Polyphenylene oxide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyvinylidene chloride, making it ideal for high-temperature food wrap applications. Polyvinylidene chloride provides excellent barrier properties against moisture and oxygen but has lower heat resistance and environmental concerns.
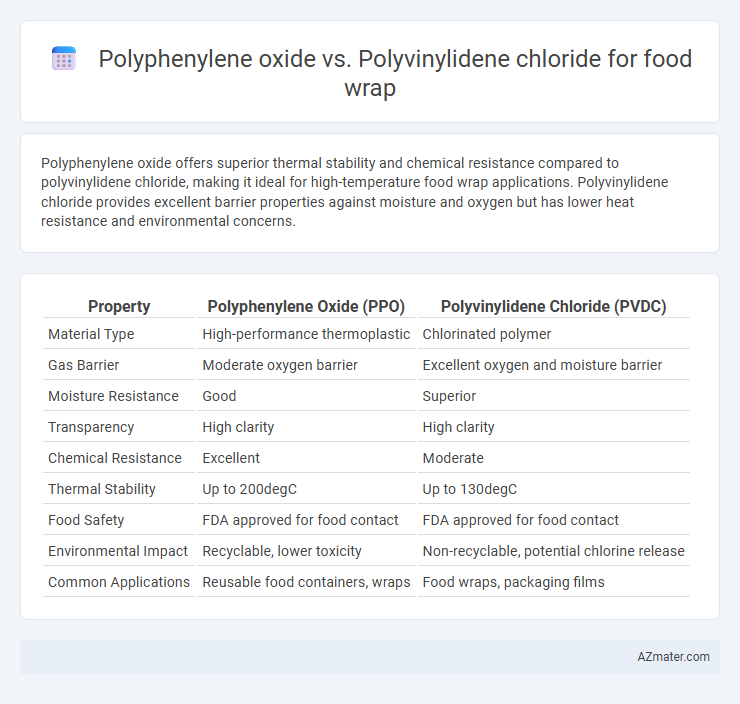
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoplastic | Chlorinated polymer |
| Gas Barrier | Moderate oxygen barrier | Excellent oxygen and moisture barrier |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Transparency | High clarity | High clarity |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 200degC | Up to 130degC |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved for food contact |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, lower toxicity | Non-recyclable, potential chlorine release |
| Common Applications | Reusable food containers, wraps | Food wraps, packaging films |
Introduction to Food Wrap Materials
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for food wraps that require durability and resistance to oils and fats. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) is known for its excellent barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and aromas, extending the shelf life of perishable foods. Both materials play critical roles in food packaging, with PPO providing mechanical strength and PVDC ensuring effective preservation of food quality.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and superior barrier properties against moisture and oxygen. In food wrap applications, PPO provides effective protection by preserving food freshness and extending shelf life through its inherent low permeability. Compared to polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), PPO offers enhanced thermal stability and recyclability, making it a sustainable choice for modern food packaging solutions.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC)
Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) is a highly effective polymer known for its superior barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and aromas, making it a popular choice for food wrap applications. Its excellent chemical resistance and low permeability extend the shelf life of perishable food products by preventing spoilage and maintaining freshness. PVDC films are often contrasted with Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO), which offers better thermal stability but lacks the same level of barrier protection essential for food preservation.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Permeability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior oxygen barrier properties compared to polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), making it more effective for preserving food freshness by reducing oxygen permeation. However, PVDC demonstrates lower moisture vapor transmission rates, providing enhanced moisture barrier performance crucial for preventing food dehydration and spoilage. The choice between PPO and PVDC for food wraps depends on prioritizing either oxygen or moisture barrier needs to optimize food preservation.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 210degC, which makes it highly suitable for food wrap applications requiring oven use or sterilization. PVDC typically withstands temperatures only up to 80-125degC before degrading, limiting its use in high-heat scenarios despite excellent barrier properties against oxygen and moisture. The enhanced thermal performance of PPO ensures better longevity and safety in heat-intensive food packaging environments.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior mechanical strength with high tensile strength and excellent dimensional stability compared to polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), making it more resistant to punctures and tears in food wrap applications. PVDC demonstrates greater flexibility and elongation, providing enhanced conformability around irregular shapes and better resistance to cracking during bending. The choice between PPO and PVDC balances PPO's rigidity and durability against PVDC's flexibility, impacting the protective performance and usability of food wrap films.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits excellent safety and food compatibility due to its high chemical resistance and thermal stability, preventing contamination and preserving food quality. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) offers superior barrier properties against oxygen and moisture, enhancing shelf life but may release harmful chlorine-related residues under certain conditions. PPO is generally favored for applications requiring non-toxic, odorless materials, while PVDC requires careful processing to maintain food safety compliance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers a more environmentally friendly profile than polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) due to its higher recyclability and lower generation of toxic byproducts during degradation. PVDC, commonly used in food wrap, releases harmful chlorine-based compounds under incineration and is challenging to recycle because of its chlorine content. PPO's thermoplastic nature facilitates mechanical recycling processes, reducing landfill accumulation and supporting sustainable packaging solutions.
Cost and Availability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers moderate cost but is less commonly used for food wrap, resulting in lower availability compared to polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), which is widely produced and favored for its excellent barrier properties despite higher costs. PVDC films are extensively available due to established manufacturing processes and global demand in the food packaging industry. Cost-efficiency of PPO is offset by limited supply chains, while PVDC's premium pricing aligns with its superior moisture and oxygen resistance essential for food preservation.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Food Wrap Material
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature food applications, while Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) excels in oxygen and moisture barrier properties, ensuring extended shelf life for perishable foods. PVDC's exceptional barrier performance reduces oxidation and spoilage, though PPO provides greater durability and environmental resistance. Choosing the optimal food wrap depends on specific needs: PVDC suits moisture-sensitive products, whereas PPO is preferred for heat resistance and structural integrity.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyvinylidene chloride for Food Wrap
 azmater.com
azmater.com