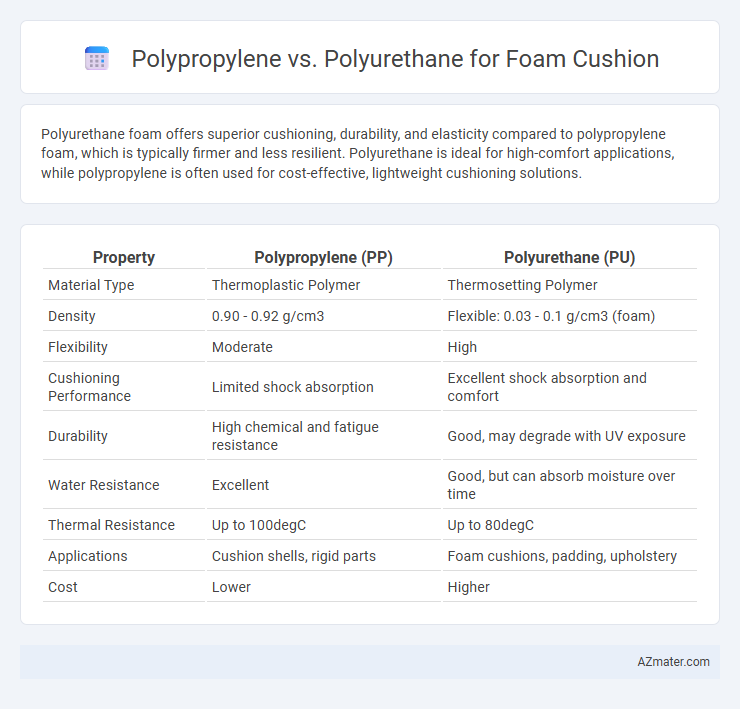
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning, durability, and elasticity compared to polypropylene foam, which is typically firmer and less resilient. Polyurethane is ideal for high-comfort applications, while polypropylene is often used for cost-effective, lightweight cushioning solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Thermosetting Polymer |
| Density | 0.90 - 0.92 g/cm3 | Flexible: 0.03 - 0.1 g/cm3 (foam) |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Cushioning Performance | Limited shock absorption | Excellent shock absorption and comfort |
| Durability | High chemical and fatigue resistance | Good, may degrade with UV exposure |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good, but can absorb moisture over time |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 80degC |
| Applications | Cushion shells, rigid parts | Foam cushions, padding, upholstery |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyurethane Foams
Polypropylene foam offers lightweight durability with excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for cushion applications requiring long-lasting performance. Polyurethane foam provides superior flexibility and cushioning properties due to its open-cell structure, commonly used for comfort and shock absorption in furniture and automotive seats. Choosing between polypropylene and polyurethane foams depends on factors like environmental exposure, load-bearing capacity, and desired softness.
Material Composition and Structure
Polypropylene foam cushions are composed of a thermoplastic polymer with a closed-cell structure that offers lightweight, moisture-resistant, and durable properties, making them ideal for outdoor and high-moisture environments. Polyurethane foam cushions consist of a polymer matrix formed from reacting diisocyanates and polyols, characterized by an open-cell structure providing superior elasticity, comfort, and breathability, suitable for indoor furniture and cushioning applications. The difference in material composition and cellular architecture directly impacts the cushioning performance, with polypropylene excelling in rigidity and environmental resistance, while polyurethane provides enhanced softness and impact absorption.
Key Differences in Physical Properties
Polypropylene foam exhibits higher rigidity and superior chemical resistance compared to polyurethane foam, which is known for its exceptional elasticity and cushioning comfort. Polyurethane foam offers greater flexibility and better compression set recovery, making it ideal for applications requiring prolonged impact absorption. Polypropylene foam's lower density and higher melting point contribute to enhanced durability in high-temperature environments, whereas polyurethane foam excels in low-temperature resilience and sound insulation.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning with excellent support and durability, making it ideal for high-impact seating applications requiring long-lasting comfort. Polypropylene foam provides a lighter, more breathable alternative, but generally lacks the same level of resilience and pressure distribution found in polyurethane. For cushions prioritizing balanced comfort and firm support, polyurethane remains the preferred choice due to its enhanced density and ability to maintain shape over time.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to polypropylene foam, making it ideal for high-use cushions due to its excellent resilience and ability to retain shape over time. Polyurethane's cellular structure provides enhanced resistance to compression and wear, while polypropylene foam, though lightweight and moisture-resistant, tends to degrade faster under prolonged pressure. Selecting polyurethane foam ensures longer-lasting comfort and support in cushion applications subjected to frequent or intense use.
Moisture and Heat Resistance
Polyurethane foam cushions exhibit superior moisture resistance compared to polypropylene, as they effectively repel water and resist mold growth, making them ideal for humid environments. Polypropylene foam offers excellent heat resistance with a melting point around 160degC, maintaining structural integrity under high temperatures, while polyurethane foam typically withstands heat up to 110degC but may degrade faster under prolonged exposure. Choosing between polypropylene and polyurethane foam cushions depends on prioritizing either enhanced moisture protection or higher thermal durability for specific applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam cushions often pose greater environmental challenges than polypropylene due to their reliance on fossil fuel-based chemicals and slower biodegradability, leading to longer landfill persistence. Polypropylene foam, derived primarily from petroleum but more easily recyclable and less toxic during production and disposal, presents a more sustainable option for foam cushions. Innovations in bio-based polypropylene and polyurethane alternatives further influence sustainability outcomes, but polypropylene currently offers superior environmental benefits in cushion applications.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Polypropylene foam cushions generally offer lower material and manufacturing costs compared to polyurethane, making them an economical choice for high-volume production and budget-sensitive applications. Polyurethane foam provides superior comfort and durability, but its higher price point can increase overall expenses, especially for large-scale or long-term use. Evaluating the balance between upfront costs and product longevity is crucial when selecting between polypropylene and polyurethane foam cushions.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type
Polypropylene foam excels in applications requiring high chemical resistance, moisture repellency, and lightweight cushioning such as automotive seating, marine flotation devices, and outdoor furniture. Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility, durability, and cushioning comfort, making it ideal for mattresses, upholstered furniture, and sound insulation in construction. Selecting between polypropylene and polyurethane foam depends on the specific demands of durability, water resistance, and comfort in the intended application.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Cushion Needs
Polyurethane foam offers superior comfort and durability, making it ideal for cushions requiring long-term support and resilience, while polypropylene foam excels in moisture resistance and affordability, suitable for outdoor or budget-conscious applications. Understanding the specific use case, such as indoor seating comfort or outdoor weather exposure, helps determine the most suitable foam type. Selecting the right foam balances cushioning needs, durability, and environmental factors for optimal user experience.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyurethane for Foam cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com