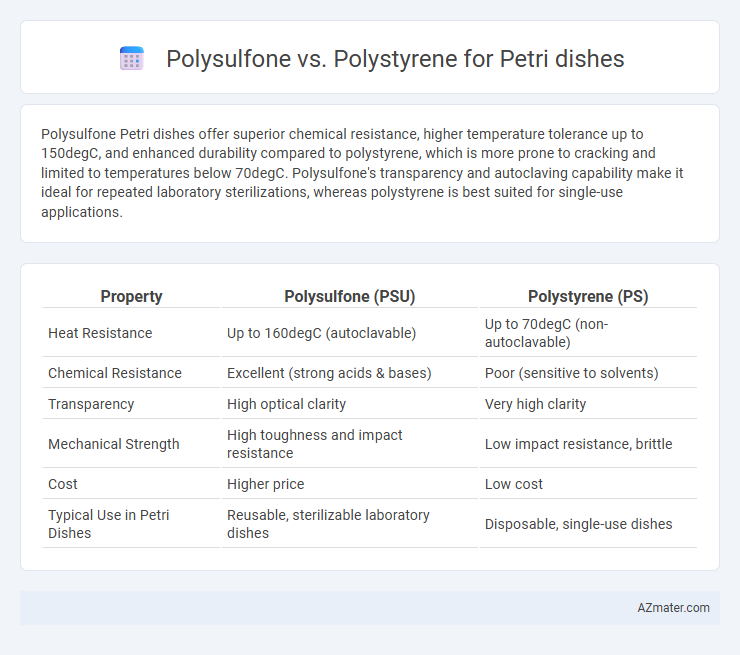
Polysulfone Petri dishes offer superior chemical resistance, higher temperature tolerance up to 150degC, and enhanced durability compared to polystyrene, which is more prone to cracking and limited to temperatures below 70degC. Polysulfone's transparency and autoclaving capability make it ideal for repeated laboratory sterilizations, whereas polystyrene is best suited for single-use applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 160degC (autoclavable) | Up to 70degC (non-autoclavable) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (strong acids & bases) | Poor (sensitive to solvents) |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | Very high clarity |
| Mechanical Strength | High toughness and impact resistance | Low impact resistance, brittle |
| Cost | Higher price | Low cost |
| Typical Use in Petri Dishes | Reusable, sterilizable laboratory dishes | Disposable, single-use dishes |
Introduction to Petri Dish Materials
Polysulfone and polystyrene are common materials used in the manufacturing of petri dishes, each offering distinct properties suited for specific laboratory applications. Polysulfone is prized for its high chemical resistance, thermal stability, and durability, making it ideal for repeated sterilization and autoclaving. Polystyrene, on the other hand, is favored for its optical clarity and cost-effectiveness, although it is more prone to cracking and limited in heat resistance compared to polysulfone.
Overview of Polysulfone and Polystyrene
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its superior chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 150degC, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for autoclaving and sterilization processes in Petri dishes. Polystyrene (PS) is a cost-effective, rigid, and transparent thermoplastic commonly used for disposable Petri dishes, characterized by its lower heat resistance (up to 80degC) and susceptibility to chemical stress cracking. The choice between polysulfone and polystyrene depends on application requirements, with polysulfone preferred for reusable, high-sterility environments and polystyrene suited for single-use, cost-sensitive laboratory settings.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polysulfone Petri dishes offer superior thermal stability with an operating temperature range up to 160degC compared to polystyrene's limit of around 70-80degC, making them more suitable for high-temperature applications. Polysulfone exhibits excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance, maintaining structural integrity under sterilization processes like autoclaving, while polystyrene is prone to deformation and chemical degradation. Transparency in polystyrene is higher, providing better optical clarity for microscopic observation, whereas polysulfone balances transparency with durability and resistance to hydrolysis.
Chemical Resistance and Compatibility
Polysulfone offers superior chemical resistance compared to polystyrene, maintaining stability when exposed to solvents, acids, and alkaline solutions commonly used in laboratory settings. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and clear, is prone to chemical degradation and can become brittle or discolored upon contact with aggressive reagents. For applications requiring sterilization and prolonged chemical exposure, polysulfone Petri dishes provide enhanced compatibility and durability, ensuring reliable performance in biomedical and industrial research.
Heat Tolerance and Sterilization Methods
Polysulfone Petri dishes offer superior heat tolerance, withstanding autoclave sterilization at temperatures up to 134degC without deforming, unlike polystyrene which typically warps above 70degC and is unsuitable for high-temperature sterilization. Polystyrene is often sterilized using gamma radiation or ethylene oxide, methods that preserve its structural integrity but limit heat resistance. The robust thermal stability and compatibility with steam sterilization make polysulfone ideal for applications requiring repeated high-temperature sterilization cycles.
Clarity and Optical Performance
Polysulfone offers superior clarity and excellent optical performance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for precise visual inspection in Petri dishes. It maintains high transparency and resists heat and chemical exposure without yellowing, ensuring consistent clarity during sterilization processes. Polystyrene, while affordable and clear initially, may degrade or become cloudy under heat, reducing long-term optical quality for microbial observation.
Durability and Reusability
Polysulfone Petri dishes exhibit superior durability compared to polystyrene, with higher resistance to heat, chemicals, and repeated sterilization cycles, making them ideal for long-term laboratory use. Polystyrene dishes are typically disposable due to their lower resistance to autoclaving and mechanical stress, resulting in limited reusability. The enhanced structural integrity of polysulfone enables multiple uses without compromising sterility or performance, reducing overall laboratory waste.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Polysulfone petri dishes generally have a higher cost compared to polystyrene due to their superior thermal and chemical resistance, making them suitable for repeated sterilization cycles. Polystyrene petri dishes are more widely available and economically favorable for disposable use, with large-scale production driving down prices significantly. Availability of polysulfone is more limited, often confined to specialized laboratory suppliers, while polystyrene is commonly stocked by general scientific suppliers globally.
Application Suitability in Laboratories
Polysulfone Petri dishes offer superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for autoclaving and repeated sterilization in microbiology and cell culture labs. Polystyrene dishes are generally preferred for single-use applications due to their affordability and clarity but may deform under high temperatures, limiting their use in heat-based sterilization processes. Laboratories conducting precise microbial assays or long-term cell growth experiments benefit from polysulfone's durability and biocompatibility compared to the cost-effective but less robust polystyrene options.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polysulfone Petri dishes offer superior environmental benefits due to their enhanced durability and potential for multiple reuses, reducing plastic waste compared to single-use polystyrene dishes. Polystyrene is derived from fossil fuels and is challenging to recycle, contributing significantly to environmental pollution and landfill accumulation. The biodegradability and recyclability of polysulfone support sustainable laboratory practices by minimizing ecological footprint and resource consumption.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polystyrene for Petri dish
 azmater.com
azmater.com