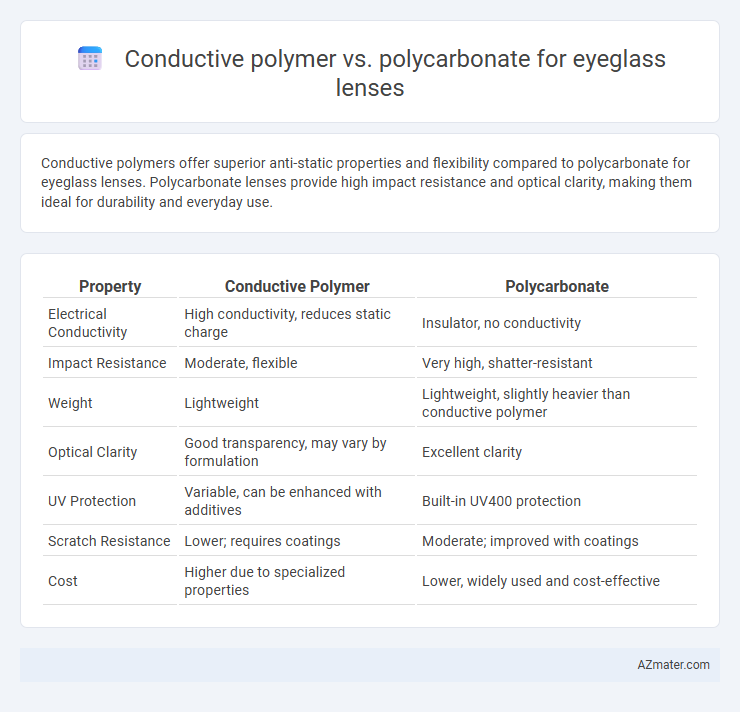
Conductive polymers offer superior anti-static properties and flexibility compared to polycarbonate for eyeglass lenses. Polycarbonate lenses provide high impact resistance and optical clarity, making them ideal for durability and everyday use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Polymer | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High conductivity, reduces static charge | Insulator, no conductivity |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, flexible | Very high, shatter-resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight, slightly heavier than conductive polymer |
| Optical Clarity | Good transparency, may vary by formulation | Excellent clarity |
| UV Protection | Variable, can be enhanced with additives | Built-in UV400 protection |
| Scratch Resistance | Lower; requires coatings | Moderate; improved with coatings |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized properties | Lower, widely used and cost-effective |
Introduction to Eyeglass Lens Materials
Conductive polymers in eyeglass lenses offer lightweight flexibility and electrochromic properties, allowing lenses to adjust tint in response to electrical stimuli. Polycarbonate, a widely used eyeglass lens material, provides high impact resistance, optical clarity, and UV protection, making it ideal for safety and everyday eyewear. While conductive polymers enhance smart lens capabilities, polycarbonate remains preferred for durability and affordability in conventional eyeglass lens manufacturing.
What Are Conductive Polymers?
Conductive polymers are organic polymers that conduct electricity, combining the electrical properties of metals with the mechanical flexibility and optical transparency of plastics, making them suitable for advanced optical applications like eyeglass lenses. Unlike polycarbonate, a rigid and impact-resistant thermoplastic widely used for durable lenses, conductive polymers offer unique electrical conductivity, enabling smart lens technologies such as anti-fog coatings and responsive tinting. The integration of conductive polymers into eyeglass lenses enhances functionality without compromising lightweight comfort or optical clarity, unlike traditional polycarbonate materials.
Overview of Polycarbonate Lenses
Polycarbonate lenses are lightweight, impact-resistant, and highly durable, making them ideal for eyeglasses, especially in safety and sports applications. They offer excellent UV protection and superior optical clarity compared to traditional glass lenses, while also being thinner and lighter than conventional plastic lenses. Conductive polymers, though innovative for smart eyewear applications, generally lack the robust impact resistance and widespread optical quality benefits that polycarbonate lenses provide.
Optical Clarity Comparison
Conductive polymers exhibit lower optical clarity compared to polycarbonate lenses due to their inherent molecular structure causing light scattering. Polycarbonate lenses provide excellent transparency with high refractive index and minimal chromatic aberration, enhancing visual acuity. The superior optical clarity of polycarbonate makes it the preferred material for eyeglass lenses requiring sharp vision and durability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Conductive polymers for eyeglass lenses offer enhanced electrical properties but typically have lower mechanical strength compared to polycarbonate, which excels in impact resistance and durability. Polycarbonate lenses provide superior shatter resistance and long-term wear resilience, making them ideal for active use and high-impact environments. The choice between conductive polymers and polycarbonate hinges on balancing conductivity needs with the demand for robust mechanical performance and lens longevity.
Weight and Comfort Analysis
Conductive polymers used in eyeglass lenses offer exceptional lightweight properties, significantly reducing the overall weight compared to polycarbonate lenses. The molecular structure of conductive polymers allows for thinner, more flexible lenses that enhance comfort during prolonged wear. Polycarbonate lenses, while durable and impact-resistant, tend to be heavier and less adaptable to ergonomic fitting, leading to potential discomfort in extended use.
Conductivity and Smart Lens Applications
Conductive polymers offer superior electrical conductivity compared to polycarbonate, making them ideal for smart eyeglass lens applications that require embedded sensors or responsive displays. Their ability to transmit electrical signals enables features such as touch sensitivity and adaptive tinting, which polycarbonate lenses cannot support due to their insulating properties. Integration of conductive polymers in smart lenses enhances functionality while maintaining lightweight and flexible design, crucial for wearable technology.
UV Protection and Safety Features
Conductive polymers used in eyeglass lenses offer enhanced UV protection due to their intrinsic ability to block harmful ultraviolet rays, reducing eye strain and potential retinal damage. Polycarbonate lenses provide superior impact resistance and shatterproof safety, making them ideal for high-risk environments and sports usage while also inherently filtering nearly 100% of UV radiation. Both materials contribute to UV protection, but polycarbonate lenses excel in safety features with their robust durability and lightweight comfort.
Cost and Manufacturing Differences
Conductive polymers used in eyeglass lenses offer enhanced functionality through touch sensitivity and anti-fog properties but come at a higher material cost and require specialized manufacturing processes involving coating and layering technologies. Polycarbonate lenses are more cost-effective, produced through well-established injection molding techniques known for high volume and rapid production efficiency. Manufacturing conductive polymer lenses demands precision and advanced equipment, resulting in longer production times and increased expenses compared to the streamlined, low-cost mass production of polycarbonate lenses.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Eyewear
Conductive polymers offer lightweight flexibility and anti-static properties, making them ideal for active lifestyles and digital device users, while polycarbonate lenses provide superior impact resistance and UV protection, essential for safety and outdoor activities. Polycarbonate's high optical clarity and durability make it a preferred choice for everyday eyewear, whereas conductive polymers excel in integrating smart eyewear technology due to their electrical conductivity. Selecting between these materials depends on the balance of protection, comfort, and functionality tailored to individual lifestyle needs.
Infographic: Conductive polymer vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com