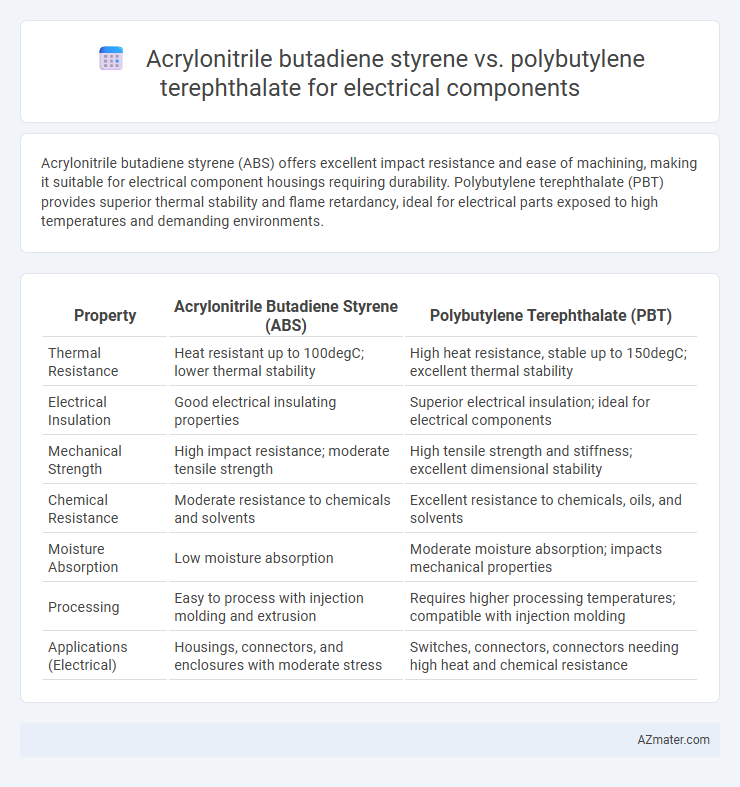
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and ease of machining, making it suitable for electrical component housings requiring durability. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides superior thermal stability and flame retardancy, ideal for electrical parts exposed to high temperatures and demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Heat resistant up to 100degC; lower thermal stability | High heat resistance, stable up to 150degC; excellent thermal stability |
| Electrical Insulation | Good electrical insulating properties | Superior electrical insulation; ideal for electrical components |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact resistance; moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength and stiffness; excellent dimensional stability |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to chemicals and solvents | Excellent resistance to chemicals, oils, and solvents |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Moderate moisture absorption; impacts mechanical properties |
| Processing | Easy to process with injection molding and extrusion | Requires higher processing temperatures; compatible with injection molding |
| Applications (Electrical) | Housings, connectors, and enclosures with moderate stress | Switches, connectors, connectors needing high heat and chemical resistance |
Introduction to ABS and PBT in Electrical Applications
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for durable electrical housings and components exposed to mechanical stress. Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) excels in thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional precision, supporting reliable performance in connectors, switches, and circuit board components subject to elevated temperatures. Both polymers contribute to enhanced safety and longevity in electrical applications, with ABS favored for shock absorption and PBT preferred for heat-resistant environments.
Material Composition: ABS vs PBT
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) consists of a thermoplastic polymer made from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering excellent impact resistance and ease of processing, making it ideal for electrical components requiring durability and insulation. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polyester known for its superior chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and high electrical insulation properties, often used in connectors and switch housings exposed to heat and moisture. The material composition difference results in ABS providing better toughness and aesthetic qualities, while PBT excels in thermal resistance and long-term electrical performance in demanding environments.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits high impact resistance and excellent toughness, making it suitable for electrical components requiring durability and resistance to mechanical stress. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior tensile strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability, which enhances performance in precision electrical parts exposed to thermal cycling. The choice between ABS and PBT depends on prioritizing impact resistance versus rigidity and thermal endurance in electrical component applications.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate electrical insulation properties suitable for general electrical component housings, with a dielectric strength around 16-20 kV/mm. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides superior electrical insulation, boasting dielectric strengths of approximately 20-25 kV/mm and excellent resistance to electrical tracking and arc resistance, making it ideal for high-performance electrical components. PBT's higher moisture resistance and thermal stability further enhance its electrical insulation reliability in demanding environments compared to ABS.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate thermal stability with a heat deflection temperature around 100degC, making it suitable for general electrical components with limited heat exposure. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior heat resistance and thermal stability, withstanding continuous operating temperatures up to 150degC and providing excellent dimensional stability under thermal stress. PBT's enhanced resistance to high temperatures and heat aging makes it the preferred choice for electrical components demanding reliable performance in harsh thermal environments.
Flame Retardancy and Safety Standards
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate flame retardancy suitable for many electrical components, often meeting UL 94 V-0 standards when properly formulated, but may require additional additives to enhance safety compliance. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) inherently provides superior flame resistance with inherent self-extinguishing properties and easily complies with stringent safety standards such as UL 94 V-0 without extensive modification. For critical electrical applications, PBT's enhanced thermal stability and flame retardant performance make it preferable where higher flame safety and regulatory compliance are prioritized.
Chemical Resistance in Electrical Environments
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate chemical resistance but can degrade when exposed to strong solvents and alkalis commonly found in electrical environments, potentially compromising insulation properties. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly to hydrocarbons, acids, and alkalis, maintaining mechanical integrity and electrical insulation under harsh chemical exposures. Choosing PBT enhances longevity and reliability of electrical components in chemically aggressive settings due to its enhanced resistance to environmental stress cracking and electrical insulation stability.
Processing and Manufacturability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and easy thermoforming, making it suitable for complex electrical component housings with high structural integrity. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) excels in dimensional stability and moisture resistance, critical for precision electrical parts, and supports injection molding processes with faster cycle times. Both materials allow for tailored flame retardancy, but PBT's superior flow characteristics enhance manufacturability in high-volume electrical component production.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a cost-effective solution for electrical components, with prices generally lower than polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) due to ABS's widespread production and demand. PBT, while more expensive, provides superior thermal resistance and electrical insulation properties, which justify its higher cost in specialized electrical applications. Market availability favors ABS because of its broad industrial use and abundant suppliers, whereas PBT's niche applications limit its supply chain, impacting cost and accessibility for large-scale manufacturing.
Applications: Selecting the Right Material for Electrical Components
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and electrical insulation, making it ideal for protective housings and enclosures in electrical components where toughness is critical. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) excels in dimensional stability, heat resistance, and electrical insulation, which suits connectors, switches, and circuit board components operating under higher thermal loads. Choosing between ABS and PBT depends on application-specific requirements such as temperature tolerance, mechanical stress, and electrical performance.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polybutylene terephthalate for Electrical Component
 azmater.com
azmater.com