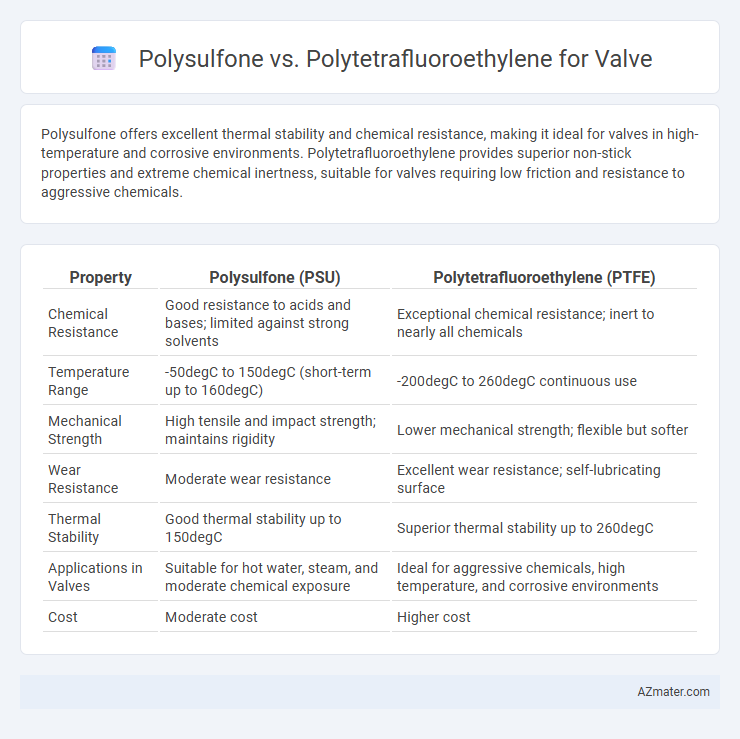
Polysulfone offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for valves in high-temperature and corrosive environments. Polytetrafluoroethylene provides superior non-stick properties and extreme chemical inertness, suitable for valves requiring low friction and resistance to aggressive chemicals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and bases; limited against strong solvents | Exceptional chemical resistance; inert to nearly all chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC (short-term up to 160degC) | -200degC to 260degC continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and impact strength; maintains rigidity | Lower mechanical strength; flexible but softer |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate wear resistance | Excellent wear resistance; self-lubricating surface |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal stability up to 150degC | Superior thermal stability up to 260degC |
| Applications in Valves | Suitable for hot water, steam, and moderate chemical exposure | Ideal for aggressive chemicals, high temperature, and corrosive environments |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Valve Material Selection
Valve material selection hinges on factors such as chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength. Polysulfone offers high impact resistance and transparency but has limited temperature tolerance up to 150degC, making it suitable for moderate conditions. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides excellent chemical inertness and heat resistance up to 260degC, ideal for aggressive chemical environments and high-temperature applications.
Overview of Polysulfone (PSU)
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for valve applications where durability and reliability are critical. Its superior resistance to hydrolysis and sustained performance at temperatures up to 150degC distinguish PSU from other polymers, providing an advantage in environments involving hot water and aggressive chemicals. Compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), PSU offers better structural rigidity and ease of fabrication, which can be beneficial in precision valve components requiring tight tolerances.
Overview of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction coefficient, and high thermal stability, making it ideal for valve applications exposed to aggressive chemicals and extreme temperatures. Its non-stick surface and resistance to corrosion outperform polysulfone in environments requiring superior durability and inertness. PTFE valves provide enhanced sealing performance and longevity in demanding industrial processes such as chemical processing, food production, and pharmaceuticals.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for valves requiring durability under mechanical stress and elevated temperatures up to 150degC. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior chemical resistance and low friction but has lower tensile strength and mechanical rigidity, limiting its use in high-pressure valve applications. For valves, polysulfone provides better load-bearing capacity and dimensional stability, while PTFE excels in corrosion resistance and self-lubricating properties.
Chemical Resistance: PSU vs PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior chemical resistance compared to Polysulfone (PSU), with excellent inertness to acids, bases, solvents, and aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for valve applications in highly corrosive environments. Polysulfone exhibits good resistance to a range of chemicals but can degrade when exposed to concentrated acids, alkalis, and certain organic solvents. Valve manufacturers often prefer PTFE for chemical resistance-critical components due to its non-reactive surface and temperature tolerance up to 260degC, whereas PSU operates effectively up to 150degC with moderate chemical resilience.
Temperature Tolerance and Stability
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits exceptional temperature tolerance, withstanding continuous service temperatures up to 260degC, compared to polysulfone's maximum limit around 150degC, making PTFE ideal for high-temperature valve applications. PTFE's chemical inertness and thermal stability ensure minimal deformation and degradation under extreme heat, whereas polysulfone offers moderate thermal resistance but superior mechanical strength at lower temperatures. Valve components made from PTFE maintain sealing integrity and resist thermal expansion, while polysulfone valves provide cost-effective performance in moderately elevated temperature environments.
Wear and Longevity in Valve Applications
Polysulfone (PSU) offers excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making it suitable for valve components subjected to moderate wear and thermal stress, with a typical lifespan of 5-10 years depending on operational conditions. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) excels in low friction and high wear resistance, often extending valve longevity beyond 10 years, particularly in aggressive chemical environments and abrasive media. PTFE's superior self-lubricating properties reduce maintenance frequency and improve performance in dynamic valve applications compared to polysulfone.
Cost Analysis: Polysulfone vs PTFE
Polysulfone valves generally offer a lower initial cost compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) valves, making them a cost-effective choice for applications requiring good chemical resistance and thermal stability. PTFE valves, although more expensive upfront, provide superior chemical inertness and a wider temperature range, which can reduce maintenance and replacement costs over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including durability and application-specific factors, helps determine the most economical option between polysulfone and PTFE valves.
Common Valve Applications for PSU and PTFE
Polysulfone (PSU) is commonly used in valve applications requiring high thermal stability and chemical resistance, such as water treatment systems and food processing industries, where durability under repeated sterilization is essential. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) valves excel in corrosive environments, including chemical processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing, due to their exceptional chemical inertness and low friction properties. Both materials are preferred for valve seats and seals, but PTFE is favored in applications involving aggressive acids, solvents, and wide temperature ranges.
Choosing the Ideal Material for Valve Performance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior chemical resistance and low friction properties, making it ideal for valves in corrosive environments and applications requiring smooth sealing. Polysulfone (PSU) provides excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability, suitable for valves subjected to higher temperatures and mechanical stress. Selecting the ideal material depends on balancing chemical compatibility, temperature tolerance, and mechanical demands for optimal valve performance.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Valve
 azmater.com
azmater.com