terephthalate and Low-Density Polyethylene
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a strong, transparent polymer widely used in packaging due to its excellent gas and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for plastic bags that require durability and clarity. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a flexible, lightweight polymer characterized by its low tensile strength and high ductility, often utilized in plastic bags for its stretchability and resistance to impact. The chemical structure of PET involves aromatic rings contributing to rigidity, whereas LDPE's branched polymer chains provide enhanced flexibility and softness in plastic bag applications.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) consists of repeating ester functional groups formed from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, giving it a rigid, crystalline structure ideal for durability and clarity in plastic bags. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE), composed of long hydrocarbon chains with significant branching, exhibits a more amorphous and flexible molecular arrangement that results in softer, more pliable bags. The chemical structure differences between PET's aromatic ester linkages and LDPE's branched alkane chains directly influence their mechanical properties and suitability for various plastic bag applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits higher tensile strength and greater rigidity compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE), making PET bags more resistant to stretching and deformation. LDPE offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and clarity, which enhances its suitability for lightweight and stretchable plastic bags. The melting point of PET is around 260degC, significantly higher than LDPE's approximate 110degC, impacting processing temperatures and thermal stability in packaging applications.
Manufacturing Processes for Plastic Bags
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is manufactured through a polycondensation reaction of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, resulting in a strong, crystalline polyester often processed by extrusion and biaxial orientation for plastic bags that require superior stiffness and clarity. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is produced via high-pressure polymerization of ethylene, yielding a flexible, branched polymer commonly fabricated using blown film extrusion or cast film processes for plastic bags emphasizing softness and toughness. The manufacturing of PET bags involves higher thermal stability and crystallinity control, while LDPE bags benefit from simpler processing and cost-effectiveness, influencing their application-specific performance.
Strength and Durability: Which Material Prevails?
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior strength and durability compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE) when used for plastic bags, due to its higher tensile strength and resistance to stretching and tearing. PET's molecular structure provides enhanced impact resistance and better resistance to environmental stress cracking, making it ideal for heavier loads and extended use. LDPE, while more flexible and less rigid, lacks the mechanical robustness of PET, resulting in lower durability under similar conditions.
Transparency and Aesthetics in Plastic Bags
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior transparency and clarity compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE), making it ideal for plastic bags where product visibility is crucial. PET's glossy finish enhances aesthetic appeal, providing a premium look that attracts consumers. In contrast, LDPE exhibits a more opaque and matte surface, which reduces the visibility and visual sharpness of items inside the bag.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic bags have higher environmental footprints due to energy-intensive production but offer superior recyclability with established recycling streams yielding high-quality recycled materials. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) bags are less energy-intensive to produce and commonly reused, yet they pose challenges in recycling because of contamination and lower-quality outputs from recycling processes. PET's recyclability supports circular economy goals better, while LDPE's widespread use in lightweight bags contributes more significantly to plastic pollution due to lower recycling rates.
Cost Analysis: PET vs LDPE Plastic Bags
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic bags generally have a higher production cost compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE) bags due to the more complex manufacturing process and greater raw material expenses associated with PET. LDPE bags are more cost-effective, benefiting from lower raw material costs and simpler extrusion methods, making them the preferred choice for mass-market plastic bag applications. When considering cost analysis, LDPE bags offer superior affordability, while PET bags deliver enhanced durability and recyclability, impacting overall lifecycle cost evaluations.
Common Applications and Uses in Packaging
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used in packaging applications requiring clarity, strength, and gas barrier properties, such as beverage bottles, food containers, and blister packs. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is favored for flexible plastic bags, shrink wraps, and liners due to its flexibility, moisture resistance, and low cost. PET offers superior rigidity and recyclability, while LDPE provides enhanced flexibility and is commonly used for grocery bags and shrink films.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Plastic Bags
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior strength, clarity, and barrier properties, making it ideal for packaging requiring durability and product visibility. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) provides flexibility, toughness, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for lightweight and reusable plastic bags. Selecting between PET and LDPE depends on the specific application needs such as strength, transparency, and environmental considerations.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Low-density polyethylene for Plastic Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com