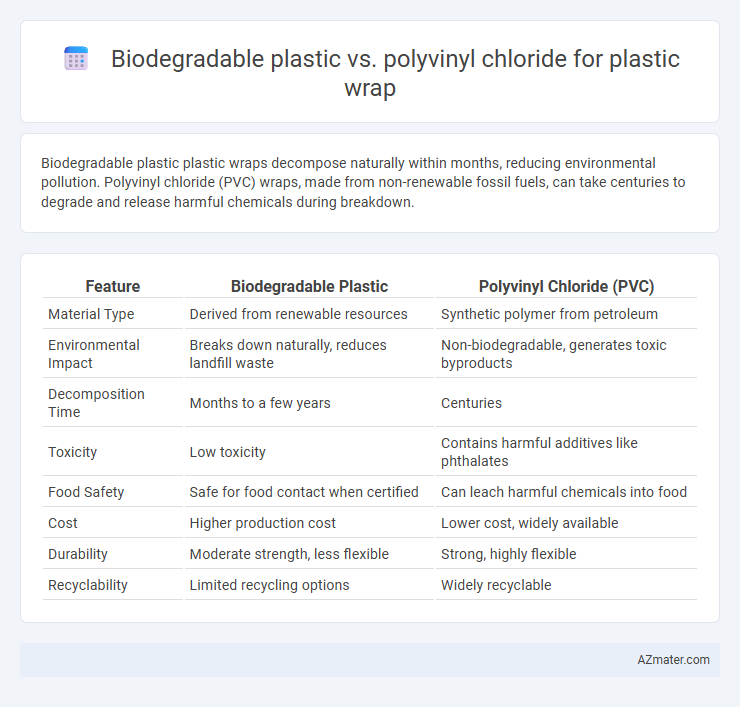
Biodegradable plastic plastic wraps decompose naturally within months, reducing environmental pollution. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) wraps, made from non-renewable fossil fuels, can take centuries to degrade and release harmful chemicals during breakdown.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biodegradable Plastic | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Derived from renewable resources | Synthetic polymer from petroleum |
| Environmental Impact | Breaks down naturally, reduces landfill waste | Non-biodegradable, generates toxic byproducts |
| Decomposition Time | Months to a few years | Centuries |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity | Contains harmful additives like phthalates |
| Food Safety | Safe for food contact when certified | Can leach harmful chemicals into food |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Durability | Moderate strength, less flexible | Strong, highly flexible |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options | Widely recyclable |
Introduction to Plastic Wrap Materials
Plastic wrap materials primarily consist of biodegradable plastics and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), each offering distinct environmental and functional properties. Biodegradable plastics are designed to break down naturally through microbial activity, reducing long-term waste and environmental impact. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a durable synthetic polymer, provides excellent clarity and flexibility but poses concerns due to its non-biodegradability and potential release of harmful chemicals during production and disposal.
Overview of Biodegradable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics used in plastic wrap are derived from renewable raw materials such as cornstarch and sugarcane, enabling them to break down naturally through microbial action, reducing environmental pollution. Unlike polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is petroleum-based and resistant to degradation, biodegradable plastics minimize landfill accumulation and toxic residue release. These eco-friendly alternatives offer comparable flexibility and transparency while supporting sustainable waste management.
Properties of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Plastic Wrap
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plastic wrap is renowned for its excellent clarity, elasticity, and strong cling properties, making it ideal for sealing and preserving food. PVC wrap exhibits high resistance to oils, fats, and chemicals, contributing to its durability and extended shelf life in food packaging applications. Despite environmental concerns, PVC's low permeability to oxygen and moisture enhances its effectiveness in maintaining product freshness compared to many biodegradable plastics.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradable Plastic vs PVC
Biodegradable plastic wraps decompose through microbial activity, reducing landfill accumulation and minimizing long-term environmental pollution. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic wrap releases harmful chemicals like dioxins during production and disposal, contributing to air and soil contamination. The lower carbon footprint and reduced toxicity of biodegradable plastics make them a more sustainable choice compared to PVC in terms of environmental impact.
Food Safety and Health Concerns
Biodegradable plastic wrap offers improved food safety by reducing the risk of chemical leaching compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which can release harmful additives such as phthalates and vinyl chloride monomers, posing potential health hazards. Studies indicate that PVC wrap may contaminate food with toxic substances during storage, especially when heated, whereas biodegradable alternatives derived from natural polymers minimize these risks by using non-toxic, eco-friendly materials. Consumer demand for safer food packaging drives the shift toward biodegradable wraps that ensure food preservation without compromising health.
Decomposition and Waste Management
Biodegradable plastic wrap decomposes within months under composting conditions, reducing landfill accumulation and environmental pollution, whereas polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic wrap can take decades to break down and often releases harmful chemicals. Effective waste management of biodegradable plastics involves industrial composting facilities to ensure complete degradation, while PVC waste requires specialized recycling or incineration to manage toxicity and persistence. Biodegradable options present a more sustainable solution by significantly lowering long-term waste and supporting circular economy models in plastic film usage.
Cost Analysis of Biodegradable Plastic and PVC Wrap
Biodegradable plastic wrap typically incurs higher production costs due to raw material expenses and specialized manufacturing processes compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) wrap, which benefits from established, large-scale polymer production and lower raw material prices. PVC wrap remains economically advantageous for manufacturers and consumers because of its low cost, durability, and widespread availability, despite environmental concerns. Cost analysis must incorporate factors such as disposal, environmental impact fees, and regulation compliance, which can make biodegradable alternatives more competitive over the long term.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Biodegradable plastic wrap sees rising consumer preference driven by increasing environmental awareness and demand for sustainable packaging solutions, with market trends indicating a shift towards eco-friendly alternatives. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic wrap maintains strong usage due to its durability, clarity, and cost-effectiveness, though concerns over toxic additives and limited recyclability impact consumer sentiment negatively. Market analysis reveals a growing expansion in biodegradable wrap segments, fueled by regulatory pressures and green marketing strategies targeting environmentally conscious consumers.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Biodegradable plastic used for plastic wrap is subject to stringent regulatory standards such as ASTM D6400 and EN 13432, ensuring it meets criteria for compostability and environmental safety. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic wrap, on the other hand, must comply with FDA regulations for food contact materials and restrict the use of harmful additives like phthalates and dioxins. Compliance with these standards directly impacts the environmental impact, recyclability, and consumer safety of plastic wrap products.
Future Prospects for Sustainable Plastic Wrap
Biodegradable plastic offers promising future prospects for sustainable plastic wrap due to its ability to decompose naturally in composting environments, reducing long-term environmental pollution compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Advances in biopolymers such as polylactic acid (PLA) and starch-based films enhance barrier properties and mechanical strength, making biodegradable wraps more viable for food preservation. Innovations in recycling technologies and regulatory support for reducing PVC use further encourage the transition towards eco-friendly plastic wrap solutions in the packaging industry.
Infographic: Biodegradable plastic vs Polyvinyl chloride for Plastic wrap
 azmater.com
azmater.com