Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent flexibility, durability, and shock absorption, making it ideal for lightweight cushioning applications. Polyurethane foam provides superior resilience and support with higher density options, suitable for heavy-duty cushioning and long-term comfort.
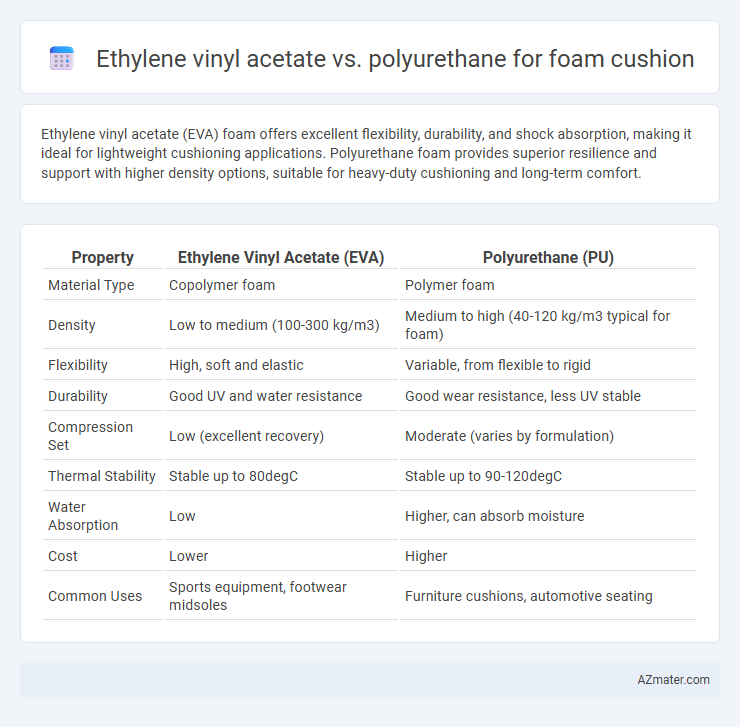
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer foam | Polymer foam |
| Density | Low to medium (100-300 kg/m3) | Medium to high (40-120 kg/m3 typical for foam) |
| Flexibility | High, soft and elastic | Variable, from flexible to rigid |
| Durability | Good UV and water resistance | Good wear resistance, less UV stable |
| Compression Set | Low (excellent recovery) | Moderate (varies by formulation) |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 80degC | Stable up to 90-120degC |
| Water Absorption | Low | Higher, can absorb moisture |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Uses | Sports equipment, footwear midsoles | Furniture cushions, automotive seating |
Introduction to Foam Cushion Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polyurethane (PU) are primary materials used in foam cushions due to their distinct properties. EVA foam offers excellent flexibility, resilience, and shock absorption, making it ideal for footwear insoles and sports padding. Polyurethane foam provides superior support, durability, and cushioning, commonly utilized in furniture, automotive seating, and mattresses.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a flexible, lightweight foam material known for its excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and resilience, making it a popular choice in foam cushions for footwear and sports equipment. Its closed-cell structure provides superior water resistance and durability compared to polyurethane, which tends to absorb moisture over time. EVA foam also offers better chemical resistance and UV stability, ensuring long-lasting performance in various environmental conditions.
Understanding Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and resilience compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), making it ideal for high-impact cushioning applications. Its open-cell structure ensures excellent breathability and pressure distribution, enhancing comfort in foam cushions. Polyurethane foam also provides versatile density options, allowing customization for diverse uses in furniture, footwear, and sports equipment.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent flexibility, resilience, and shock absorption, making it ideal for lightweight cushioning and impact protection. Polyurethane (PU) foam provides superior density, durability, and compression set resistance, supporting long-term structural stability in high-use cushions. EVA foam typically has a lower density range of 70-300 kg/m3, while PU foam ranges from 25-150 kg/m3, affecting firmness and energy return in foam cushions.
Comfort and Support Analysis
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent shock absorption and moderate support, making it ideal for comfortable cushioning in lightweight applications. Polyurethane foam provides superior support and durability with higher density options, enhancing long-term comfort through better pressure distribution. EVA foam generally excels in flexibility and softness, while polyurethane foam delivers firmer support crucial for prolonged use and structural integrity.
Durability and Longevity
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam cushions offer moderate durability with excellent flexibility and resistance to cracking, but they tend to compress and degrade faster under heavy use compared to polyurethane (PU) foam. Polyurethane foam provides superior longevity due to its high resilience and ability to retain shape over extended periods, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications and sustained cushioning performance. Choosing PU foam ensures enhanced durability and long-term comfort, especially in environments requiring frequent or prolonged pressure resistance.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior moisture resistance with its closed-cell structure that prevents water absorption, making it ideal for damp environments. Polyurethane (PU) foam, while flexible and comfortable, tends to absorb moisture due to its open-cell composition, leading to potential degradation and microbial growth over time. Chemically, EVA foam exhibits greater resistance to oils, solvents, and UV exposure compared to polyurethane, which can deteriorate or become sticky when exposed to harsh chemicals or prolonged moisture.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is favored for its recyclability, non-toxicity, and lower carbon footprint compared to polyurethane (PU) foam, which typically relies on petroleum-based chemicals and emits volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production. EVA foam's biodegradability and reduced off-gassing contribute to healthier indoor air quality, making it a more sustainable option in cushion manufacturing. Polyurethane foam presents challenges in end-of-life disposal due to its limited recyclability and potential microplastic pollution, impacting long-term environmental sustainability.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam cushions generally offer a lower manufacturing cost due to simpler production processes and less expensive raw materials compared to polyurethane (PU) foam, which requires more complex chemical reactions and curing times. EVA foam is favored in applications prioritizing cost-efficiency and basic cushioning, while polyurethane foam, despite its higher price, provides superior durability, resilience, and customization options in density and firmness. Manufacturers often weigh EVA's cost-effectiveness against PU's performance benefits when selecting materials for foam cushions in footwear, automotive, and sports equipment industries.
Best Applications for EVA and Polyurethane in Cushioning
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam excels in applications requiring lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing cushioning such as sports footwear insoles, yoga mats, and protective gear due to its excellent durability and water resistance. Polyurethane foam is preferred for high-comfort cushioning in automotive seats, furniture, and bedding, offering superior support, resilience, and energy absorption for prolonged use. Choosing EVA or polyurethane depends on the balance between flexibility, durability, and comfort needs in specific cushioning applications.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyurethane for Foam Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com