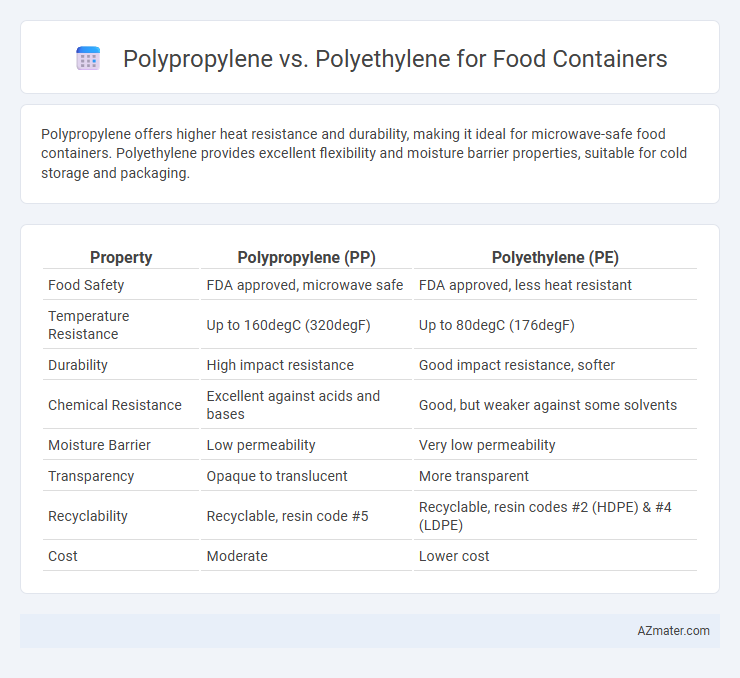
Polypropylene offers higher heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for microwave-safe food containers. Polyethylene provides excellent flexibility and moisture barrier properties, suitable for cold storage and packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Food Safety | FDA approved, microwave safe | FDA approved, less heat resistant |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 160degC (320degF) | Up to 80degC (176degF) |
| Durability | High impact resistance | Good impact resistance, softer |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids and bases | Good, but weaker against some solvents |
| Moisture Barrier | Low permeability | Very low permeability |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | More transparent |
| Recyclability | Recyclable, resin code #5 | Recyclable, resin codes #2 (HDPE) & #4 (LDPE) |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower cost |
Introduction to Food-Grade Plastics
Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) are two of the most common food-grade plastics used in container manufacturing due to their chemical resistance and safety for direct food contact. Polypropylene offers higher heat resistance and rigidity, making it ideal for microwaveable and reusable food containers, while polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), provides excellent moisture barrier properties and flexibility for disposable or freezer-safe packaging. Both materials comply with FDA and European food safety regulations, ensuring they do not leach harmful substances into food products.
What Is Polypropylene?
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in food containers due to its high chemical resistance, durability, and heat tolerance up to 100degC, making it ideal for microwave-safe and dishwasher-safe applications. Its non-toxic nature and resistance to moisture and oils ensure food safety and prevent contamination, distinguishing it from polyethylene variants that may lack comparable heat resistance or rigidity. Polypropylene's low density and excellent sealing properties contribute to its popularity for packaging perishable goods, offering superior protection and extended shelf life.
What Is Polyethylene?
Polyethylene is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for food container applications. It is available in various densities, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE), each offering different properties such as rigidity or softness. Polyethylene's non-toxic nature and excellent moisture barrier capabilities ensure food safety and prolonged freshness in packaging solutions.
Key Chemical Differences
Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene (PE) differ fundamentally in their chemical structures, with PP featuring a methyl group attached to every other carbon atom in its polymer chain, whereas PE consists solely of repeating ethylene units. This structural variation gives PP a higher melting point (around 160degC) compared to PE (ranging from 105degC to 130degC), making PP more suitable for food containers requiring heat resistance and microwave use. PE's simpler structure provides greater flexibility and chemical resistance, but lower thermal stability, influencing its application in softer or disposable food packaging.
Food Safety and Regulatory Standards
Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) are widely used in food containers due to their excellent food safety profiles and compliance with regulatory standards such as FDA and EFSA approvals. Polypropylene offers higher heat resistance and chemical stability, making it suitable for microwaveable and reusable food containers without leaching harmful substances. Polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is favored for its robustness and resistance to moisture, ensuring safe food storage while meeting stringent migration limits set by food safety authorities.
Temperature Resistance and Performance
Polypropylene (PP) offers superior temperature resistance up to 160degC, making it ideal for hot food storage and microwave use, while Polyethylene (PE) generally withstands temperatures up to 120degC and is better suited for cold or room temperature applications. PP provides excellent chemical resistance and rigidity, ensuring durable food containers that maintain shape under heat, whereas PE is more flexible and impact-resistant but less heat tolerant. For food containers requiring repeated heating or dishwasher safety, polypropylene outperforms polyethylene in maintaining structural integrity and food safety standards.
Durability and Longevity
Polypropylene offers superior durability and higher heat resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for food containers that undergo frequent microwave or dishwasher use. Polyethylene, particularly HDPE, provides excellent impact resistance and chemical stability, contributing to long-lasting food storage solutions resistant to cracking and degradation. Both materials ensure food safety, but polypropylene typically delivers enhanced longevity under thermal stress and repeated use scenarios.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) are both widely used in food containers, but PP offers superior durability and higher heat resistance, making it more suitable for microwave-safe applications. Environmentally, polyethylene, especially HDPE, has a more established recycling infrastructure and typically achieves higher recycling rates compared to polypropylene. Despite polypropylene's lower recyclability, its lighter weight and longer lifespan can contribute to reduced environmental impact when properly managed in recycling programs.
Cost Comparison for Manufacturers
Polypropylene (PP) typically offers a lower production cost compared to polyethylene (PE) due to its higher melting point and better processability in injection molding, making it a cost-efficient choice for food container manufacturers. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), generally requires higher raw material expenses and energy consumption during processing. Manufacturers favor polypropylene when balancing durability and cost-effectiveness in large-scale food container production.
Choosing the Best Material for Food Containers
Polypropylene (PP) offers higher heat resistance and better chemical stability, making it ideal for microwaveable food containers and hot food storage, while Polyethylene (PE), especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), provides excellent impact resistance and moisture barrier properties suitable for cold food packaging. PP's low moisture absorption and ability to withstand repeated sterilization ensure food safety and durability, whereas PE's flexibility and cost-efficiency make it favorable for disposable or flexible containers. Choosing the best material depends on specific use cases, such as temperature requirements, container reusability, and food type, with PP preferred for hot, microwavable applications and PE favored for flexible, cold storage solutions.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyethylene for Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com