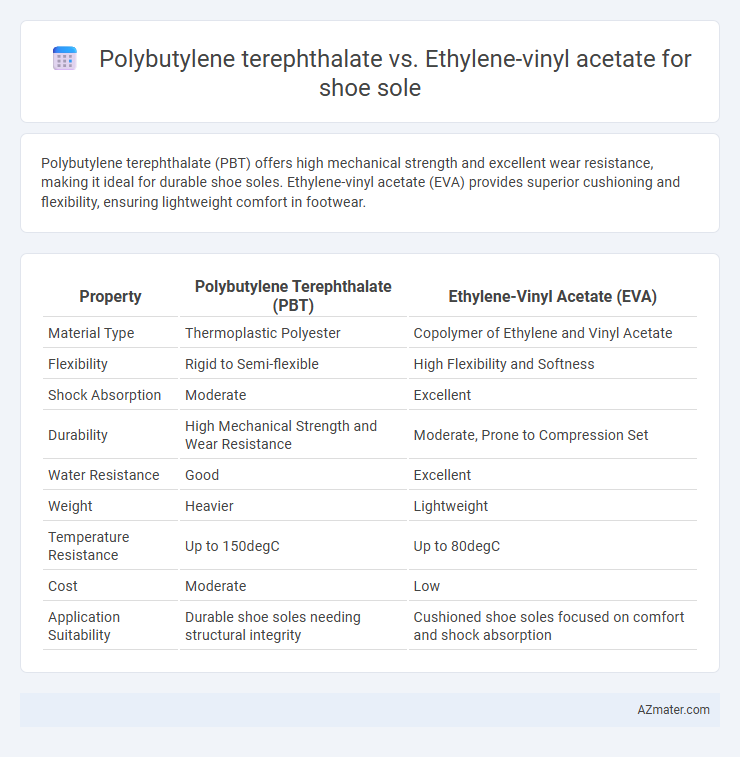
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers high mechanical strength and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for durable shoe soles. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning and flexibility, ensuring lightweight comfort in footwear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Copolymer of Ethylene and Vinyl Acetate |
| Flexibility | Rigid to Semi-flexible | High Flexibility and Softness |
| Shock Absorption | Moderate | Excellent |
| Durability | High Mechanical Strength and Wear Resistance | Moderate, Prone to Compression Set |
| Water Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC | Up to 80degC |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Application Suitability | Durable shoe soles needing structural integrity | Cushioned shoe soles focused on comfort and shock absorption |
Introduction to PBT and EVA in Footwear
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) are widely used polymers in shoe sole manufacturing, each offering distinct properties. PBT is a thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent mechanical strength, high resistance to abrasion, and heat tolerance, making it suitable for durable and wear-resistant soles. EVA, a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate, is prized for its lightweight, exceptional cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption, enhancing comfort and reducing foot fatigue in footwear.
Material Composition and Structure
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its high crystallinity, rigidity, and good chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable and structurally stable shoe soles. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer composed of ethylene and vinyl acetate units, characterized by its low density, excellent flexibility, and cushioning properties derived from its amorphous, rubber-like structure. The semi-crystalline nature of PBT provides superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, while EVA's elastomeric matrix offers enhanced shock absorption and lightweight comfort for footwear applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior mechanical strength and rigidity compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), making it ideal for shoe soles requiring high load-bearing capacity and impact resistance. EVA offers excellent flexibility and shock absorption but generally lacks the tensile strength and abrasion resistance found in PBT composites. Durability assessments reveal that PBT soles maintain structural integrity under prolonged stress and harsh environmental conditions better than EVA, which tends to compress and degrade faster over time.
Cushioning and Comfort Underfoot
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior mechanical strength and durability for shoe soles but provides moderate cushioning and stiffness underfoot compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). EVA is renowned for its exceptional shock absorption, lightweight properties, and excellent cushioning, making it a preferred choice for comfort-focused footwear. The elastic nature of EVA promotes better energy return and underfoot softness, while PBT excels in structural support and wear resistance.
Flexibility and Responsiveness
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent flexibility and high tensile strength, making it ideal for durable shoe soles that require long-lasting responsiveness. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning and lightweight flexibility, enhancing shock absorption and energy return for dynamic movement in athletic footwear. When comparing both materials, EVA generally delivers greater responsiveness and softer flexibility, while PBT excels in structural support and resistance to deformation.
Slip Resistance and Traction Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior slip resistance and traction performance for shoe soles due to its high abrasion resistance and excellent mechanical strength, providing durable grip on various surfaces. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) is lightweight and flexible but typically delivers lower slip resistance because of its softer, more cushioned texture, which can wear down faster under aggressive traction conditions. For applications requiring enhanced safety and durability, PBT soles are preferred over EVA, especially in environments where slip resistance is critical.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), making it a preferred material for durable shoe soles. The high crystallinity and mechanical strength of PBT contribute to its excellent resistance against surface wear and tearing under repeated friction. Conversely, EVA offers more flexibility and cushioning but typically shows lower durability in harsh abrasion conditions, reducing its lifespan in high-wear footwear applications.
Lightweight Properties and Energy Return
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent lightweight properties due to its low density and rigidity, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring structural support and durability. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) excels in energy return with its superior cushioning and resilience, providing enhanced shock absorption and rebound during movement. Combining PBT's lightweight stability with EVA's dynamic energy return can optimize shoe sole performance for both comfort and longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior recyclability and biodegradability compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which is a petroleum-based polymer with limited recyclability and longer degradation periods in landfills. PBT's production involves less greenhouse gas emissions and uses fewer non-renewable resources, contributing to lower environmental impact during the manufacturing process. EVA soles, while providing excellent flexibility and cushioning, pose challenges in sustainability efforts due to their resistance to natural decomposition and reliance on fossil fuels.
Cost Efficiency and Market Applications
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior durability and heat resistance, making it cost-efficient for high-performance shoe soles used in athletic and industrial markets. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) is favored for its lightweight and cushioning properties, leading to widespread use in casual and running shoes due to its lower material and manufacturing costs. Market applications for PBT focus on premium and specialized footwear, while EVA dominates mass-market and budget-friendly shoe segments, optimizing cost efficiency based on product requirements.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com