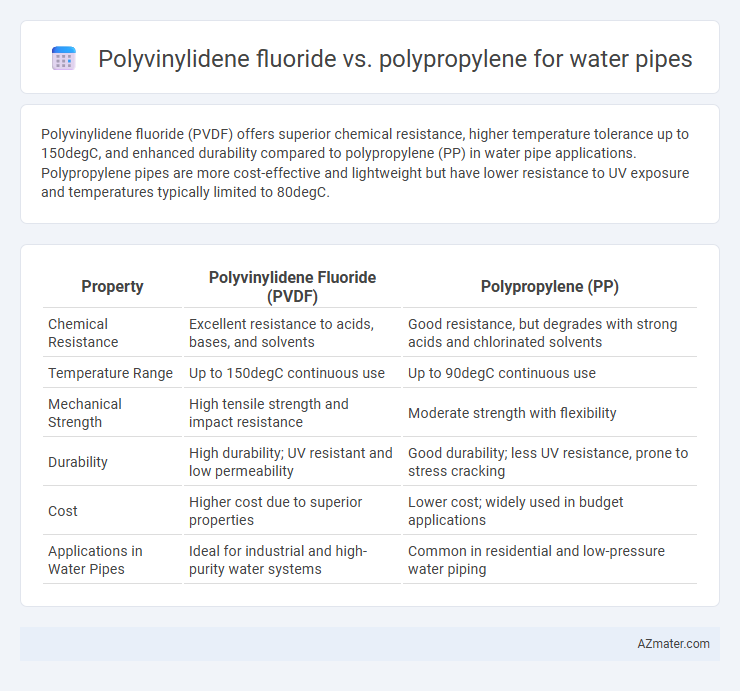
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, higher temperature tolerance up to 150degC, and enhanced durability compared to polypropylene (PP) in water pipe applications. Polypropylene pipes are more cost-effective and lightweight but have lower resistance to UV exposure and temperatures typically limited to 80degC.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance, but degrades with strong acids and chlorinated solvents |
| Temperature Range | Up to 150degC continuous use | Up to 90degC continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and impact resistance | Moderate strength with flexibility |
| Durability | High durability; UV resistant and low permeability | Good durability; less UV resistance, prone to stress cracking |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior properties | Lower cost; widely used in budget applications |
| Applications in Water Pipes | Ideal for industrial and high-purity water systems | Common in residential and low-pressure water piping |
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) and Polypropylene (PP)
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and UV stability, making it ideal for demanding water pipe applications in harsh environments. Polypropylene (PP) offers cost-effective corrosion resistance, good flexibility, and ease of installation, commonly used in residential and non-aggressive water distribution systems. PVDF pipes outperform PP in temperature tolerance and long-term durability, while PP remains a preferred choice where budget constraints and lower operating temperatures dominate.
Material Properties Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance, higher temperature tolerance up to 150degC, and excellent mechanical strength compared to polypropylene (PP), which typically withstands temperatures only up to 90degC. PVDF's low permeability and enhanced UV resistance make it ideal for aggressive and outdoor water pipe applications, whereas polypropylene offers economical benefits with good flexibility and impact resistance but lower durability under harsh conditions. The molecular structure of PVDF provides enhanced long-term stability and resistance to corrosion, whereas PP's semicrystalline nature results in lower rigidity and vulnerability to cracking under stress.
Chemical Resistance of PVDF vs PP
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), making it highly suitable for water pipe applications exposed to aggressive chemicals and corrosive environments. PVDF withstands a broader range of acids, bases, and solvents without degradation, while polypropylene may suffer from chemical attack or stress cracking under similar conditions. This enhanced durability of PVDF ensures longer service life and reliability in chemical-intensive water piping systems.
Temperature Tolerance in Water Pipe Applications
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior temperature tolerance compared to polypropylene (PP) in water pipe applications, maintaining structural integrity at continuous operating temperatures up to 150degC, whereas polypropylene typically withstands only up to 90degC. PVDF's high melting point around 177degC and excellent chemical resistance make it ideal for high-temperature water systems, including hot water supply and industrial processes. Conversely, polypropylene's lower thermal stability limits its use to lower temperature water distribution, often restricting it to cold water or low-temperature heating systems.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polypropylene (PP), making it highly resistant to impact, pressure, and deformation in demanding water pipe applications. PVDF offers excellent durability due to its outstanding chemical resistance, UV stability, and long-term performance in harsh environments, whereas polypropylene may degrade faster under similar conditions. The enhanced toughness and resilience of PVDF ensure longer service life and reduced maintenance in water piping systems.
Installation and Fabrication Differences
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) pipes feature superior chemical resistance and flexibility compared to polypropylene (PP), allowing easier bending and fewer fittings during installation. PVDF requires solvent welding or fusion techniques with specialized equipment, whereas polypropylene pipes can be joined using heat fusion, mechanical joints, or electrofusion methods that are generally simpler and quicker. Fabrication of PVDF pipes demands higher precision and controlled environments due to its sensitivity to temperature and solvents, while polypropylene offers more versatility with injection molding and extrusion processes, facilitating rapid manufacturing and on-site adjustments.
Cost Analysis: PVDF vs PP Pipes
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) pipes exhibit higher upfront costs compared to polypropylene (PP) pipes due to superior chemical resistance and temperature tolerance. PP pipes offer a more economical solution for non-critical applications, with lower material and installation expenses. Long-term cost analysis favors PVDF in aggressive environments because of reduced maintenance and longer service life.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability compared to polypropylene (PP), resulting in a longer service life for water pipes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. PVDF pipes require less frequent maintenance due to their high resistance to scaling, biodegradation, and thermal fatigue, while polypropylene pipes may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV light and chemical stress. The enhanced durability and minimal upkeep needs of PVDF make it a more cost-effective choice for long-term water piping systems.
Suitability for Drinking Water Systems
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is highly suitable for drinking water systems due to its excellent chemical resistance, low permeability, and compliance with stringent health standards such as NSF/ANSI 61. Polypropylene (PP) also finds application in drinking water pipes thanks to its cost-effectiveness and good chemical stability, though it has lower temperature tolerance and slightly higher permeability compared to PVDF. PVDF is preferred in applications requiring superior durability and long-term performance, while polypropylene is favored for economical solutions with moderate water quality requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and durability in water pipes, resulting in longer service life and reduced waste compared to polypropylene (PP). PVDF's recyclability and lower permeability contribute to minimizing environmental contamination and resource depletion, enhancing sustainability in water infrastructure. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and lightweight, typically exhibits shorter lifespan and higher environmental impact due to more frequent replacements and lower resistance to environmental stress cracking.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polypropylene for Water Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com