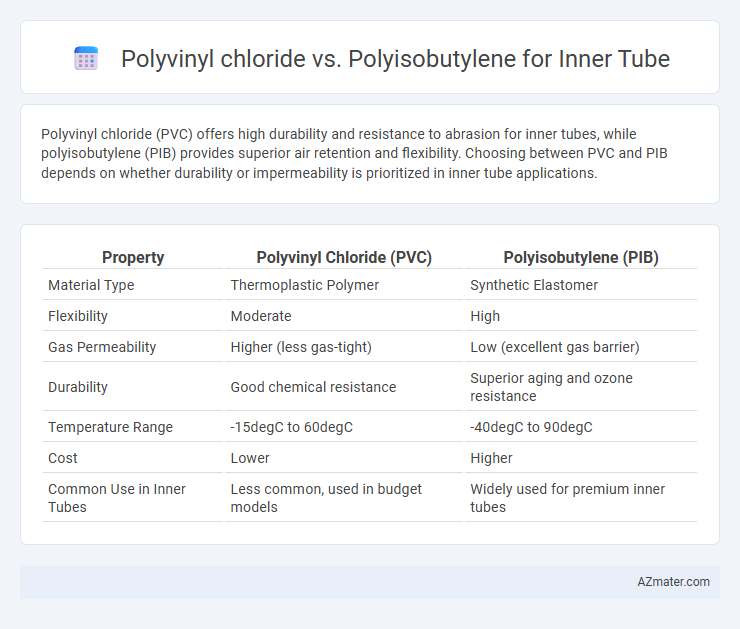
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers high durability and resistance to abrasion for inner tubes, while polyisobutylene (PIB) provides superior air retention and flexibility. Choosing between PVC and PIB depends on whether durability or impermeability is prioritized in inner tube applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polyisobutylene (PIB) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Synthetic Elastomer |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Gas Permeability | Higher (less gas-tight) | Low (excellent gas barrier) |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance | Superior aging and ozone resistance |
| Temperature Range | -15degC to 60degC | -40degC to 90degC |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Use in Inner Tubes | Less common, used in budget models | Widely used for premium inner tubes |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyisobutylene (PIB) are commonly used materials for inner tubes due to their distinct properties. PVC offers durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for standard bicycle and automotive inner tubes. In contrast, PIB provides superior air retention and flexibility, which is essential for high-performance and heavy-duty inner tubes where airtightness and elasticity are critical.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in inner tube manufacturing due to its excellent chemical resistance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. PVC offers strong tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for applications requiring long-lasting performance under varying pressure conditions. Its rigid molecular structure ensures minimal gas permeability, which enhances air retention in inner tubes compared to other materials like polyisobutylene.
Overview of Polyisobutylene (PIB)
Polyisobutylene (PIB) is a synthetic rubber known for its exceptional impermeability to gases, making it highly effective as an inner tube material for tires. Compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), PIB offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability under varying temperature conditions, which prolongs tube lifespan and performance. Its low gas permeability significantly reduces air loss, enhancing tire pressure retention and overall efficiency in automotive and bicycle applications.
Material Properties Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers high durability, weather resistance, and excellent flexibility, making it suitable for inner tubes in various applications. Polyisobutylene (PIB), known for its superior impermeability to gases and excellent elasticity, provides enhanced air retention, which is critical for maintaining tire pressure over time. Compared to PVC, PIB exhibits better resistance to UV degradation and chemical corrosion, resulting in longer inner tube lifespan and improved overall performance.
Durability and Longevity
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) inner tubes offer enhanced durability due to their resistance to abrasion, chemical exposure, and environmental stress cracking, providing reliable long-term performance. Polyisobutylene (PIB) inner tubes excel in flexibility and impermeability to gases, resulting in superior air retention and extended lifespan despite potential susceptibility to UV degradation. Choosing between PVC and PIB inner tubes depends on application-specific durability needs, with PVC favored for mechanical toughness and PIB preferred for air retention and longevity.
Air Retention Capabilities
Polyisobutylene offers superior air retention compared to polyvinyl chloride due to its low gas permeability and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for inner tubes requiring long-lasting inflation. Polyvinyl chloride tends to allow more air diffusion over time, leading to more frequent inflation needs and potential performance loss. Air retention in inner tubes directly impacts durability and reliability, positioning polyisobutylene as a preferred material in high-performance and commercial applications.
Flexibility and Handling
Polyisobutylene offers superior flexibility and elasticity compared to polyvinyl chloride, making it ideal for inner tubes that require better handling and resistance to deformation under pressure. Polyvinyl chloride, while durable and cost-effective, tends to be less flexible, resulting in a stiffer inner tube that can affect ride comfort and responsiveness. The enhanced pliability of polyisobutylene contributes to improved shock absorption and overall performance in bicycle and automotive inner tubes.
Cost and Availability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) inner tubes are widely available and generally cost-effective due to large-scale manufacturing and abundant raw materials. Polyisobutylene (PIB) tubes, while offering superior air retention and flexibility, tend to be more expensive and less readily available because of specialized production processes. PVC's low cost and widespread distribution make it the preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications, whereas PIB is favored for performance-focused uses despite higher costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) inner tubes pose significant environmental concerns due to the release of toxic chemicals like dioxins during production and disposal, hindering sustainability efforts. Polyisobutylene (PIB) offers a more eco-friendly alternative with better chemical stability and lower emissions, contributing to reduced environmental impact. Choosing PIB supports sustainability by promoting recyclability and minimizing hazardous waste compared to PVC inner tubes.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Inner Tube Material
Polyisobutylene offers superior air retention and flexibility compared to polyvinyl chloride, making it ideal for high-performance inner tubes that demand durability and reduced air loss. Polyvinyl chloride, while more cost-effective and resistant to abrasion, falls short in elasticity and tends to become brittle over time. Selecting polyisobutylene as the inner tube material ensures enhanced longevity and performance, especially suitable for demanding cycling or automotive applications.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polyisobutylene for Inner Tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com