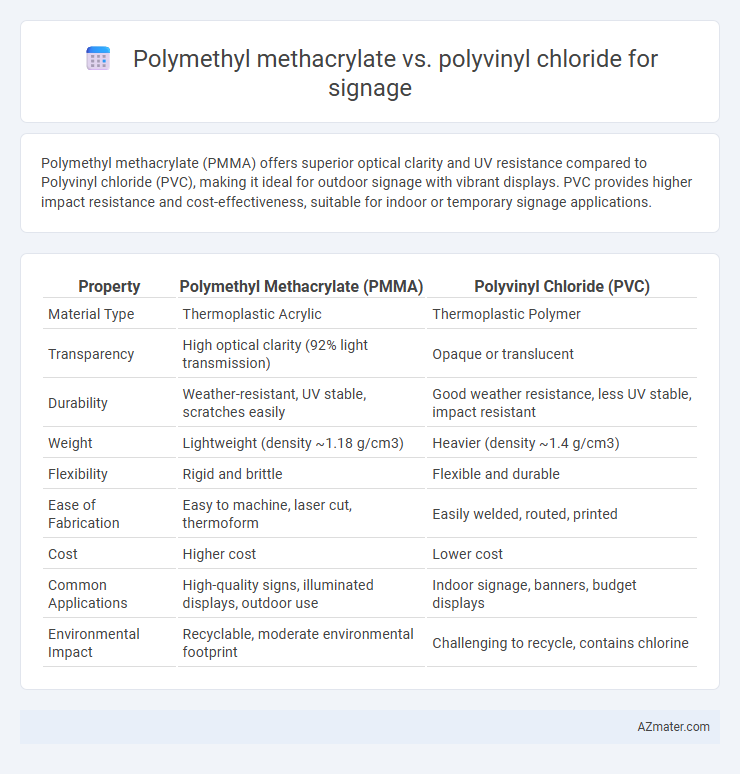
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity and UV resistance compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for outdoor signage with vibrant displays. PVC provides higher impact resistance and cost-effectiveness, suitable for indoor or temporary signage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Acrylic | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Transparency | High optical clarity (92% light transmission) | Opaque or translucent |
| Durability | Weather-resistant, UV stable, scratches easily | Good weather resistance, less UV stable, impact resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight (density ~1.18 g/cm3) | Heavier (density ~1.4 g/cm3) |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Flexible and durable |
| Ease of Fabrication | Easy to machine, laser cut, thermoform | Easily welded, routed, printed |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Common Applications | High-quality signs, illuminated displays, outdoor use | Indoor signage, banners, budget displays |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, moderate environmental footprint | Challenging to recycle, contains chlorine |
Introduction to Polymethyl Methacrylate and Polyvinyl Chloride
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic commonly used in signage for its excellent light transmittance, weather resistance, and ease of fabrication. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a versatile plastic known for its durability, affordability, and chemical resistance, often employed in indoor and outdoor signs that require rigidity and impact resistance. Both materials offer unique properties; PMMA excels in clarity and UV stability, while PVC stands out for cost-effectiveness and versatility in different environmental conditions.
Material Composition and Properties
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, making it ideal for outdoor signage that requires durability and high light transmission. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a versatile, rigid or flexible thermoplastic polymer composed primarily of vinyl chloride monomers, offering cost-effective, impact-resistant, and flame-retardant properties suitable for indoor and temporary signage applications. PMMA's hardness and scratch resistance contrast with PVC's flexibility and chemical resistance, influencing the choice based on signage exposure and longevity requirements.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior UV resistance and maintains clarity without yellowing, making it highly durable for outdoor signage in harsh weather conditions. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) provides good impact resistance and flexibility but tends to degrade and discolor faster under prolonged sun exposure and extreme weather. PMMA's enhanced weather resistance and long-lasting durability make it the preferred choice for signage requiring clear visibility and structural integrity over extended periods.
Visual Clarity and Aesthetic Appeal
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior visual clarity compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with light transmittance reaching up to 92%, making it ideal for vibrant and crisp signage displays. PMMA provides a glossy, high-quality finish that enhances aesthetic appeal, whereas PVC tends to have a more matte and less refined look. Its resistance to yellowing and ability to maintain clarity over time make PMMA a premium choice for long-lasting, visually striking signage.
Ease of Fabrication and Installation
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior ease of fabrication compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its excellent clarity, lightweight nature, and ability to be easily cut, engraved, and thermoformed without compromising structural integrity. PVC, while more flexible and impact-resistant, requires specialized tools and techniques for cutting and shaping, which can increase fabrication time and complexity. Installation of PMMA signage is streamlined by its rigidity and smooth finish that allows for seamless mounting, whereas PVC may require additional supports or treatments to ensure durability and a polished appearance in outdoor environments.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) typically has a higher upfront cost compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), but its superior durability and UV resistance can reduce long-term maintenance expenses in signage applications. PVC offers a more budget-friendly option with lower initial investment, making it suitable for short-term or indoor signage with limited exposure to harsh environmental conditions. When planning a signage project, weighing PMMA's longevity against PVC's affordability is essential for balancing capital expenditure and lifecycle costs effectively.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers greater environmental sustainability than polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its higher recyclability and lower emission of toxic chemicals during production and disposal. PVC manufacturing releases harmful dioxins and uses chlorine-based additives that pose significant environmental and health risks, whereas PMMA is derived from acrylic monomers that are less hazardous and more environmentally benign. Choosing PMMA for signage reduces long-term environmental impact and supports eco-friendly practices in the signage industry.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior UV resistance and retains clarity longer than polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for outdoor signage with minimal maintenance. PVC requires regular cleaning and protection from prolonged sun exposure to prevent yellowing and brittleness, shortening its effective lifespan. PMMA typically lasts 10-15 years in signage applications, while PVC often endures 5-8 years under similar conditions.
Typical Applications in Signage
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is widely used in signage for its excellent transparency, weather resistance, and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for illuminated signs, display panels, and outdoor advertising where clarity and UV stability are essential. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is preferred for signage applications requiring durability and cost-effectiveness, such as indoor signs, wayfinding, promotional displays, and temporary exhibition graphics, due to its impact resistance and ease of printing. Both materials serve specific roles in signage, with PMMA dominating high-end, long-lasting displays and PVC being favored for versatile, economical signage solutions.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Signage Needs
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior clarity, UV resistance, and weather durability, making it ideal for high-visibility outdoor signage requiring long-term exposure. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) provides cost-effective versatility, easy fabrication, and good chemical resistance, suitable for indoor signs and budget-friendly projects. Selecting between PMMA and PVC depends on factors such as environmental exposure, desired longevity, and budget constraints to ensure optimal signage performance.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyvinyl chloride for Signage
 azmater.com
azmater.com