Cellulose-based plastic offers enhanced biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is durable but contains harmful additives and releases toxic chemicals during degradation. PVC remains widely used for plumbing pipes due to its chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness, while cellulose-based alternatives are gaining attention for sustainable construction.
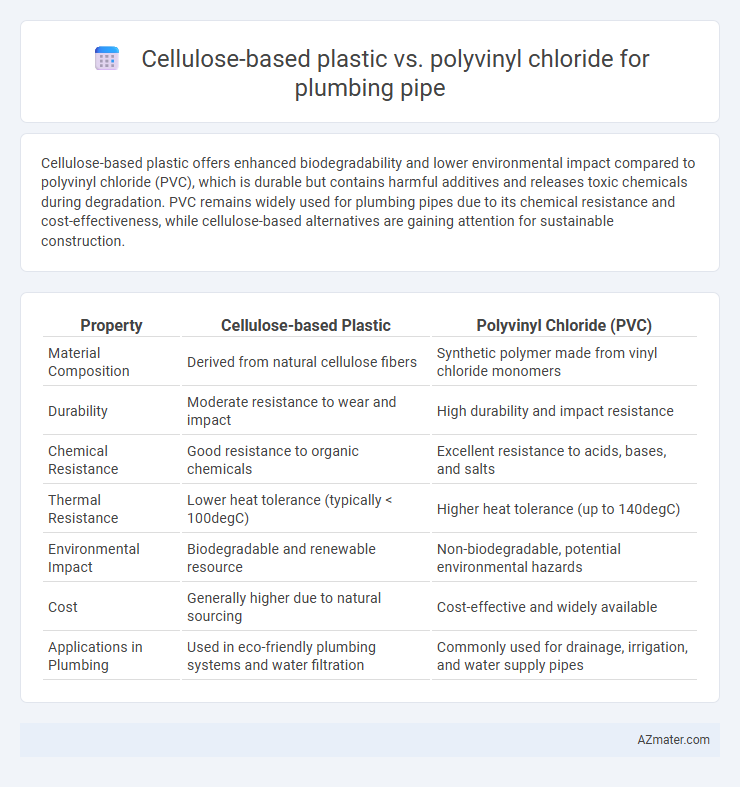
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellulose-based Plastic | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Derived from natural cellulose fibers | Synthetic polymer made from vinyl chloride monomers |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to wear and impact | High durability and impact resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to organic chemicals | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and salts |
| Thermal Resistance | Lower heat tolerance (typically < 100degC) | Higher heat tolerance (up to 140degC) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and renewable resource | Non-biodegradable, potential environmental hazards |
| Cost | Generally higher due to natural sourcing | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Applications in Plumbing | Used in eco-friendly plumbing systems and water filtration | Commonly used for drainage, irrigation, and water supply pipes |
Introduction to Cellulose-Based Plastics and Polyvinyl Chloride in Plumbing
Cellulose-based plastics, derived from renewable plant fibers, offer an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics in plumbing applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a widely used synthetic plastic polymer, is known for its durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness in pipe manufacturing. In plumbing, cellulose-based plastics provide biodegradability and reduced environmental impact, while PVC ensures long-lasting performance and widespread industry acceptance.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Cellulose-based plastics for plumbing pipes consist primarily of natural polymer chains derived from glucose units, featuring a crystalline and amorphous structure that enhances biodegradability and mechanical strength. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a synthetic polymer composed of repeating vinyl chloride monomers, characterized by a rigid, linear chain with chlorine atoms contributing to high chemical resistance and durability. The cellulose-based pipes offer natural renewability and lower environmental impact, whereas PVC pipes provide superior chemical stability and long-term performance in diverse plumbing applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellulose-based plastic plumbing pipes offer superior environmental benefits due to their biodegradability and reduced reliance on fossil fuels, contrasting with polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes that are derived from non-renewable petrochemicals and release hazardous chemicals during production and disposal. PVC's persistence in the environment and challenges in recycling contribute to long-term ecological harm, while cellulose-based alternatives promote circular economy principles by decomposing naturally and supporting sustainable forestry practices. Choosing cellulose-based pipes significantly lowers carbon footprint and mitigates pollution, aligning with global sustainability goals in construction materials.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Cellulose-based plastic plumbing pipes offer moderate mechanical strength with good flexibility but tend to have lower impact resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, which exhibit high tensile strength and rigidity. PVC pipes demonstrate superior durability due to their resistance to chemical corrosion, UV exposure, and physical wear, making them more suitable for long-term plumbing applications. The biodegradability of cellulose-based plastics may reduce environmental impact but often compromises the lifespan and mechanical performance in demanding plumbing environments.
Resistance to Chemicals and Corrosion
Cellulose-based plastic exhibits superior resistance to corrosion and many common chemicals, making it ideal for plumbing systems exposed to aggressive environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers good chemical resistance but can degrade when exposed to certain solvents and prolonged UV radiation, potentially leading to brittleness. The inherent biodegradability and environmental safety of cellulose-based plastics enhance their appeal for sustainable plumbing applications requiring long-term durability against chemical and corrosive damage.
Installation, Maintenance, and Longevity
Cellulose-based plastic pipes offer easier installation due to their lightweight nature and flexibility compared to the rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes commonly used in plumbing. Maintenance for cellulose-based pipes typically involves less risk of chemical corrosion, while PVC pipes resist chemical damage but can become brittle over time, leading to potential leaks. Longevity-wise, PVC pipes generally last longer, with an average lifespan of 50 years, whereas cellulose-based plastics may degrade faster under constant moisture exposure but are more environmentally friendly.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Cellulose-based plastic plumbing pipes generally feature higher material costs compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to more complex manufacturing processes and limited production scales. PVC pipes dominate the market with widespread availability, benefiting from established supply chains and lower raw material expenses, resulting in significantly lower prices per meter. Market trends indicate increasing interest in cellulose-based pipes driven by environmental regulations, but PVC remains the cost-effective choice for large-scale plumbing installations.
Health and Safety Considerations
Cellulose-based plastics for plumbing pipes offer enhanced biodegradability and reduced toxic chemical leaching compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is known to release harmful additives like phthalates and lead during manufacturing and use. PVC pipes pose health risks related to the emission of dioxins and other carcinogenic compounds under high heat or fire conditions, whereas cellulose-based pipes present lower flammability and fewer hazardous byproducts. The use of cellulose-based materials reduces exposure to endocrine disruptors and supports safer indoor air quality in residential and commercial plumbing systems.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Cellulose-based plastic plumbing pipes often comply with stringent environmental regulations such as NSF/ANSI 61 for drinking water safety and may carry certifications like ASTM D6832 for biopolymers, highlighting their sustainability and non-toxic properties. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are widely accepted under regulatory standards including ASTM D1785 and ASTM D2241, and they meet NSF/ANSI 61 for potable water use but face increasing scrutiny due to concerns over chemical additives like phthalates and vinyl chloride monomer residues. Regulatory agencies prioritize compliance with safe drinking water acts and environmental impact certifications, influencing the selection between cellulose-based and PVC pipes in plumbing applications.
Future Trends in Plumbing Pipe Materials
Cellulose-based plastics are gaining traction as sustainable alternatives to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in plumbing pipes due to their biodegradability and lower environmental impact. Advances in bio-composite technology enhance cellulose-based pipe durability and resistance, addressing traditional limitations of mechanical strength and chemical stability. Future trends emphasize eco-friendly materials with improved lifecycle performance, reducing reliance on PVC's petrochemical base amid increasing regulatory restrictions and consumer demand for green construction solutions.
Infographic: Cellulose-based plastic vs Polyvinyl chloride for Plumbing pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com