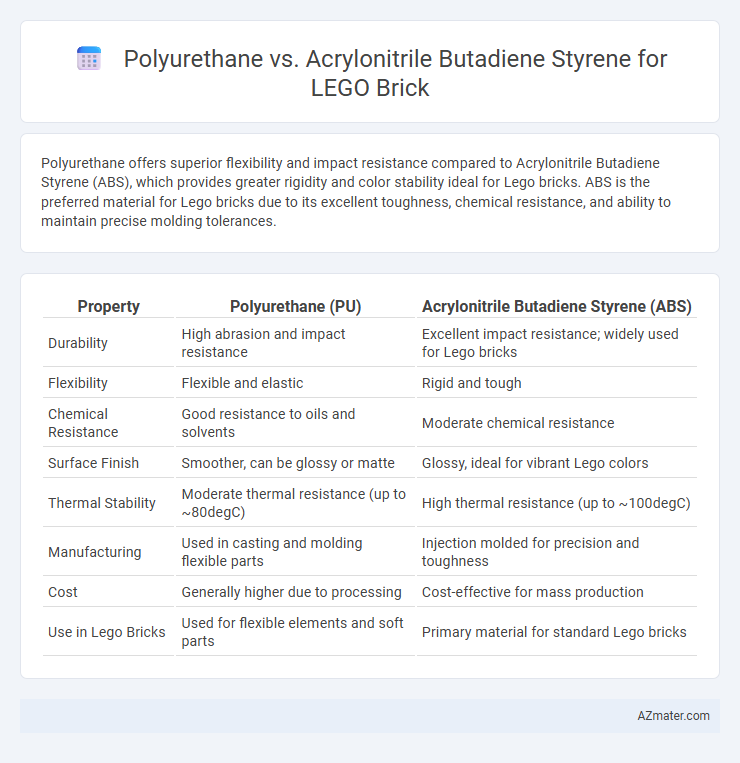
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides greater rigidity and color stability ideal for Lego bricks. ABS is the preferred material for Lego bricks due to its excellent toughness, chemical resistance, and ability to maintain precise molding tolerances.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High abrasion and impact resistance | Excellent impact resistance; widely used for Lego bricks |
| Flexibility | Flexible and elastic | Rigid and tough |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, can be glossy or matte | Glossy, ideal for vibrant Lego colors |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate thermal resistance (up to ~80degC) | High thermal resistance (up to ~100degC) |
| Manufacturing | Used in casting and molding flexible parts | Injection molded for precision and toughness |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Cost-effective for mass production |
| Use in Lego Bricks | Used for flexible elements and soft parts | Primary material for standard Lego bricks |
Introduction to Polyurethane and ABS in Lego Bricks
Polyurethane offers exceptional flexibility and durability, making it suitable for specialized Lego elements requiring resilience and impact resistance. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is the primary material for standard Lego bricks due to its strong structural integrity, vibrant color retention, and precise molding capabilities. The combination of these polymers ensures Lego bricks maintain consistent quality, longevity, and safety for children's play.
Material Composition: Polyurethane vs ABS
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer composed of organic units linked by carbamate (urethane) bonds, offering flexibility and durability, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene monomers, providing rigidity, impact resistance, and ease of molding. ABS's high impact strength and dimensional stability make it the preferred material for Lego bricks, ensuring consistent clutch power and longevity. Polyurethane's elastomeric properties can introduce flexibility, which is less ideal for the precise interlocking mechanism essential in Lego bricks.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyurethane exhibits superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it highly durable under high-stress conditions. ABS is well-known for its toughness and rigidity, providing excellent dimensional stability and resistance to cracking, which is essential for maintaining Lego brick integrity over repeated use. Polyurethane offers enhanced abrasion resistance and flexibility, contributing to longer-lasting Lego bricks that better withstand deformation and wear over time.
Color Vibrancy and Surface Finish
Polyurethane offers superior color vibrancy for Lego bricks due to its excellent pigment retention and resistance to fading under UV exposure, ensuring long-lasting, bright hues. In contrast, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides a smooth, glossy surface finish that enhances the tactile feel and visual appeal of the bricks but may exhibit slight color dulling over time. The choice between polyurethane and ABS hinges on prioritizing intense, enduring colors or a durable, polished surface finish for optimal Lego brick aesthetics.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Recycling
Polyurethane and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) differ significantly in environmental impact regarding sustainability and recycling for Lego bricks. ABS, widely used in Lego blocks, is a petroleum-based thermoplastic that poses recycling challenges due to its complex polymer structure, although it is durable and can be mechanically recycled. Polyurethane offers potential environmental benefits through increased biodegradability and the ability to be produced from bio-based sources, but its use in hard, durable Lego bricks remains limited and recycling processes are less established compared to ABS.
Safety Standards and Non-Toxicity
Polyurethane and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) used in Lego bricks both comply with stringent safety standards such as EN71 and ASTM F963, ensuring non-toxicity and suitability for children's toys. ABS is widely favored for its durability and resistance to impact while maintaining low toxicity levels, making it a benchmark material in toy manufacturing. Polyurethane offers flexibility but requires thorough testing to meet non-toxic certifications, as improper formulations may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that could compromise safety.
Precision and Interlocking Performance
Polyurethane and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) differ significantly in precision and interlocking performance for Lego bricks. ABS offers superior dimensional stability and consistent molding precision, resulting in highly accurate parts that fit together seamlessly with minimal tolerance variation. Polyurethane, while flexible and durable, lacks the rigidity and precise molding qualities of ABS, which can lead to less consistent interlocking strength and reduced structural integrity in assembled Lego constructions.
Cost-Effectiveness for Manufacturing
Polyurethane typically incurs higher raw material and processing costs compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), impacting overall manufacturing expenses for Lego bricks. ABS offers a balance of durability, ease of molding, and affordability, making it the preferred choice for cost-effective mass production. Manufacturing with ABS reduces production time and material waste, further enhancing cost-efficiency in large-scale Lego brick fabrication.
Historical Usage of ABS in Lego Bricks
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) has been the primary material for Lego bricks since the 1960s due to its exceptional durability, strength, and color retention, which are crucial for maintaining the quality and longevity of the toys. Historically, ABS provided a superior balance of rigidity and impact resistance compared to other plastics available at the time, including polyurethane, enabling precise molding and consistent clutch power essential for Lego's interlocking system. This long-term reliance on ABS underscores its unmatched performance in toy manufacturing, setting a benchmark that alternative materials like polyurethane have struggled to meet in terms of structural integrity and playability.
Future Prospects: Could Polyurethane Replace ABS?
Polyurethane offers promising future prospects for Lego bricks due to its superior durability, elasticity, and environmental benefits compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). Innovations in polyurethane formulations aim to enhance its moldability and color retention, addressing current limitations that hinder its mass adoption. As sustainability becomes a critical factor in manufacturing, polyurethane's potential for biodegradability and lower carbon footprint positions it as a viable alternative to ABS in the evolving toy industry.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Lego Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com