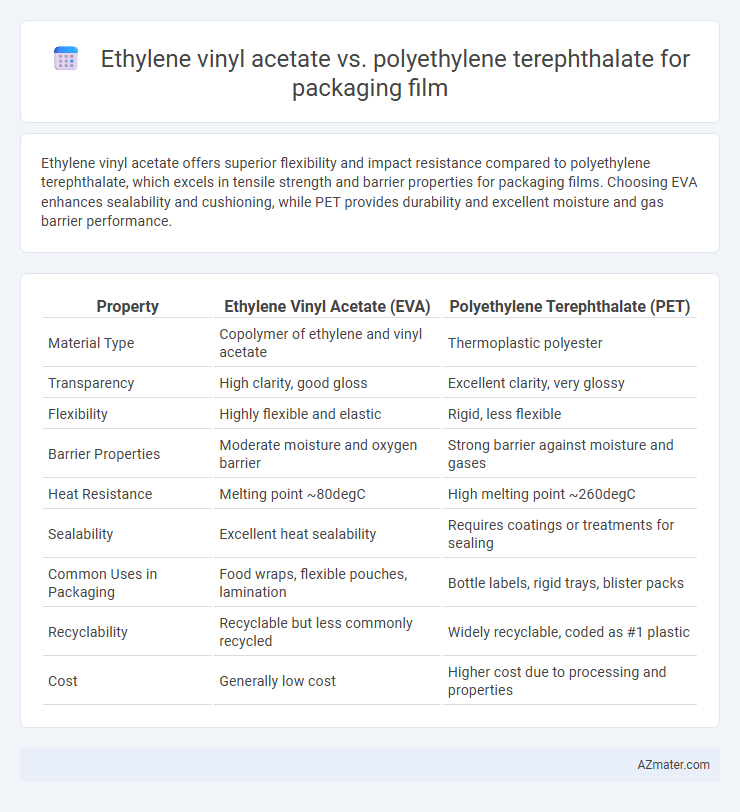
Ethylene vinyl acetate offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate, which excels in tensile strength and barrier properties for packaging films. Choosing EVA enhances sealability and cushioning, while PET provides durability and excellent moisture and gas barrier performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Thermoplastic polyester |
| Transparency | High clarity, good gloss | Excellent clarity, very glossy |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and elastic | Rigid, less flexible |
| Barrier Properties | Moderate moisture and oxygen barrier | Strong barrier against moisture and gases |
| Heat Resistance | Melting point ~80degC | High melting point ~260degC |
| Sealability | Excellent heat sealability | Requires coatings or treatments for sealing |
| Common Uses in Packaging | Food wraps, flexible pouches, lamination | Bottle labels, rigid trays, blister packs |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but less commonly recycled | Widely recyclable, coded as #1 plastic |
| Cost | Generally low cost | Higher cost due to processing and properties |
Introduction to Packaging Film Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a flexible, transparent copolymer known for its excellent clarity, toughness, and resistance to UV radiation, making it ideal for packaging films requiring high impact resistance and good sealability. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior tensile strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, which enhances packaging durability and provides effective barriers against moisture and gases. Selection between EVA and PET depends on the specific packaging requirements, including flexibility, protection level, and environmental factors.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a flexible copolymer widely used in packaging films due to its excellent clarity, elasticity, and impact resistance. It offers superior sealing properties and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it ideal for applications requiring airtight and moisture-resistant packaging. EVA's low-temperature flexibility and strong adhesion capabilities enhance its performance in multilayer packaging films.
Overview of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used in packaging films due to its excellent strength, dimensional stability, and clarity, making it ideal for food and beverage containers. Its inherent barrier properties protect against moisture and oxygen, extending product shelf life and preserving freshness. PET films also offer high chemical resistance and recyclability, supporting sustainability initiatives in the packaging industry.
Mechanical Properties: EVA vs PET
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it ideal for applications requiring high elongation and toughness. PET exhibits greater tensile strength and stiffness, providing excellent dimensional stability and puncture resistance in packaging films. For packaging films that demand enhanced mechanical durability with moderate flexibility, PET is preferred, whereas EVA is selected for softer, more pliable film requirements.
Barrier Performance: Oxygen and Moisture Protection
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers moderate oxygen barrier properties but excels in moisture resistance due to its flexible and adhesive nature, making it suitable for packaging that requires moisture protection. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides superior oxygen barrier performance, effectively preventing oxygen permeation and thus extending product shelf life in packaging applications. For packaging films requiring high oxygen and moisture barriers, PET is generally preferred, although EVA can be blended or coated to enhance barrier performance.
Transparency and Clarity Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior transparency and clarity compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET) due to its amorphous structure, which allows for higher light transmission and a clearer appearance in packaging films. PET exhibits excellent mechanical strength but tends to have slightly lower optical clarity because of its semi-crystalline nature, causing some light scattering. For applications demanding high visibility and aesthetic appeal, EVA films are often preferred over PET films.
Flexibility and Formability in Packaging Applications
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and excellent elongation, making it ideal for packaging films requiring high stretch and impact resistance. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides greater formability with enhanced structural rigidity and thermal stability, suitable for applications demanding shape retention and barrier properties. EVA's softness and pliability favor flexible packaging, while PET's toughness supports rigid and thermoformed packaging solutions.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility and clarity, making it suitable for food packaging films that require high barrier properties against moisture and oxygen, while complying with FDA and EFSA food safety regulations. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and excellent gas barrier performance, widely accepted under global food contact standards including FDA 21 CFR and EU Regulation 10/2011. Both materials demonstrate compliance with migration limits and toxicity requirements, but PET is often preferred for extended shelf-life applications due to its durability and recyclability in food packaging.
Cost Efficiency and Sustainability Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers cost efficiency in packaging film production due to its lower raw material and processing costs compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which involves higher energy consumption during manufacturing. From a sustainability standpoint, PET excels with its superior recyclability and lower carbon footprint when recycled properly, while EVA's biodegradability remains limited, leading to challenges in waste management. Selecting between EVA and PET depends on balancing immediate cost savings with long-term environmental impact and recyclability goals in packaging applications.
Best Use Cases: EVA or PET for Packaging Film
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) excels in flexible packaging film applications requiring high clarity, moisture barrier, and impact resistance, making it ideal for food packaging, stretch wraps, and medical supplies. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior tensile strength, thermal stability, and excellent gas barrier properties, making it the preferred choice for rigid or semi-rigid packaging such as beverage bottles, food containers, and shrink films. PET's recyclability and resistance to chemicals further enhance its suitability for sustainable packaging solutions compared to EVA.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Packaging Film
 azmater.com
azmater.com