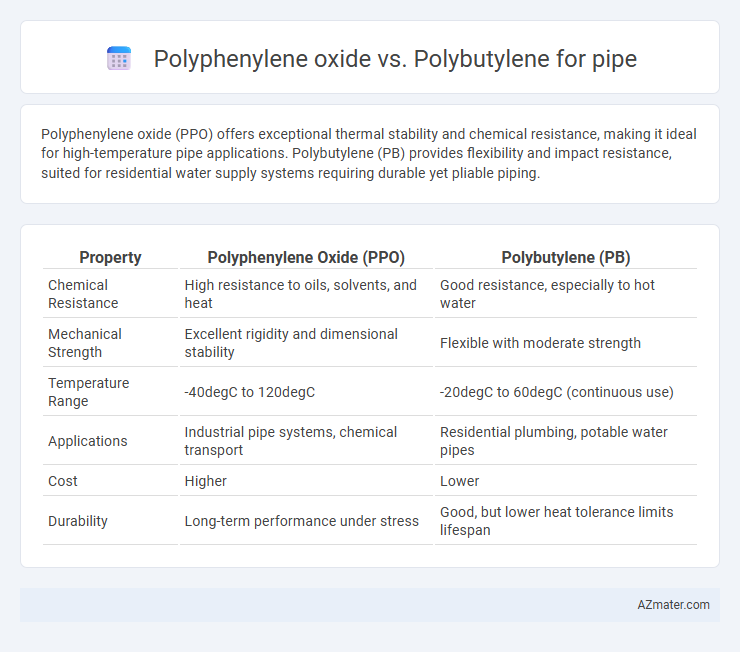
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature pipe applications. Polybutylene (PB) provides flexibility and impact resistance, suited for residential water supply systems requiring durable yet pliable piping.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polybutylene (PB) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils, solvents, and heat | Good resistance, especially to hot water |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent rigidity and dimensional stability | Flexible with moderate strength |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -20degC to 60degC (continuous use) |
| Applications | Industrial pipe systems, chemical transport | Residential plumbing, potable water pipes |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Durability | Long-term performance under stress | Good, but lower heat tolerance limits lifespan |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide and Polybutylene
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it suitable for demanding piping applications. Polybutylene (PB), a flexible polymer, offers good impact resistance and long-term durability, commonly used in residential and commercial plumbing systems. Comparing PPO and PB highlights differences in rigidity, temperature tolerance, and chemical resistance crucial for selecting the optimal pipe material.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) consists of a backbone of repeating phenylene oxide units, characterized by strong aromatic rings linked through oxygen atoms, which provides high thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion. Polybutylene (PB) is composed of long chains of butylene monomers, a saturated hydrocarbon polymer with flexible aliphatic carbon-carbon bonds, offering excellent impact resistance and flexibility. The aromatic structure of PPO enhances rigidity and dimensional stability, while the aliphatic composition of PB results in superior ductility and ease of installation in piping systems.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polybutylene (PB), making it more resistant to deformation under stress and high pressure conditions. PPO offers higher tensile strength and better dimensional stability, which ensures long-term durability in pipe applications exposed to thermal and mechanical loads. In contrast, polybutylene has more flexibility but lower tensile and impact strength, which may limit its use in high-pressure or heavy-duty piping systems.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polybutylene, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 130degC, whereas polybutylene typically withstands maximum continuous operating temperatures around 90degC. PPO's high glass transition temperature and oxidative resistance make it ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. Polybutylene offers more flexibility but lower temperature resistance, limiting its use in high-heat plumbing or industrial pipe systems.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to polybutylene (PB), making it highly suitable for applications involving harsh chemical environments. PPO maintains structural integrity when exposed to aggressive chemicals, including acids and alkalis, whereas PB is more prone to swelling and degradation under similar conditions. The enhanced chemical resistance of PPO extends pipe lifespan and reduces maintenance costs in industrial and water distribution systems.
Installation Methods and Ease of Use
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) pipes feature excellent dimensional stability and are compatible with standard solvent cement and heat fusion methods, simplifying installation with reliable chemical resistance. Polybutylene (PB) pipes utilize heat fusion and mechanical fittings, offering flexibility and ease in maneuvering tight bends during installation but may require careful temperature control to avoid joint failures. PPO's rigidity reduces the need for additional supports, whereas PB's flexibility allows for fewer fittings, impacting overall installation time and labor costs.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) pipes typically incur higher upfront costs compared to Polybutylene (PB) pipes due to more complex manufacturing processes and superior thermal stability. Polybutylene offers greater cost-effectiveness and wider availability in residential plumbing applications, benefiting from established supply chains and lower raw material expenses. Availability of PPO pipes is more limited, often reserved for specialized industrial uses, while PB pipes remain readily accessible across multiple markets, influencing overall project budget considerations.
Longevity and Durability in Piping Applications
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior longevity and chemical resistance compared to polybutylene (PB), making it ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments in piping applications. PPO maintains structural integrity under prolonged thermal stress and oxidative conditions, whereas PB tends to degrade faster when exposed to water and varying temperatures. The enhanced mechanical strength and dimensional stability of PPO contribute to extended service life and reduced maintenance costs in demanding piping systems.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) pipes exhibit higher thermal stability and chemical resistance, leading to longer service life and reduced replacement frequency, which lowers environmental impact compared to polybutylene (PB) pipes known for shorter lifespan and susceptibility to degradation. PPO is more challenging to recycle due to its complex aromatic polymer structure, while polybutylene, with a simpler polyether backbone, can be mechanically recycled more efficiently but often results in downcycling. The overall environmental footprint of PPO pipes is offset by durability, whereas polybutylene pipelines contribute to more frequent landfill waste and potential microplastic release in disposal.
Suitable Applications: Selecting the Right Material for Pipes
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for hot water plumbing and industrial fluid transport. Polybutylene (PB) provides flexibility and impact resistance, commonly used in residential water supply systems and radiant floor heating. Choosing between PPO and polybutylene depends on temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress requirements for the specific piping application.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polybutylene for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com