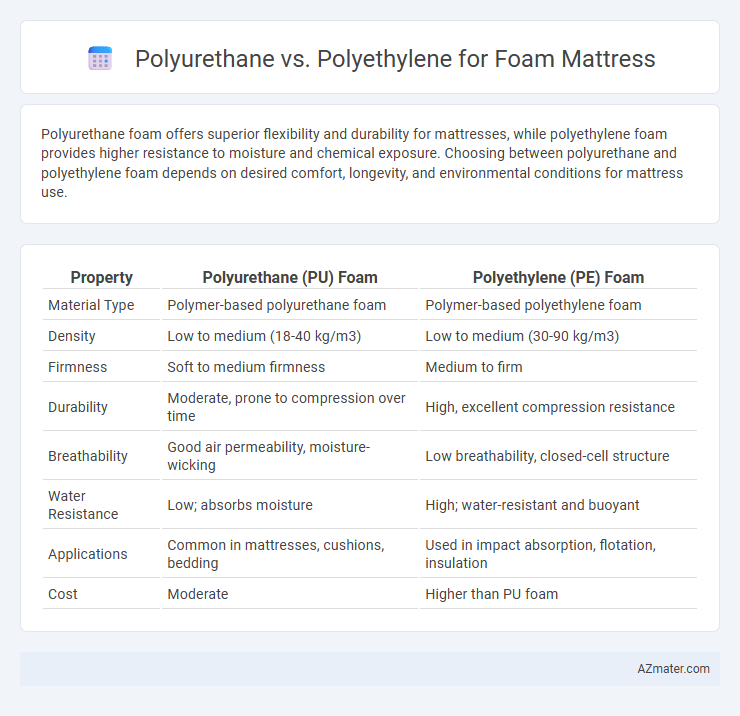
Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and durability for mattresses, while polyethylene foam provides higher resistance to moisture and chemical exposure. Choosing between polyurethane and polyethylene foam depends on desired comfort, longevity, and environmental conditions for mattress use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) Foam | Polyethylene (PE) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymer-based polyurethane foam | Polymer-based polyethylene foam |
| Density | Low to medium (18-40 kg/m3) | Low to medium (30-90 kg/m3) |
| Firmness | Soft to medium firmness | Medium to firm |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to compression over time | High, excellent compression resistance |
| Breathability | Good air permeability, moisture-wicking | Low breathability, closed-cell structure |
| Water Resistance | Low; absorbs moisture | High; water-resistant and buoyant |
| Applications | Common in mattresses, cushions, bedding | Used in impact absorption, flotation, insulation |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than PU foam |
Introduction to Foam Mattress Materials
Polyurethane foam and polyethylene foam are two primary materials used in foam mattresses, each offering distinct properties for comfort and durability. Polyurethane foam is known for its excellent cushioning and breathability, making it popular for pressure relief and support in mattress cores. Polyethylene foam, while less common, provides greater resilience and moisture resistance, often used in specialized mattress layers or protective padding.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a flexible, durable material commonly used in foam mattresses for its excellent support and pressure relief properties. It is made through the chemical reaction of polyols and isocyanates, resulting in open-cell foam that allows breathability and comfort. Compared to polyethylene foam, polyurethane offers superior cushioning and contouring, making it ideal for mattress comfort layers.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell foam made from polyethylene resin, known for its lightweight, durable, and water-resistant properties, which make it ideal for mattress cushioning and support. It provides excellent shock absorption and thermal insulation, maintaining firmness and structure over time compared to polyurethane foam. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals ensures enhanced longevity and hypoallergenic benefits, making it a preferred choice for foam mattresses requiring durability and consistent comfort.
Material Composition and Structure
Polyurethane foam consists of flexible polymer chains formed by the reaction of polyols and isocyanates, creating an open-cell structure that offers high elasticity and breathability. Polyethylene foam is made from a thermoplastic polymer with a closed-cell structure, providing greater density, durability, and resistance to moisture absorption. The open-cell polyurethane foam enhances airflow and cushioning, while polyethylene foam's closed cells deliver firmer support and enhanced water resistance.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Polyurethane foam offers superior contouring and pressure relief, providing enhanced comfort by adapting to body curves, while polyethylene foam is firmer and less conforming, delivering more rigid support. Polyurethane's open-cell structure promotes better breathability and temperature regulation, ensuring a cooler sleep surface compared to the denser, less breathable polyethylene foam. In terms of durability, polyurethane maintains consistent support over time, whereas polyethylene's rigidity can lead to less comfort as it ages.
Durability and Longevity Differences
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability due to its higher density and resilience, allowing it to maintain shape and support longer under regular use compared to polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and resistant to moisture, tends to compress and degrade faster when subjected to extended pressure or heat, reducing its longevity in foam mattress applications. Choosing high-density polyurethane foam enhances mattress lifespan by resisting sagging and deformation over time, making it a preferred material for durable mattress construction.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation
Polyurethane foam offers moderate breathability but tends to retain more heat due to its denser cell structure, impacting temperature regulation. Polyethylene foam provides better airflow with its more open-cell design, enhancing breathability and promoting cooler sleep conditions. Choosing polyethylene foam mattresses supports improved ventilation and temperature control, ideal for individuals sensitive to heat during sleep.
Safety and Hypoallergenic Properties
Polyurethane foam often contains chemical additives that may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), raising safety concerns for sensitive individuals, whereas polyethylene foam is typically inert and less likely to cause respiratory irritation. Hypoallergenic properties favor polyethylene due to its closed-cell structure, which resists dust mites, mold, and allergens more effectively than the open-cell structure of polyurethane foam. For those with allergies or chemical sensitivities, choosing polyethylene foam mattresses reduces the risk of allergic reactions and improves indoor air quality.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Polyurethane foam mattress materials typically cost less per cubic foot than polyethylene foam, making them a more budget-friendly option for mattress production. Polyurethane is widely available from numerous manufacturers worldwide, ensuring consistent supply and diverse product variations, while polyethylene foam, though less common, is often used for niche applications and may come at a higher price due to limited suppliers. The cost-effectiveness and accessibility of polyurethane foam contribute significantly to its dominance in the foam mattress market.
Which Foam is Best for Your Mattress?
Polyurethane foam offers superior comfort and support due to its high-density structure, making it ideal for pressure relief and contouring in mattresses. Polyethylene foam, known for its durability and resistance to moisture, provides firmer support but lacks the same level of cushioning as polyurethane. Choosing between polyurethane and polyethylene foam depends on your preference for softness and body-conforming qualities versus firmness and longevity in mattress performance.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyethylene for Foam Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com