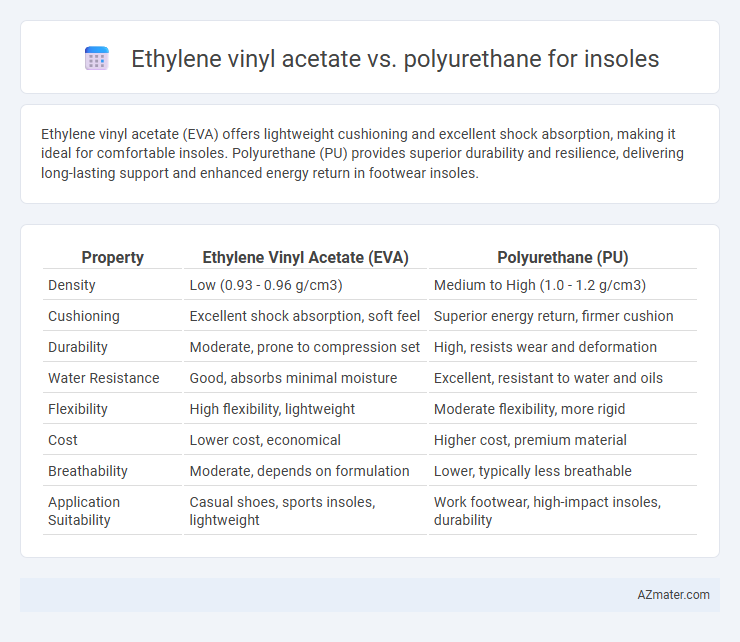
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers lightweight cushioning and excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for comfortable insoles. Polyurethane (PU) provides superior durability and resilience, delivering long-lasting support and enhanced energy return in footwear insoles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (0.93 - 0.96 g/cm3) | Medium to High (1.0 - 1.2 g/cm3) |
| Cushioning | Excellent shock absorption, soft feel | Superior energy return, firmer cushion |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to compression set | High, resists wear and deformation |
| Water Resistance | Good, absorbs minimal moisture | Excellent, resistant to water and oils |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, lightweight | Moderate flexibility, more rigid |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical | Higher cost, premium material |
| Breathability | Moderate, depends on formulation | Lower, typically less breathable |
| Application Suitability | Casual shoes, sports insoles, lightweight | Work footwear, high-impact insoles, durability |
Introduction to EVA and PU Insoles
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) insoles provide lightweight cushioning and excellent shock absorption, making them ideal for everyday comfort and moderate impact activities. Polyurethane (PU) insoles offer superior durability and support with enhanced resilience, often preferred for high-performance footwear and prolonged wear. Both materials balance flexibility and comfort, but EVA emphasizes softness and breathability while PU excels in structural integrity and long-lasting support.
Material Composition: EVA vs Polyurethane
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) outsole material consists of a copolymer formed by combining ethylene and vinyl acetate, offering excellent cushioning and flexibility due to its closed-cell foam structure. Polyurethane (PU) is a polymer composed of organic units joined by carbamate links, known for its durability, resistance to abrasion, and superior support in insoles. EVA generally provides lightweight comfort and shock absorption, while polyurethane ensures enhanced durability and structural integrity under prolonged use.
Comfort and Cushioning Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) insoles offer superior lightweight cushioning and shock absorption, making them ideal for all-day comfort with moderate support. Polyurethane (PU) insoles provide enhanced durability and higher density cushioning, delivering long-lasting comfort and excellent impact resistance for intense activities. EVA insoles excel in flexibility and breathability, while PU insoles maintain structural integrity under heavy pressure, resulting in a more supportive fit for extended wear.
Durability and Longevity
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) insoles offer lightweight cushioning with moderate durability, making them suitable for everyday use but prone to compression over time. Polyurethane insoles provide superior durability and long-lasting support due to their high density and resilience, maintaining structural integrity under frequent stress. For extended wear and enhanced longevity, polyurethane is preferred over EVA insole materials.
Shock Absorption Capabilities
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent shock absorption due to its lightweight, flexible, and resilient properties, making it ideal for cushioning insole applications. Polyurethane (PU) provides superior durability and energy return, maintaining consistent shock absorption over prolonged use and heavy impact. While EVA excels in initial comfort and impact dispersion, PU insoles deliver enhanced long-term protection against repeated shock stresses.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) insoles are significantly lighter than polyurethane (PU) insoles, making EVA ideal for lightweight footwear applications. EVA offers superior flexibility due to its softer, more cushioning properties, which enhance comfort during prolonged wear. In contrast, PU insoles are denser and less flexible but provide greater durability and structural support for high-impact activities.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers moderate breathability and moisture management due to its closed-cell structure, which provides cushioning but limits air circulation. Polyurethane (PU) insoles excel in moisture-wicking capabilities and breathability because their open-cell foam design promotes better airflow and sweat evaporation. Choosing PU over EVA for insoles enhances comfort in high-activity scenarios by reducing moisture buildup and improving foot ventilation.
Cost and Affordability Factors
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) insoles are generally more affordable due to lower material and manufacturing costs, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers. Polyurethane (PU) insoles, while more expensive, offer superior durability and cushioning, contributing to longer lifespan and enhanced comfort. Cost considerations often weigh EVA as a cost-effective option, whereas PU delivers higher performance with greater initial investment.
Best Applications for EVA and PU Insoles
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) insoles are best suited for lightweight cushioning and shock absorption in running shoes and casual footwear, providing durability and flexibility with excellent impact resistance. Polyurethane (PU) insoles excel in high-performance applications such as orthopedic footwear and work boots due to their superior support, compression resistance, and long-lasting comfort in demanding environments. Choosing between EVA and PU depends on specific needs like shock absorption for everyday wear or structural support for heavy-duty use.
Choosing the Right Insole: EVA or Polyurethane?
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) insoles are lightweight, flexible, and provide excellent shock absorption, making them ideal for everyday comfort and moderate activity. Polyurethane (PU) insoles offer superior durability and support with higher density cushioning, which is beneficial for prolonged wear and high-impact activities. Choosing between EVA and PU depends on factors such as required cushioning level, durability needs, and type of physical activity to ensure optimal foot support and comfort.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyurethane for Insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com