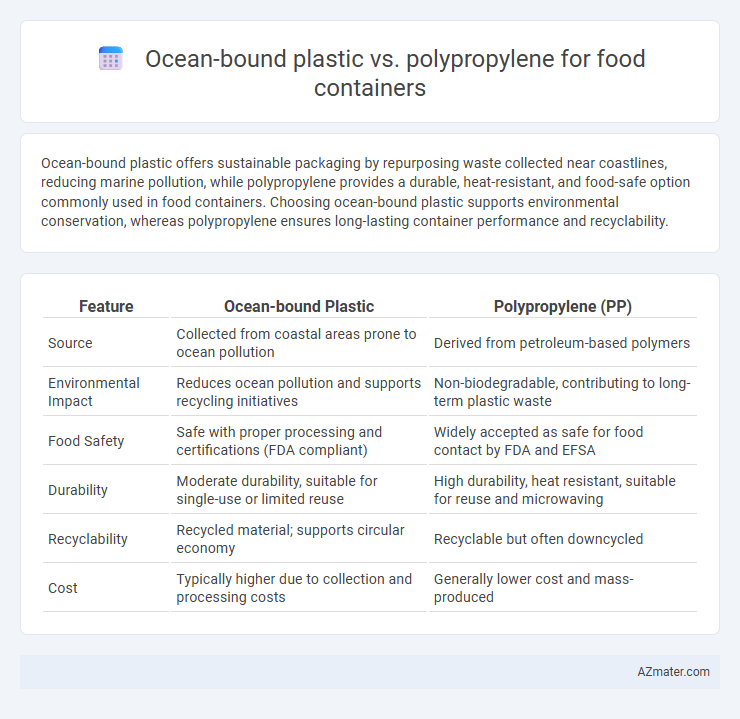
Ocean-bound plastic offers sustainable packaging by repurposing waste collected near coastlines, reducing marine pollution, while polypropylene provides a durable, heat-resistant, and food-safe option commonly used in food containers. Choosing ocean-bound plastic supports environmental conservation, whereas polypropylene ensures long-lasting container performance and recyclability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ocean-bound Plastic | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Collected from coastal areas prone to ocean pollution | Derived from petroleum-based polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces ocean pollution and supports recycling initiatives | Non-biodegradable, contributing to long-term plastic waste |
| Food Safety | Safe with proper processing and certifications (FDA compliant) | Widely accepted as safe for food contact by FDA and EFSA |
| Durability | Moderate durability, suitable for single-use or limited reuse | High durability, heat resistant, suitable for reuse and microwaving |
| Recyclability | Recycled material; supports circular economy | Recyclable but often downcycled |
| Cost | Typically higher due to collection and processing costs | Generally lower cost and mass-produced |
Introduction: Addressing Food Packaging Waste
Ocean-bound plastic repurposes waste retrieved from coastal areas, reducing marine pollution while offering eco-friendly food container solutions. Polypropylene remains a popular food packaging material due to its durability, heat resistance, and chemical stability, ensuring safety and product preservation. Comparing environmental impacts, ocean-bound plastic containers contribute to circular economy efforts by diverting plastics from oceans, whereas polypropylene relies on fossil-fuel-derived resources with lower biodegradability.
Understanding Ocean-Bound Plastic
Ocean-bound plastic refers to plastic waste collected from coastal areas at high risk of entering the ocean, offering an environmentally responsible alternative to virgin polypropylene in food containers. This material is cleaned, processed, and repurposed, reducing ocean pollution and conserving resources while maintaining food safety standards. Using ocean-bound plastic supports circular economy initiatives by transforming potential marine debris into durable, food-grade containers.
What Is Polypropylene?
Polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in food containers due to its durability, heat resistance, and food safety compliance. Ocean-bound plastic, collected from coastal areas before entering the ocean, is repurposed to reduce marine pollution but may vary in quality and contamination levels compared to virgin polypropylene. Polypropylene offers consistent performance and chemical resistance, making it a preferred choice for food-grade containers, while ocean-bound plastic contributes to sustainability by diverting waste from marine environments.
Environmental Impact: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Polypropylene
Ocean-bound plastic significantly reduces environmental pollution by diverting waste from marine ecosystems, lowering ocean plastic contamination compared to polypropylene, which is derived from fossil fuels and contributes to carbon emissions. The use of ocean-bound plastic supports circular economy practices by recycling coastal waste, whereas polypropylene production involves energy-intensive processes and results in persistent plastic pollution when improperly disposed. Choosing ocean-bound plastic for food containers enhances sustainability and mitigates the ecological damage linked to conventional polypropylene materials.
Safety and Food Contact Compliance
Ocean-bound plastic used in food containers undergoes rigorous cleaning and certification processes to meet strict food contact safety standards, ensuring it is free from contaminants and safe for consumer use. Polypropylene (PP), a widely adopted food-grade plastic, inherently offers excellent chemical resistance, heat tolerance, and compliance with FDA and EFSA food contact regulations, making it a reliable material for food storage. The key distinction lies in traceability and consistency; polypropylene benefits from established regulatory approvals, while ocean-bound plastic requires thorough validation to guarantee safety and compliance for food applications.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Ocean-bound plastic offers moderate durability with good environmental benefits but may have variable structural integrity compared to polypropylene, which provides superior strength and consistent performance in food containers. Polypropylene exhibits excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and moisture, ensuring long-term use and safety for food storage. In contrast, ocean-bound plastic containers often require blending with other materials to meet similar durability standards, making polypropylene the preferred choice for high-performance food packaging.
Cost Analysis: Ocean-Bound Plastic vs Polypropylene Containers
Ocean-bound plastic containers typically incur higher initial costs due to the collection, sorting, and processing required to convert waste into usable materials, whereas polypropylene containers benefit from established manufacturing processes with lower raw material expenses. However, ocean-bound plastic offers potential long-term savings linked to sustainability incentives and reduced environmental impact fees, which are increasingly influencing market pricing. Polypropylene remains more cost-effective for large-scale production, but ocean-bound plastic is gaining competitive pricing as recycling technologies improve and demand for eco-friendly products rises.
Recycling and End-of-Life Management
Ocean-bound plastic offers an eco-friendly alternative for food containers by diverting waste from coastal areas, reducing marine pollution while promoting circular economy practices. Polypropylene, widely used for its durability and heat resistance, is recyclable but often faces challenges in sorting and contamination, impacting its end-of-life efficiency. Effective recycling programs and advanced sorting technologies are critical to maximizing the recovery and reuse of both materials, ensuring sustainable end-of-life management for food containers.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception favors ocean-bound plastic food containers for their environmental impact, associating them with sustainability and waste reduction efforts. Market trends indicate a rising demand for eco-friendly polypropylene alternatives infused with recycled ocean-bound plastics to combine durability with green credentials. Brands leveraging this hybrid material report increased appeal among environmentally conscious consumers seeking practical and responsible packaging solutions.
Choosing the Best Material for Sustainable Food Containers
Ocean-bound plastic used in food containers significantly reduces environmental impact by repurposing waste destined for marine pollution, promoting circular economy principles. Polypropylene offers excellent durability, heat resistance, and food safety compliance, making it a reliable choice for long-lasting containers. Selecting ocean-bound plastic supports sustainability efforts, while polypropylene ensures practicality and safety; combining both materials in hybrid designs can optimize eco-friendliness and performance for sustainable food containers.
Infographic: Ocean-bound plastic vs Polypropylene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com