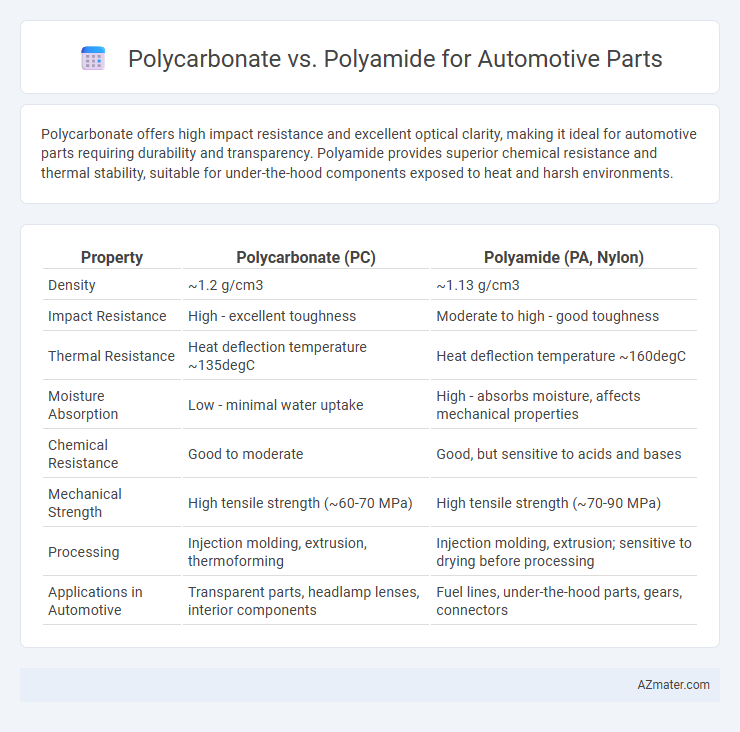
Polycarbonate offers high impact resistance and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for automotive parts requiring durability and transparency. Polyamide provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, suitable for under-the-hood components exposed to heat and harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polyamide (PA, Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | ~1.2 g/cm3 | ~1.13 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | High - excellent toughness | Moderate to high - good toughness |
| Thermal Resistance | Heat deflection temperature ~135degC | Heat deflection temperature ~160degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low - minimal water uptake | High - absorbs moisture, affects mechanical properties |
| Chemical Resistance | Good to moderate | Good, but sensitive to acids and bases |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength (~60-70 MPa) | High tensile strength (~70-90 MPa) |
| Processing | Injection molding, extrusion, thermoforming | Injection molding, extrusion; sensitive to drying before processing |
| Applications in Automotive | Transparent parts, headlamp lenses, interior components | Fuel lines, under-the-hood parts, gears, connectors |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Material for Automotive Parts
Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for exterior automotive parts such as headlights and instrument panels. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, provides superior wear resistance, chemical resistance, and flexibility, often preferred for engine components, fuel systems, and under-the-hood applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing mechanical performance, environmental exposure, and cost-efficiency for specific automotive part requirements.
Overview of Polycarbonate and Polyamide
Polycarbonate is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic widely used in automotive parts for its excellent clarity, high heat resistance, and strong mechanical properties. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, offers superior wear resistance, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for components subjected to friction and harsh environments. Both materials provide distinct advantages in automotive applications, with polycarbonate favored for structural and aesthetic parts, while polyamide excels in performance-driven mechanical components.
Key Properties and Performance Characteristics
Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for automotive parts requiring high durability and transparency, such as headlamp lenses and interior components. Polyamide (nylon) provides superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, making it a preferred choice for under-the-hood components like air intake manifolds and fuel system parts. Both materials exhibit excellent dimensional stability and lightweight properties, yet polyamide's better resistance to high temperatures and wear positions it as more suitable for demanding automotive environments.
Durability and Impact Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance and high durability, making it ideal for automotive parts subjected to sudden shocks and stress. Polyamide offers excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance but is more prone to wear under continuous impact compared to polycarbonate. Choosing polycarbonate ensures enhanced longevity and resilience for automotive components exposed to dynamic forces and harsh environments.
Heat and Chemical Resistance in Automotive Applications
Polycarbonate offers excellent heat resistance up to 120degC and superior transparency, making it ideal for automotive lenses and interior components exposed to moderate temperatures. Polyamide (Nylon) provides higher chemical resistance against automotive fluids like oils and fuels, along with better thermal stability above 150degC, suitable for engine covers and under-the-hood parts. Selecting between polycarbonate and polyamide depends on balancing the required heat tolerance and chemical exposure in specific automotive applications.
Weight and Design Flexibility: Polycarbonate vs Polyamide
Polycarbonate offers superior design flexibility due to its high impact resistance and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for complex automotive components requiring transparency or detailed molding. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, provides a lighter weight alternative with exceptional thermal resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for under-the-hood parts. Balancing weight and design requirements, polycarbonate enhances aesthetic and functional design versatility, while polyamide optimizes performance in demanding structural and thermal environments.
Cost Implications and Manufacturing Processes
Polycarbonate offers a cost-effective solution for automotive parts due to its ease of injection molding and faster cycle times, reducing overall manufacturing expenses compared to polyamide. Polyamide, though generally more expensive due to its higher raw material cost and complex processing requirements like drying and longer cycle times, delivers superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength. Choosing between polycarbonate and polyamide involves balancing upfront material and manufacturing costs with long-term performance and durability in automotive applications.
Environmental Considerations and Recyclability
Polycarbonate offers superior recyclability in automotive parts due to its thermoplastic nature, allowing repeated melting and reforming without significant degradation, which aligns with circular economy goals. Polyamide, while durable and resistant to chemicals, poses challenges in recycling processes because of its thermosetting characteristics and potential contamination from additives. Environmental considerations favor polycarbonate as it enables lower lifecycle emissions through efficient recycling, whereas polyamide's complex recycling often leads to downcycling or limited reuse options.
Common Automotive Parts Using Polycarbonate and Polyamide
Common automotive parts using polycarbonate include headlamp lenses, interior trim panels, and instrument clusters due to its high impact resistance, optical clarity, and heat resistance. Polyamide (nylon) is frequently used in under-the-hood components such as fuel lines, engine covers, and electrical connectors because of its excellent chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability. Both materials contribute to lightweight, durable automotive parts, enhancing vehicle performance and longevity.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Material for Automotive Needs
Polycarbonate offers exceptional impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for automotive parts requiring high durability and aesthetic appeal, such as headlamp covers and interior panels. Polyamide excels in mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, suitable for under-the-hood components like engine covers and fuel lines. Choosing between polycarbonate and polyamide depends on specific automotive application requirements, balancing factors such as mechanical performance, environmental exposure, and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polyamide for Automotive part
 azmater.com
azmater.com