Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-performance 3D printing applications. Polylactic acid (PLA) is biodegradable and easier to print, but it lacks the durability and heat resistance of PEEK, limiting its use to prototyping and less demanding parts.
Table of Comparison
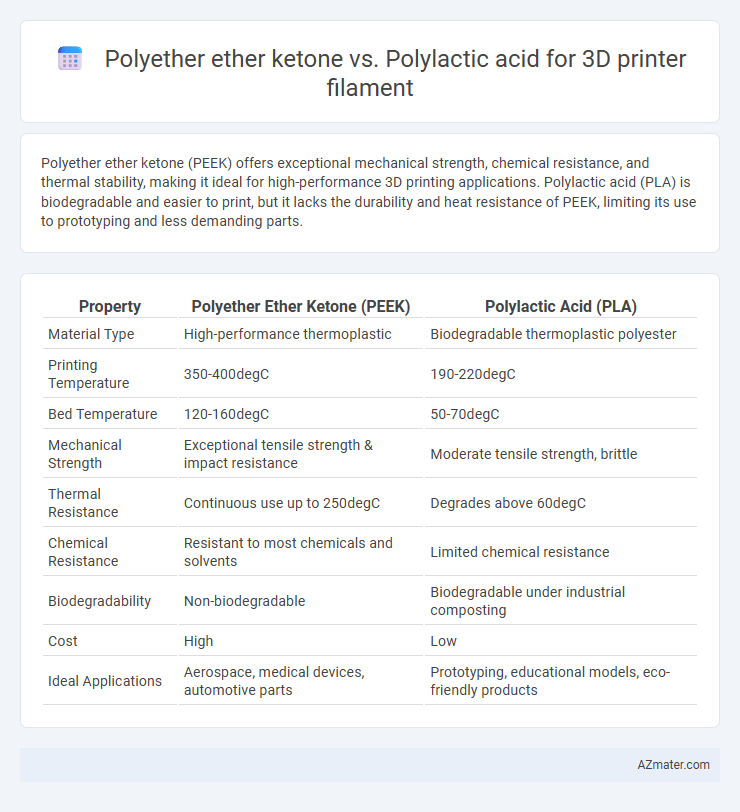
| Property | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoplastic | Biodegradable thermoplastic polyester |
| Printing Temperature | 350-400degC | 190-220degC |
| Bed Temperature | 120-160degC | 50-70degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Exceptional tensile strength & impact resistance | Moderate tensile strength, brittle |
| Thermal Resistance | Continuous use up to 250degC | Degrades above 60degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most chemicals and solvents | Limited chemical resistance |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable | Biodegradable under industrial composting |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Ideal Applications | Aerospace, medical devices, automotive parts | Prototyping, educational models, eco-friendly products |
Introduction to PEEK and PLA as 3D Printing Filaments
PEEK (Polyether ether ketone) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for advanced industrial and medical 3D printing applications. PLA (Polylactic acid), derived from renewable resources like corn starch, is a biodegradable and user-friendly filament, popular for its ease of printing and environmental benefits in prototyping and consumer-grade 3D printing. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with PEEK excelling in demanding, high-stress environments, while PLA offers cost-effective, sustainable options for less rigorous uses.
Chemical Structure and Material Properties
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) features a high-performance semi-crystalline polymer structure with repeating ketone and ether groups, providing exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Polylactic acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources, is a biodegradable aliphatic polyester with a simpler linear ester backbone, resulting in lower melting temperatures and reduced thermal resistance compared to PEEK. PEEK's rigidity and resistance to harsh environments make it ideal for demanding industrial applications, whereas PLA's ease of printing and environmental friendliness suit prototyping and consumer-grade 3D printing.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior mechanical strength compared to Polylactic acid (PLA), with tensile strength typically around 90-100 MPa versus PLA's 50-70 MPa, making PEEK ideal for high-performance applications. PEEK exhibits exceptional durability and chemical resistance, maintaining structural integrity under high temperatures up to 250degC, whereas PLA tends to degrade and becomes brittle under prolonged heat and UV exposure. The high impact resistance and fatigue endurance of PEEK surpass PLA's relatively low durability, reinforcing PEEK's suitability for industrial and engineering-grade 3D printed parts.
Thermal Performance: Heat Resistance and Stability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits exceptional thermal performance with a heat resistance exceeding 250degC, making it ideal for high-temperature 3D printing applications requiring dimensional stability under sustained heat exposure. In contrast, polylactic acid (PLA) has a lower heat resistance threshold around 60degC to 65degC, which limits its use in environments with elevated temperatures due to its tendency to soften and deform. PEEK's superior thermal stability and high glass transition temperature enhance its durability and mechanical strength in demanding industrial and aerospace applications, whereas PLA is better suited for low-heat scenarios and prototyping.
Biocompatibility and Environmental Impact
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior biocompatibility due to its chemical resistance and stability, making it suitable for medical implants and devices. Polylactic acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources such as corn starch, is biodegradable and environmentally friendly, but its biocompatibility is limited for long-term medical applications. PLA's low environmental impact contrasts with PEEK's high energy consumption during production and limited biodegradability.
Printability: Ease of Use and Printer Requirements
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers exceptional mechanical strength and thermal resistance but requires specialized high-temperature 3D printers with heated chambers and hardened nozzles, making its printability more demanding. Polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable thermoplastic, excels in ease of use due to low printing temperatures (around 190-220degC) and compatibility with most standard FDM printers, providing minimal warping and reliable layer adhesion. The printer requirements for PLA are significantly less rigorous compared to PEEK, which necessitates advanced hardware and precise temperature control for successful printing.
Surface Finish and Detail Resolution
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) filament delivers superior surface finish and high-detail resolution due to its excellent thermal stability and minimal warping during 3D printing. Polylactic acid (PLA) offers good surface smoothness and fine detail but tends to lack the strength and heat resistance that enhances the precision of complex features in PEEK prints. For applications requiring intricate details and a polished finish, PEEK outperforms PLA despite its higher printing temperature and cost.
Application Suitability in Various Industries
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 480degF (250degC), and mechanical strength, making it suitable for demanding applications in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries where durability and sterilization are critical. Polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable and easy-to-print filament, is preferred for rapid prototyping, educational purposes, and consumer products due to its lower melting point around 180-220degC and environmentally friendly profile. PEEK's high-performance characteristics suit end-use parts exposed to harsh environments, while PLA is ideal for cost-effective, eco-conscious projects with less mechanical stress.
Cost Analysis and Material Availability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) filament commands a significantly higher price than polylactic acid (PLA), often costing up to 10 times more due to its advanced thermal and mechanical properties. PLA is widely available and affordable, sourced from renewable materials, making it the preferred choice for cost-sensitive and general-purpose 3D printing. PEEK's limited material availability and requirement for specialized high-temperature printers contribute to its elevated overall production costs and restricted accessibility.
Choosing the Right Filament: PEEK vs PLA
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to Polylactic acid (PLA), making it ideal for high-performance industrial applications and parts subjected to extreme conditions. PLA, a biodegradable and easy-to-print polymer, is preferred for prototyping, hobbyist projects, and environmentally conscious users due to its lower printing temperature and minimal warping. Selecting between PEEK and PLA depends on the application's durability requirements, printing capability, and environmental impact considerations.
Infographic: Polyether ether ketone vs Polylactic acid for 3D printer filament
 azmater.com
azmater.com