Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and durability for display cases, while Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides exceptional optical clarity and UV resistance. Choose ABS for rugged environments and PMMA for enhanced transparency and aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
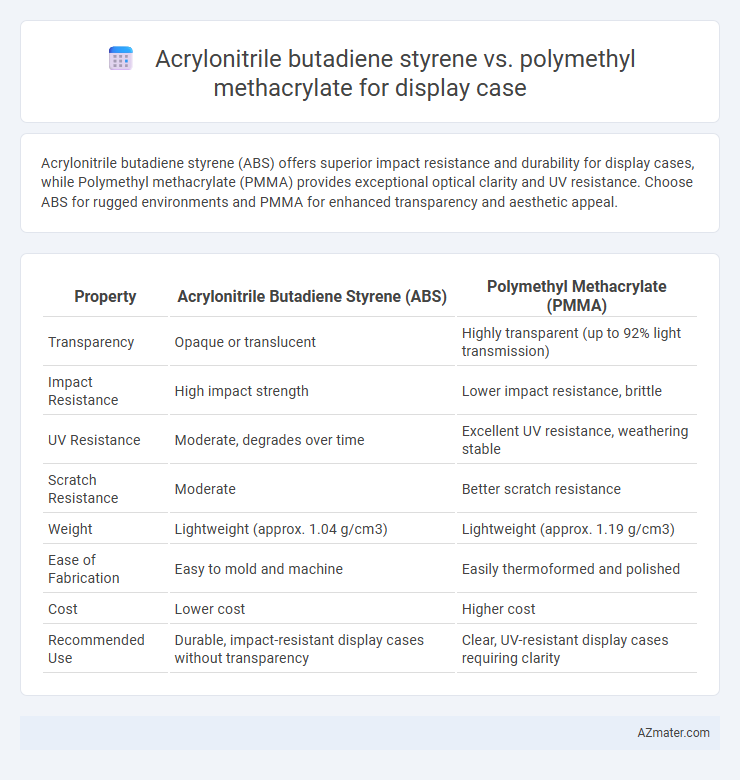
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Highly transparent (up to 92% light transmission) |
| Impact Resistance | High impact strength | Lower impact resistance, brittle |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, degrades over time | Excellent UV resistance, weathering stable |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | Better scratch resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight (approx. 1.04 g/cm3) | Lightweight (approx. 1.19 g/cm3) |
| Ease of Fabrication | Easy to mold and machine | Easily thermoformed and polished |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Recommended Use | Durable, impact-resistant display cases without transparency | Clear, UV-resistant display cases requiring clarity |
Introduction to ABS and PMMA for Display Cases
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance, durability, and ease of fabrication, making it an ideal choice for robust display cases requiring toughness and structural integrity. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic, provides exceptional optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, ensuring display cases maintain transparency and aesthetic appeal over time. Both materials serve distinct purposes: ABS excels in mechanical strength, while PMMA is preferred when visual presentation and light transmission are critical.
Material Composition and Properties Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) consists of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering high impact resistance and toughness, making it ideal for durable display cases. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), composed of methyl methacrylate monomers, provides excellent clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, ensuring superior optical properties for display visibility. ABS is favored for strength and impact absorption, whereas PMMA excels in transparency and surface hardness, guiding material selection based on display case performance requirements.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits superior optical clarity and transparency compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making it ideal for display cases requiring high light transmission and minimal distortion. PMMA allows up to 92% light transmittance with excellent UV resistance, while ABS typically provides lower transparency and exhibits a more opaque or matte finish. For applications demanding crystal-clear visibility and aesthetic appeal, PMMA outperforms ABS in maintaining clarity over time.
Strength and Impact Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and toughness compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for display cases in environments with higher risk of impact. ABS exhibits excellent strength and durability, resisting cracks and breaks under heavy use, whereas PMMA provides good rigidity but is more prone to shattering on impact. For applications prioritizing both strength and impact resistance, ABS is the preferred material choice due to its balance of toughness and strength properties.
Weight and Structural Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a lightweight profile with superior impact resistance, making it ideal for display cases that require durable structural integrity without excessive weight. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), while heavier, provides better optical clarity and rigidity but is more prone to cracking under stress compared to ABS. Choosing between ABS and PMMA depends on balancing the need for robust weight-bearing capability against the requirement for clear, glass-like transparency in display applications.
Scratch and Chemical Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate scratch resistance but falls short compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which exhibits superior hardness and better resists abrasions, making it ideal for display cases requiring clear visibility without surface damage. Chemically, PMMA shows enhanced resistance to many solvents and cleaning agents, whereas ABS is more susceptible to degradation and discoloration when exposed to harsh chemicals. For display cases demanding durability against both scratches and chemical exposure, PMMA provides a more resilient and long-lasting solution.
Ease of Fabrication and Customization
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior ease of fabrication due to its excellent thermoforming properties, allowing for complex shapes and rapid prototyping in display cases. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), while more brittle, excels in clarity and surface finish but requires specialized tools for cutting and shaping, limiting customization speed. ABS provides greater flexibility and impact resistance during fabrication, making it ideal for custom-designed, durable display cases.
Cost Effectiveness and Budget Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior cost effectiveness for display cases due to its lower raw material price and ease of manufacturing compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which tends to be more expensive but provides greater optical clarity. Budget considerations often favor ABS in large-scale production where durability and impact resistance are prioritized over transparency. PMMA remains ideal for premium display cases where higher upfront costs are justified by its aesthetic qualities and scratch resistance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits higher environmental concerns due to its petroleum-based origin and lower recyclability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which is more easily recycled and often sourced from more sustainable production processes. PMMA's chemical structure allows for efficient mechanical recycling and biodegradation under specific conditions, reducing landfill accumulation and environmental pollution. ABS's tougher mechanical properties come at the cost of increased carbon footprint and challenges in closed-loop recycling systems for display cases.
Best Applications: Choosing Between ABS and PMMA for Display Cases
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and durability, making it ideal for protective display cases exposed to frequent handling or potential impact. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides exceptional optical clarity and UV resistance, preferred for showcasing items requiring high transparency and aesthetic appeal. Selecting between ABS and PMMA depends on prioritizing toughness for heavy-duty protection or clarity for enhanced visual presentation in display case applications.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Display case
 azmater.com
azmater.com