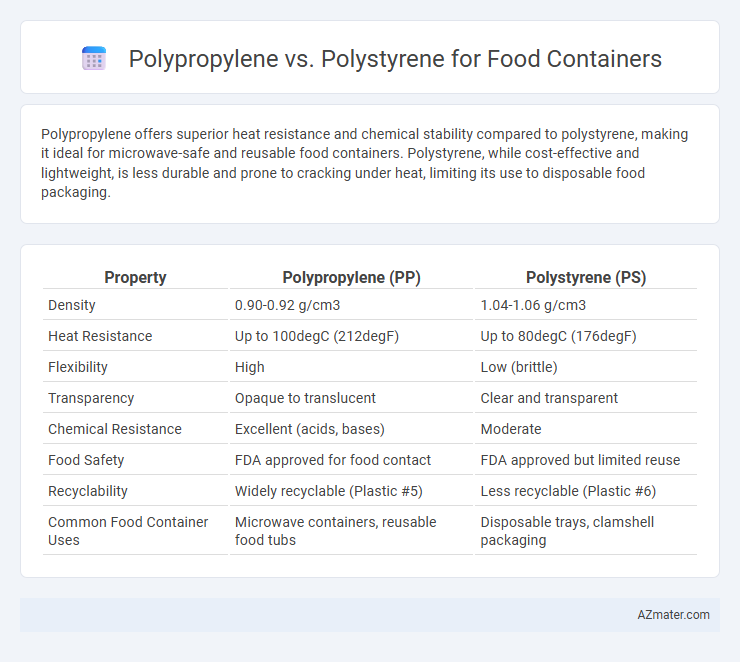
Polypropylene offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for microwave-safe and reusable food containers. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, is less durable and prone to cracking under heat, limiting its use to disposable food packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.90-0.92 g/cm3 | 1.04-1.06 g/cm3 |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 100degC (212degF) | Up to 80degC (176degF) |
| Flexibility | High | Low (brittle) |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (acids, bases) | Moderate |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved but limited reuse |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable (Plastic #5) | Less recyclable (Plastic #6) |
| Common Food Container Uses | Microwave containers, reusable food tubs | Disposable trays, clamshell packaging |
Understanding Polypropylene and Polystyrene
Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, high melting point around 160degC, and superior durability, making it ideal for microwave-safe and reusable food containers. Polystyrene is rigid, inexpensive, and provides good clarity but has lower heat resistance (around 100degC) and tends to be brittle, limiting its use to single-use or cold food packaging. Understanding these properties helps choose polypropylene for versatile, heat-tolerant food storage and polystyrene for cost-effective, disposable options.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polypropylene (PP) exhibits a higher melting point of approximately 160degC, making it more suitable for hot food containers compared to polystyrene's (PS) melting point around 240degC, which is brittle under high temperatures. PP offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, while PS is rigid and prone to cracking, affecting durability during handling. Both materials are lightweight, but PP's chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption enhance its performance in various food storage applications.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Polypropylene (PP) is widely recognized for its safety in food container applications due to its high melting point, chemical resistance, and compliance with FDA and EFSA regulations, making it suitable for microwave use and prolonged food contact. Polystyrene (PS) poses more concerns because it can leach styrene monomers, which are subject to strict migration limits under food contact regulations set by the FDA and European authorities, limiting its use mostly to short-term or cold food storage. Emphasizing regulatory compliance, polypropylene offers a safer and more versatile option for food containers, aligning better with stringent food safety standards and consumer health protection.
Heat Resistance and Microwave Suitability
Polypropylene offers superior heat resistance with a melting point of around 160degC, making it ideal for microwave use and safe reheating of food containers. Polystyrene, with a lower heat tolerance near 100degC, tends to deform or release harmful chemicals when microwaved, limiting its suitability for hot food applications. For food containers requiring durability under microwave conditions, polypropylene is the preferred choice due to its thermal stability and food safety compliance.
Durability and Longevity
Polypropylene offers superior durability and longevity compared to polystyrene for food containers, resisting impact and chemical degradation under varying temperatures. Its high melting point around 160degC ensures repeated microwave and dishwasher use without deformation. Polystyrene, being more brittle and prone to cracking, lacks the thermal resilience critical for long-term food storage and reheating applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) offers superior recyclability compared to polystyrene (PS), as it is widely accepted in curbside recycling programs and breaks down more efficiently in recycling processes. PS poses significant environmental challenges due to its low recycling rates and tendency to fragment into microplastics, contributing to pollution and landfill accumulation. Choosing polypropylene food containers minimizes ecological footprint through better recyclability and reduced persistence in the environment.
Cost Effectiveness for Manufacturers
Polypropylene offers greater cost efficiency for manufacturers due to its lower raw material price and higher durability, reducing replacement costs in food container production. Polystyrene, while cheaper initially, often incurs higher overall expenses because of brittleness leading to increased breakage and waste. The balance of material costs and longevity makes polypropylene the more economical choice in large-scale food container manufacturing.
Suitability for Hot and Cold Foods
Polypropylene (PP) excels in food container applications due to its high melting point around 160degC, making it ideal for hot food storage and microwave use without warping or leaching chemicals. Polystyrene (PS), with a lower melting point near 100degC, is more suitable for cold food storage and single-use packaging but risks deformation and chemical leaching at elevated temperatures. The thermal stability and chemical resistance of polypropylene ensure safer and more versatile performance for both hot and cold food containers compared to polystyrene.
Common Applications in the Food Industry
Polypropylene (PP) is widely used for reusable food containers, microwave-safe trays, and packaging films due to its excellent heat resistance and chemical stability. Polystyrene (PS) is commonly employed in disposable food containers, such as yogurt cups, takeout boxes, and clear lids because of its rigidity and cost-effectiveness. Both materials serve distinct roles in the food industry, with PP favored for durability and repeated use, while PS is preferred for lightweight, single-use applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Polypropylene (PP) offers excellent heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for microwave-safe and reusable food containers, while polystyrene (PS) is lightweight and provides good clarity but is brittle and not suitable for high-temperature applications. When selecting food containers, consider polypropylene for hot food storage due to its high melting point and chemical resistance, whereas polystyrene is better for cost-effective, single-use cold food packaging. Understanding each polymer's thermal properties, safety standards, and environmental impact helps ensure the best choice for specific food storage and usage needs.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polystyrene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com