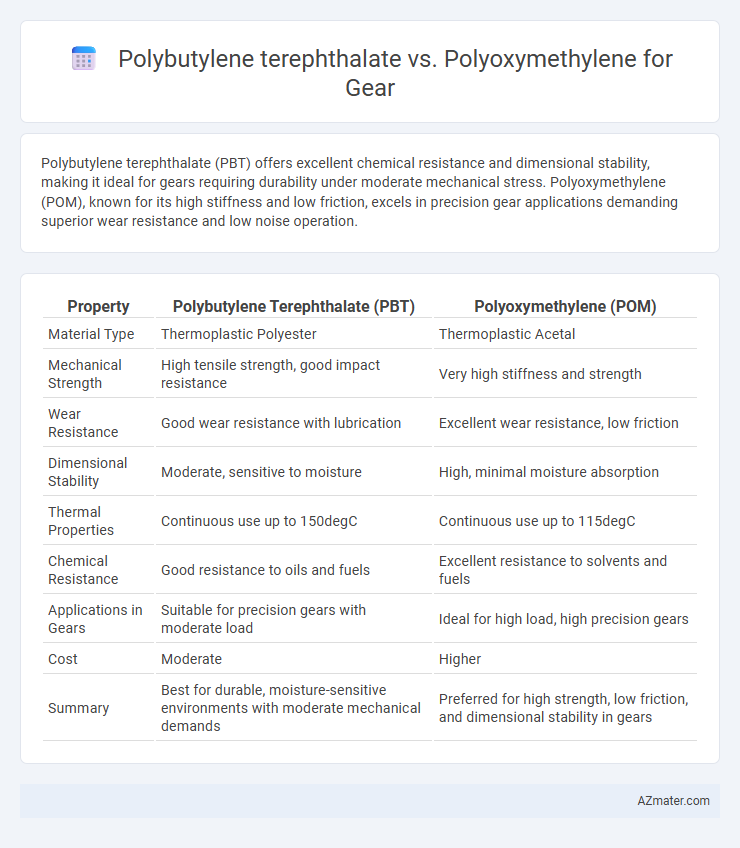
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for gears requiring durability under moderate mechanical stress. Polyoxymethylene (POM), known for its high stiffness and low friction, excels in precision gear applications demanding superior wear resistance and low noise operation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyoxymethylene (POM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Thermoplastic Acetal |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good impact resistance | Very high stiffness and strength |
| Wear Resistance | Good wear resistance with lubrication | Excellent wear resistance, low friction |
| Dimensional Stability | Moderate, sensitive to moisture | High, minimal moisture absorption |
| Thermal Properties | Continuous use up to 150degC | Continuous use up to 115degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and fuels | Excellent resistance to solvents and fuels |
| Applications in Gears | Suitable for precision gears with moderate load | Ideal for high load, high precision gears |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Summary | Best for durable, moisture-sensitive environments with moderate mechanical demands | Preferred for high strength, low friction, and dimensional stability in gears |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) and Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent dimensional stability, high mechanical strength, and resistance to chemicals and moisture, making it suitable for precision gears in automotive and electrical applications. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also called acetal, offers superior stiffness, low friction, and wear resistance, which enhances gear performance under dynamic loading and high-speed conditions. Both materials provide distinct advantages for gear manufacturing, with PBT favored for its thermal stability and POM for its enhanced mechanical durability.
Material Properties Comparison: PBT vs POM
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for gears requiring durability under thermal stress. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, provides superior mechanical strength, low friction, and exceptional wear resistance, which enhances gear performance in high-load applications. When comparing these materials for gear manufacturing, POM's higher tensile strength and lower moisture absorption often make it preferable for precision and longevity, while PBT excels in environments with chemical exposure and elevated temperatures.
Mechanical Strength and Durability in Gear Applications
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent mechanical strength and good impact resistance, making it suitable for gears requiring moderate load-bearing and dimensional stability. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, exhibits superior tensile strength, stiffness, and wear resistance, resulting in enhanced durability and high-performance gear operation under heavy loads. POM's lower moisture absorption compared to PBT further contributes to maintaining mechanical properties and extending gear lifespan in demanding environments.
Wear Resistance and Friction Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent wear resistance and low friction, making it suitable for gears subjected to moderate loads and speeds, with good dimensional stability and resistance to chemicals and moisture. Polyoxymethylene (POM), known as acetal, provides superior wear resistance and lower friction coefficients compared to PBT, delivering higher mechanical strength and stiffness, which enables better performance in high-load and high-speed gear applications. The choice between PBT and POM depends on specific gear requirements, with POM generally preferred for demanding wear and friction performance due to its self-lubricating properties and exceptional dimensional stability under stress.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance to hydrocarbons, solvents, and alkalis, making it ideal for gears exposed to harsh chemical environments. Polyoxymethylene (POM) provides excellent environmental stability with high resistance to moisture absorption and dimensional stability under varying temperature conditions. PBT's enhanced resistance to hydrolysis contrasts with POM's susceptibility to acidic and basic environments, influencing gear material selection based on specific chemical exposure and operational requirements.
Dimensional Stability and Precision in Gear Manufacturing
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent dimensional stability due to its low moisture absorption and high crystallinity, making it suitable for precision gear manufacturing where minimal deformation is critical. Polyoxymethylene (POM), known for its exceptional stiffness and low friction, provides superior dimensional accuracy and wear resistance, ensuring consistent gear performance under dynamic loads. In gear applications demanding tight tolerances and long-term reliability, POM is often preferred, while PBT serves well where chemical resistance and thermal stability complement dimensional precision.
Processing and Machinability Differences
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal stability and ease of injection molding, making it ideal for complex gear shapes with tight tolerances. Polyoxymethylene (POM), known for its excellent dimensional stability and low friction, excels in precision machining but requires careful control of cutting parameters to avoid material degradation. PBT's faster cycle times contrast with POM's more demanding machining processes, influencing production efficiency and gear performance longevity in industrial applications.
Cost Analysis: PBT vs POM for Gear Production
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers a lower material cost compared to Polyoxymethylene (POM), making it a more economical choice for high-volume gear production. POM generally provides superior mechanical strength and wear resistance, but its higher price can impact the overall manufacturing budget. When analyzing cost-effectiveness, PBT is preferred for applications where moderate strength and reduced expense are critical, while POM's performance benefits justify its higher cost in precision gear applications.
Industry-Specific Use Cases and Application Examples
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits excellent electrical insulation and chemical resistance, making it ideal for automotive gear applications such as in seat adjustment motors and power window systems where durability under thermal stress is crucial. Polyoxymethylene (POM), known for its high stiffness and low friction, is widely used in precision gear mechanisms for consumer electronics and industrial automation, including printer gears and conveyor components requiring minimal wear. Both materials are valued for their ability to maintain dimensional stability and mechanical performance in demanding industrial environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Gears
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and good wear resistance, making it suitable for gears requiring moderate strength and precision. Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior stiffness, low friction, and high fatigue resistance, ideal for high-load and high-speed gear applications. Selecting the right material depends on operational conditions, with PBT favored for environments needing chemical resistance and POM preferred for mechanical performance and durability.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyoxymethylene for Gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com