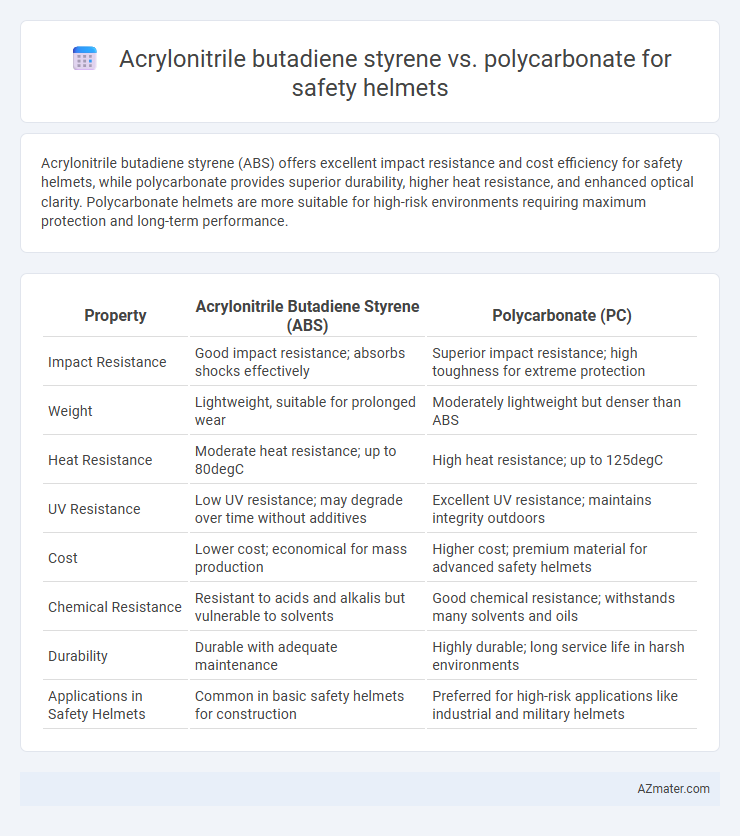
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and cost efficiency for safety helmets, while polycarbonate provides superior durability, higher heat resistance, and enhanced optical clarity. Polycarbonate helmets are more suitable for high-risk environments requiring maximum protection and long-term performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance; absorbs shocks effectively | Superior impact resistance; high toughness for extreme protection |
| Weight | Lightweight, suitable for prolonged wear | Moderately lightweight but denser than ABS |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance; up to 80degC | High heat resistance; up to 125degC |
| UV Resistance | Low UV resistance; may degrade over time without additives | Excellent UV resistance; maintains integrity outdoors |
| Cost | Lower cost; economical for mass production | Higher cost; premium material for advanced safety helmets |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis but vulnerable to solvents | Good chemical resistance; withstands many solvents and oils |
| Durability | Durable with adequate maintenance | Highly durable; long service life in harsh environments |
| Applications in Safety Helmets | Common in basic safety helmets for construction | Preferred for high-risk applications like industrial and military helmets |
Introduction to Safety Helmet Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polycarbonate (PC) are widely used materials for safety helmets due to their impact resistance and durability. ABS offers excellent toughness and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for standard protective headgear, while polycarbonate provides higher impact strength and superior clarity for enhanced visibility. Understanding the mechanical properties and performance differences of ABS and polycarbonate is crucial for selecting the optimal material for specific safety helmet applications.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in safety helmets due to its high impact resistance, toughness, and affordability. Its molecular structure provides excellent shock absorption and durability while maintaining a lightweight profile essential for prolonged wear. ABS also offers good chemical resistance and ease of molding, making it a preferred choice for manufacturing protective headgear with reliable safety performance.
Overview of Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a thermoplastic known for its exceptional impact resistance and high optical clarity, making it an ideal material for safety helmets where durability and visibility are critical. Compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), PC offers superior strength, better heat resistance up to 135degC, and enhanced toughness to withstand high-velocity impacts. Its lightweight nature and ability to absorb shocks without cracking provide enhanced protection and user comfort in safety helmet applications.
Mechanical Strength: ABS vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), providing enhanced impact resistance crucial for safety helmets. ABS offers good toughness and flexibility but falls short in withstanding higher impact forces and maintaining structural integrity under extreme stress. Polycarbonate's higher tensile strength and durability make it the preferred material for helmets requiring maximum protection and long-term reliability.
Impact Resistance Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance with good toughness and rigidity, commonly used in safety helmets due to its ability to absorb shock without deforming. Polycarbonate (PC) surpasses ABS in impact resistance, providing superior strength and higher resistance to penetration, making it ideal for environments requiring maximum protection. In comparison, polycarbonate helmets are more durable against repeated impacts and extreme conditions, while ABS helmets offer a cost-effective balance of performance and safety.
Weight and Ergonomics
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) helmets are generally lighter than polycarbonate (PC) helmets, enhancing comfort during prolonged use. Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance but tends to be heavier, which can affect ergonomics and user fatigue. Ergonomically, ABS helmets provide a better balance of weight and durability, making them more suitable for extended wear in safety-critical environments.
Thermal and UV Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers good thermal resistance with a heat deflection temperature around 100degC, making it suitable for safety helmets in moderate heat conditions, while polycarbonate (PC) excels with higher thermal stability, sustaining temperatures up to 140degC. Polycarbonate provides superior UV resistance due to its inherent chemical structure and can often be enhanced with UV stabilizers, ensuring prolonged durability and color retention in outdoor environments. ABS tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure, limiting its lifespan for helmets used in intense sunlight compared to the more resilient polycarbonate.
Cost and Availability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is generally more cost-effective and widely available compared to polycarbonate (PC), making it a popular choice for safety helmets in budget-sensitive markets. Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and durability but comes at a higher price point, often limiting its use to premium or specialized helmets. The broader manufacturing base for ABS ensures easier procurement and replacement parts availability, while polycarbonate helmets may require specific suppliers.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polycarbonate (PC) both meet key industry standards such as ANSI Z89.1 and EN 397 for safety helmets, but polycarbonate typically offers higher impact resistance and better heat resistance, making it suitable for more demanding industrial environments. ABS helmets often comply with basic certification requirements and are preferred for general safety applications due to cost-effectiveness, while polycarbonate helmets tend to exceed rigorous standards, including electrical insulation tests and UV exposure durability.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Safety Helmets
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and affordability, making it a common choice for safety helmets used in industrial and construction applications. Polycarbonate (PC) provides superior strength, higher heat resistance, and improved optical clarity, which enhances protection in high-risk environments such as firefighting and law enforcement. For optimal safety helmets, polycarbonate is the best choice due to its enhanced durability, toughness, and resistance to extreme conditions.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polycarbonate for Safety helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com