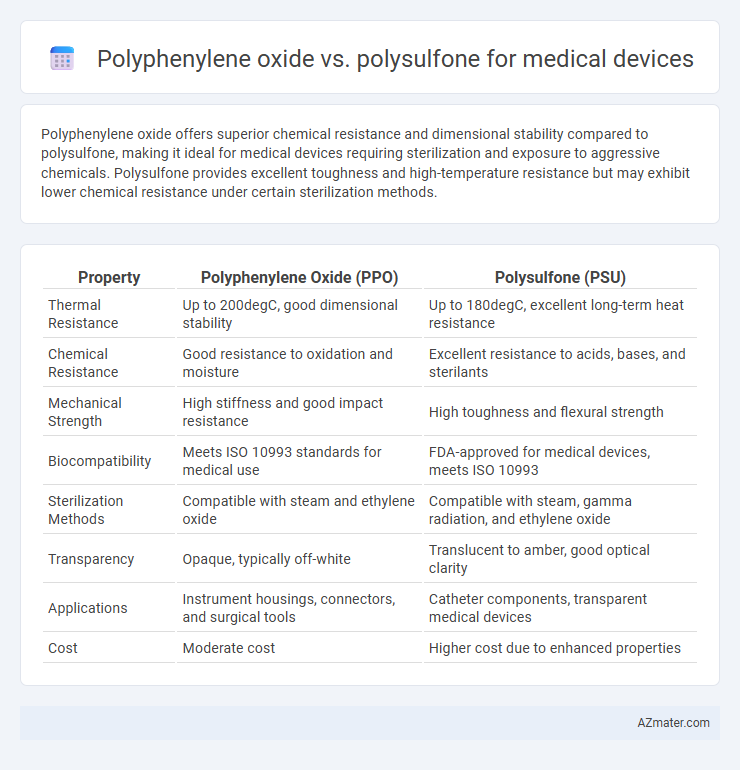
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability compared to polysulfone, making it ideal for medical devices requiring sterilization and exposure to aggressive chemicals. Polysulfone provides excellent toughness and high-temperature resistance but may exhibit lower chemical resistance under certain sterilization methods.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polysulfone (PSU) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 200degC, good dimensional stability | Up to 180degC, excellent long-term heat resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oxidation and moisture | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and sterilants |
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness and good impact resistance | High toughness and flexural strength |
| Biocompatibility | Meets ISO 10993 standards for medical use | FDA-approved for medical devices, meets ISO 10993 |
| Sterilization Methods | Compatible with steam and ethylene oxide | Compatible with steam, gamma radiation, and ethylene oxide |
| Transparency | Opaque, typically off-white | Translucent to amber, good optical clarity |
| Applications | Instrument housings, connectors, and surgical tools | Catheter components, transparent medical devices |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Polymer Selection in Medical Devices
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and polysulfone (PSU) are high-performance polymers widely used in medical device manufacturing due to their excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility. PPO offers superior dimensional stability and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for precision components in diagnostic equipment and drug delivery systems, while polysulfone provides exceptional toughness and sterilization resistance, commonly utilized in surgical instruments and respiratory devices. Selecting between PPO and polysulfone depends on specific medical application requirements such as sterilization methods, mechanical strength, and regulatory compliance for biocompatibility.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) and Polysulfone (PSU)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent dimensional stability, high heat resistance up to 210degC, and outstanding electrical insulation, making it suitable for medical device components requiring sterilization and chemical resistance. Polysulfone (PSU) provides superior toughness, high thermal stability with use temperatures up to 160degC, and exceptional hydrolytic resistance, ideal for medical applications involving repeated steam sterilization and exposure to harsh cleaning agents. Both materials demonstrate biocompatibility and can be precisely molded for complex medical device parts, but PPO generally excels in electrical properties while PSU is favored for mechanical durability and chemical resistance.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic backbone with oxygen atoms linking phenylene rings, offering high thermal stability and excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for sterilizable medical devices. Polysulfone (PSU) contains repeating sulfone groups (-SO2-) within its aromatic polymer chain, providing enhanced toughness, hydrolytic stability, and resistance to oxidative degradation, critical for long-term medical applications. The chemical composition difference--ether linkages in PPO versus sulfone linkages in PSU--directly influences their mechanical properties and sterilization compatibility in medical device manufacturing.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits high dimensional stability and excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for medical devices requiring robust mechanical strength and long-term durability. Polysulfone (PSU) offers superior tensile strength and thermal resistance, which enhances device longevity under repeated sterilization cycles. Both polymers provide a balance of toughness and rigidity, with PSU favored for applications demanding higher endurance against mechanical and thermal stress.
Thermal Resistance and Sterilization Compatibility
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits excellent thermal resistance with a continuous use temperature up to 270degC, making it suitable for high-temperature sterilization processes such as autoclaving and steam sterilization. Polysulfone (PSU) also offers strong thermal stability with continuous use temperatures around 160-190degC, supporting sterilization methods like steam, ethylene oxide (EtO), and gamma radiation without significant degradation. Both materials provide reliable chemical resistance and mechanical strength, but PPO's higher thermal threshold gives it an advantage for repeated high-temperature sterilization cycles in demanding medical device applications.
Biocompatibility and Safety in Medical Applications
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits excellent biocompatibility with low cytotoxicity and chemical resistance, making it suitable for medical devices requiring sterilization and long-term contact with tissues. Polysulfone (PSU) offers superior thermal stability and resistance to hydrolytic degradation, ensuring safety in high-temperature sterilization processes and prolonged medical use. Both polymers are FDA-approved for medical applications, but polysulfone's enhanced toughness and dimensional stability provide advantages in devices exposed to mechanical stress or harsh environments.
Chemical Resistance to Drugs and Cleaning Agents
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior chemical resistance to various drugs and aggressive cleaning agents, making it highly suitable for medical devices requiring frequent sterilization and exposure to harsh chemicals. Polysulfone (PSU) also provides excellent chemical stability but may show slight degradation when exposed to strong acids or oxidizing agents compared to PPO. Both polymers possess high thermal resistance, but PPO's enhanced resistance to a broader spectrum of pharmaceutical substances ensures longer durability and performance in demanding medical environments.
Manufacturing and Processing Considerations
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent thermal stability and dimensional accuracy, making it suitable for high-precision medical device components that require repeated sterilization cycles. Polysulfone (PSU) provides superior chemical resistance and toughness, which benefits devices exposed to aggressive sterilants and mechanical stress during use. Manufacturing processes for PPO typically involve injection molding with controlled cooling to maintain transparency, while PSU requires higher processing temperatures and longer cycle times, impacting overall production efficiency.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers a cost-effective solution for medical devices due to its lower raw material price and ease of processing, resulting in reduced manufacturing expenses compared to polysulfone (PSU). Polysulfone provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability but at a higher cost and more limited availability, especially in specialized medical-grade formulations. The widespread availability of PPO grades tailored for medical applications further enhances its economic advantage in volume production scenarios.
Conclusion: Optimal Polymer Choice for Medical Devices
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for medical devices requiring sterilization and long-term durability. Polysulfone (PSU) exhibits superior thermal resistance and biocompatibility, crucial for devices exposed to high temperatures and repeated sterilization cycles. Selecting the optimal polymer depends on specific device requirements, with PPO favored for chemical and mechanical stability, while PSU is preferred for thermal endurance and biocompatibility in medical applications.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polysulfone for Medical device
 azmater.com
azmater.com