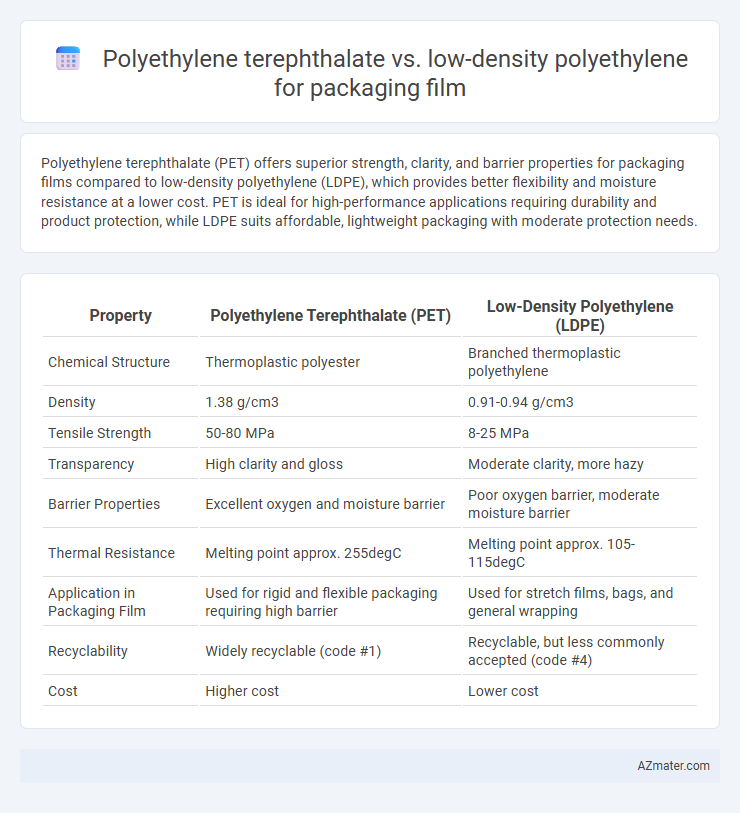
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior strength, clarity, and barrier properties for packaging films compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE), which provides better flexibility and moisture resistance at a lower cost. PET is ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability and product protection, while LDPE suits affordable, lightweight packaging with moderate protection needs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Thermoplastic polyester | Branched thermoplastic polyethylene |
| Density | 1.38 g/cm3 | 0.91-0.94 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 50-80 MPa | 8-25 MPa |
| Transparency | High clarity and gloss | Moderate clarity, more hazy |
| Barrier Properties | Excellent oxygen and moisture barrier | Poor oxygen barrier, moderate moisture barrier |
| Thermal Resistance | Melting point approx. 255degC | Melting point approx. 105-115degC |
| Application in Packaging Film | Used for rigid and flexible packaging requiring high barrier | Used for stretch films, bags, and general wrapping |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable (code #1) | Recyclable, but less commonly accepted (code #4) |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Packaging Films: PET vs LDPE
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) are widely used materials in packaging films, each offering distinct physical properties suited for different applications. PET exhibits superior tensile strength, clarity, and gas barrier capabilities, making it ideal for food and beverage packaging requiring durability and freshness preservation. LDPE provides excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-efficiency, commonly used for bags, shrink wraps, and flexible packaging where pliability and low weight are critical.
Material Composition and Structure
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a thermoplastic polymer resin composed of repeating units of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, known for its strong, rigid, and crystalline structure, making it suitable for high clarity and barrier packaging films. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE), made from ethylene monomers with a highly branched molecular structure, offers a more flexible, softer, and less crystalline film, providing excellent moisture barrier but lower tensile strength compared to PET. The distinct material compositions and molecular arrangements directly influence their mechanical properties and suitability for various packaging film applications, with PET excelling in durability and LDPE favoring flexibility and sealability.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior tensile strength, stiffness, and thermal stability compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE), making PET ideal for rigid or semi-rigid packaging applications. LDPE offers greater flexibility, impact resistance, and elongation at break, which enhances its suitability for flexible packaging films requiring stretchability and durability. The higher melting point of PET (around 250degC) supports heat sealing and sterilization processes, while LDPE's lower melting point (approximately 115degC) favors ease of processing but limits its use in high-temperature conditions.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Gas, and Aroma Resistance
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior barrier properties compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE), especially in moisture, gas, and aroma resistance, making it ideal for packaging sensitive products. PET's crystalline structure significantly reduces oxygen and moisture permeability, thereby extending shelf life and preserving flavor integrity. In contrast, LDPE's amorphous, less dense structure results in higher permeability, limiting its effectiveness for high-barrier packaging applications.
Clarity, Printability, and Aesthetics
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity and gloss, making it ideal for high-quality packaging films requiring excellent visual appeal and sharp print resolution. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) provides a more matte finish with lower clarity, limiting its printability and aesthetic sharpness but offering greater flexibility and moisture resistance. PET's structural rigidity supports detailed, vibrant graphics crucial for premium branding, whereas LDPE suits applications prioritizing durability over visual precision.
Processing Methods and Flexibility
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) differ significantly in processing methods and flexibility for packaging film applications. PET typically undergoes extrusion and biaxial orientation processes that enhance its strength and barrier properties, making it suitable for rigid and semi-rigid packaging. LDPE, processed primarily through blown film extrusion, offers superior flexibility and elongation, ideal for applications requiring more stretch and conformity to irregular shapes.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior recyclability compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE), benefiting from established collection and recycling infrastructures that reduce environmental impact through efficient material recovery. LDPE, while flexible and lightweight, often faces challenges in recycling due to limited facilities and contamination issues, leading to higher landfill accumulation and environmental persistence. The lower greenhouse gas emissions during PET recycling and its higher value in the recycled materials market make PET a more environmentally sustainable option for packaging film applications.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) packaging film typically incurs higher production costs compared to low-density polyethylene (LDPE) due to its more complex manufacturing process and superior barrier properties. Market trends show growing demand for PET films in food and beverage packaging driven by their recyclability and strength, while LDPE maintains popularity in flexible applications due to lower price and flexibility. Cost analysis reveals that despite PET's higher price point, its enhanced durability and sustainability features position it favorably in premium packaging segments, whereas LDPE remains dominant in cost-sensitive markets.
Application Suitability in Various Industries
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) excels in packaging applications requiring high strength, clarity, and barrier properties, making it ideal for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) offers superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suiting it for agricultural films, retail bags, and flexible packaging. The choice between PET and LDPE depends on specific industry demands such as durability, transparency, and environmental resistance.
Future Perspectives and Innovations in Packaging Films
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) continues to dominate packaging films due to its superior barrier properties, thermal stability, and recyclability, driving innovations in multi-layer and bio-based PET composites. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) maintains relevance with its flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, fostering advancements in blend formulations and biodegradable variants for sustainable packaging solutions. Emerging trends include the integration of smart packaging technologies and enhanced recyclability protocols, positioning both PET and LDPE as key materials in the evolving circular economy for packaging films.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Low-density polyethylene for Packaging Film
 azmater.com
azmater.com