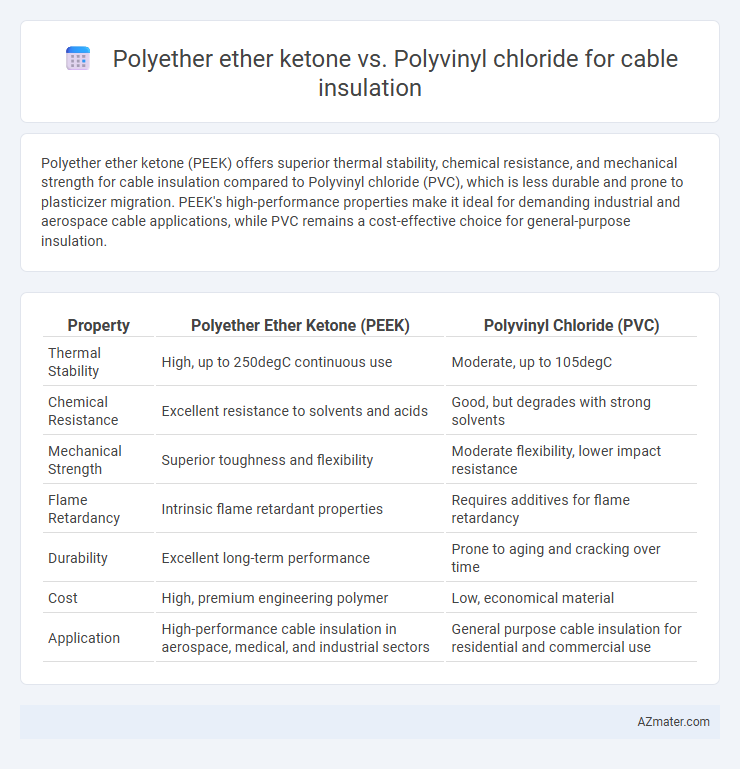
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength for cable insulation compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is less durable and prone to plasticizer migration. PEEK's high-performance properties make it ideal for demanding industrial and aerospace cable applications, while PVC remains a cost-effective choice for general-purpose insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High, up to 250degC continuous use | Moderate, up to 105degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents and acids | Good, but degrades with strong solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior toughness and flexibility | Moderate flexibility, lower impact resistance |
| Flame Retardancy | Intrinsic flame retardant properties | Requires additives for flame retardancy |
| Durability | Excellent long-term performance | Prone to aging and cracking over time |
| Cost | High, premium engineering polymer | Low, economical material |
| Application | High-performance cable insulation in aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors | General purpose cable insulation for residential and commercial use |
Introduction to Cable Insulation Materials
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) serve as prominent cable insulation materials, each exhibiting distinct thermal and mechanical properties critical for electrical performance. PEEK offers superior heat resistance up to 260degC, excellent chemical stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance and harsh environment applications. PVC, widely used for general-purpose insulation, provides cost-effective flexibility, flame retardancy, and good electrical insulating properties but has lower thermal endurance typically limited to 70-105degC.
Overview of Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding cable insulation applications. Unlike Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), PEEK maintains integrity at continuous operating temperatures up to 260degC, offering superior durability in harsh environments such as aerospace and automotive industries. Its excellent electrical insulation properties combined with resistance to hydrocarbon oils and radiation further enhance PEEK's suitability for advanced electrical and electronic cable systems.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer renowned for its excellent electrical insulation properties, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness in cable insulation applications. PVC offers flexibility, flame retardancy, and durability, making it suitable for a broad range of low to medium voltage cables in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Its ability to withstand moisture and environmental factors, combined with ease of processing, ensures reliable performance and extended service life in cable insulation compared to alternative materials.
Mechanical Properties: PEEK vs PVC
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in cable insulation applications, offering high tensile strength up to 90 MPa versus PVC's typical range of 40-50 MPa. PEEK provides excellent impact resistance and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures up to 250degC, whereas PVC softens and degrades around 80-105degC. The enhanced mechanical robustness and thermal endurance of PEEK ensure improved durability and longevity in demanding electrical environments compared to the more flexible but less resilient PVC.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), maintaining structural integrity at continuous temperatures up to 260degC, while PVC typically degrades above 105degC. PEEK's high glass transition temperature of approximately 143degC and melting point around 343degC enable it to withstand harsh thermal environments without deformation. In contrast, PVC's lower thermal limits and tendency to release harmful gases when overheated limit its application in high-temperature cable insulation.
Electrical Performance and Insulation Capacity
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior electrical performance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its high dielectric strength of approximately 200 kV/mm and excellent thermal stability up to 250degC, ensuring reliable insulation under extreme conditions. PEEK's low dielectric constant (around 3.2) and minimal dissipation factor enhance signal integrity and reduce energy losses, making it ideal for high-frequency cable applications. In contrast, PVC offers lower dielectric strength (typically 40-60 kV/mm) and degrades at elevated temperatures, limiting its insulation capacity and long-term electrical reliability.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Durability
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), withstanding strong acids, bases, and organic solvents without degrading. PEEK offers excellent environmental durability due to its high thermal stability, UV resistance, and minimal moisture absorption, making it ideal for harsh outdoor and industrial cable insulation applications. In contrast, PVC tends to degrade under prolonged UV exposure and is less resistant to chemical attack, limiting its use in demanding environments.
Flexibility and Processability in Cable Manufacturing
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior flexibility compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), enhancing cable bend radius and durability in dynamic applications. PEEK's high thermal stability and chemical resistance enable efficient processing at elevated temperatures without degradation, facilitating the extrusion and molding processes in cable manufacturing. While PVC provides cost-effective and easy processing at lower temperatures, PEEK's combination of flexibility and processability supports high-performance cable insulation requirements in demanding environments.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) cable insulation offers superior thermal and chemical resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is known for its affordability and widespread availability. While PEEK's price can be up to 10 times greater than PVC, its durability and longer lifespan may reduce overall lifecycle costs in demanding industrial applications. Economic considerations favor PVC for budget-sensitive projects, whereas PEEK presents a cost-effective solution when performance requirements justify the initial investment.
Applications and Industry Recommendations
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance aerospace, automotive, and medical cable insulation applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) remains cost-effective and versatile, widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial cabling where moderate temperature and chemical exposure are expected. Industry recommendations favor PEEK for critical environments requiring long-term durability and safety compliance, while PVC is preferred for general-purpose wiring due to its ease of processing and flame-retardant properties.
Infographic: Polyether ether ketone vs Polyvinyl chloride for Cable insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com