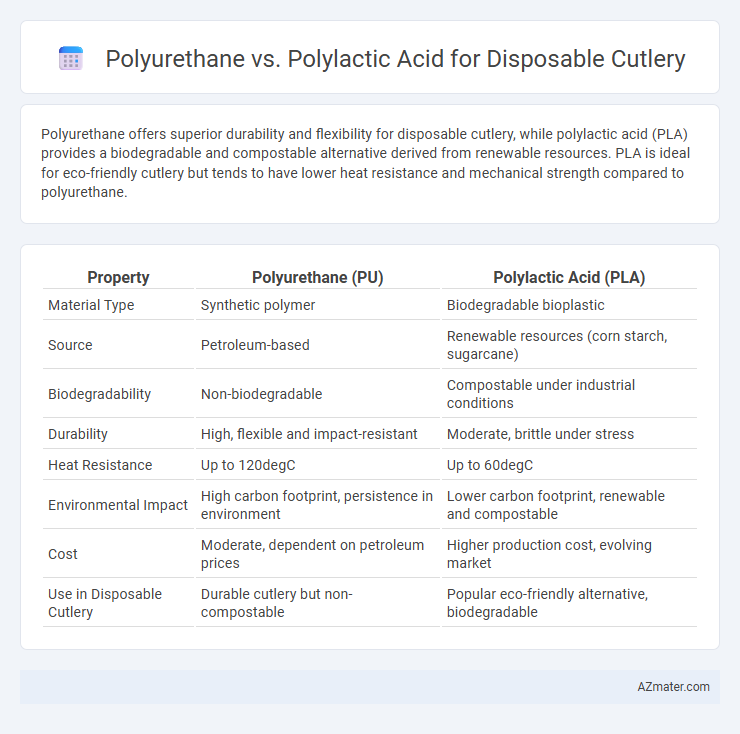
Polyurethane offers superior durability and flexibility for disposable cutlery, while polylactic acid (PLA) provides a biodegradable and compostable alternative derived from renewable resources. PLA is ideal for eco-friendly cutlery but tends to have lower heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to polyurethane.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer | Biodegradable bioplastic |
| Source | Petroleum-based | Renewable resources (corn starch, sugarcane) |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable | Compostable under industrial conditions |
| Durability | High, flexible and impact-resistant | Moderate, brittle under stress |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120degC | Up to 60degC |
| Environmental Impact | High carbon footprint, persistence in environment | Lower carbon footprint, renewable and compostable |
| Cost | Moderate, dependent on petroleum prices | Higher production cost, evolving market |
| Use in Disposable Cutlery | Durable cutlery but non-compostable | Popular eco-friendly alternative, biodegradable |
Introduction to Disposable Cutlery Materials
Polyurethane and polylactic acid (PLA) are prominent materials used in disposable cutlery manufacturing, each offering distinct environmental and functional properties. Polyurethane provides durability and heat resistance, making it suitable for thicker, reusable options, whereas PLA is a biodegradable, compostable bioplastic derived from renewable resources like cornstarch, ideal for single-use utensils. The choice between these materials impacts biodegradability, production cost, and user safety, influencing manufacturers' sustainability strategies in disposable cutlery markets.
What is Polyurethane?
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer widely used for disposable cutlery due to its durability, flexibility, and resistance to heat and chemicals. This synthetic material is formed by reacting diisocyanates with polyols, resulting in a strong yet lightweight plastic that can be molded into various shapes and sizes. Its ability to provide a sturdy, high-quality finish makes polyurethane a popular choice compared to biodegradable alternatives like polylactic acid.
What is Polylactic Acid (PLA)?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, making it an eco-friendly alternative for disposable cutlery. PLA offers the advantage of being compostable under industrial conditions, reducing plastic pollution compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics like polyurethane. Its sustainable origins and biodegradability make PLA a preferred choice in environmentally conscious foodservice applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Polyurethane vs PLA
Polyurethane disposable cutlery is typically manufactured through injection molding or casting processes, allowing precise control over thickness and durability by adjusting polymer formulations and curing times. Polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery is produced mainly via injection molding, utilizing heat and pressure to shape the biodegradable thermoplastic derived from fermented plant starches. PLA manufacturing requires controlled temperature settings to prevent degradation, while polyurethane processes often involve chemical curing agents to enhance flexibility and strength.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources like corn starch, breaking down into water and carbon dioxide within a few months under industrial composting conditions, making it a more environmentally friendly option for disposable cutlery. Polyurethane, typically petroleum-based, exhibits limited biodegradability and can persist in the environment for decades, contributing to long-term pollution and landfill accumulation. Choosing PLA significantly reduces plastic waste and greenhouse gas emissions compared to polyurethane, aligning with sustainable waste management and circular economy principles.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Polyurethane offers superior durability and resistance to heat, making it ideal for disposable cutlery designed to withstand hot and heavy food items without bending or breaking. Polylactic acid (PLA), while biodegradable and environmentally friendly, tends to be more brittle and less heat-resistant, often warping or degrading when exposed to hot temperatures. The performance gap emphasizes polyurethane's advantage in strength and longevity, whereas PLA suits short-term, eco-conscious applications.
Safety and Food Contact Compliance
Polyurethane and polylactic acid (PLA) both serve as materials for disposable cutlery, but PLA is generally favored for food contact compliance due to its biodegradable nature and recognition as food-safe by regulatory agencies like the FDA and EFSA. Polyurethane, while durable, may contain additives or residual chemicals that necessitate rigorous safety testing to ensure it meets migration limits for direct food contact applications. PLA cutlery offers a lower risk of harmful leachates under typical use conditions, making it a safer option for single-use food service environments focused on regulatory compliance and consumer health.
Cost Analysis: Polyurethane vs PLA Cutlery
Polyurethane (PU) disposable cutlery generally incurs higher production costs due to its synthetic polymer base and energy-intensive manufacturing process compared to polylactic acid (PLA), which is derived from renewable resources like corn starch. PLA cutlery benefits from lower raw material costs and bioplastic production economies, making it more cost-effective for large-scale disposable applications. However, PU offers enhanced durability, which might justify its higher price in premium markets focused on strength and longevity.
Consumer Trends and Market Demand
Polyurethane disposable cutlery offers durability and heat resistance, appealing to consumers seeking reusable, high-performance options, while polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery attracts eco-conscious buyers favoring compostable and biodegradable materials. Market demand for PLA cutlery is rising rapidly due to increasing environmental awareness and regulatory bans on single-use plastics, with the global biodegradable cutlery market projected to grow at a CAGR of over 12% through 2030. Consumer trends indicate a significant shift toward sustainability-driven purchasing decisions, prioritizing renewable resources like PLA, despite polyurethane's advantage in mechanical strength and longer lifespan.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Cutlery Materials
Polyurethane offers durability and flexibility but presents challenges in biodegradability, pushing innovation toward bio-based polyurethanes to enhance sustainability. Polylactic acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources like corn starch, exhibits strong biodegradability and compostability, making it a promising candidate for eco-friendly disposable cutlery. Future trends emphasize advancing PLA's thermal resistance and mechanical properties while developing hybrid materials combining polyurethane's strength with PLA's sustainability to meet growing environmental regulations and consumer demand.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polylactic acid for Disposable cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com