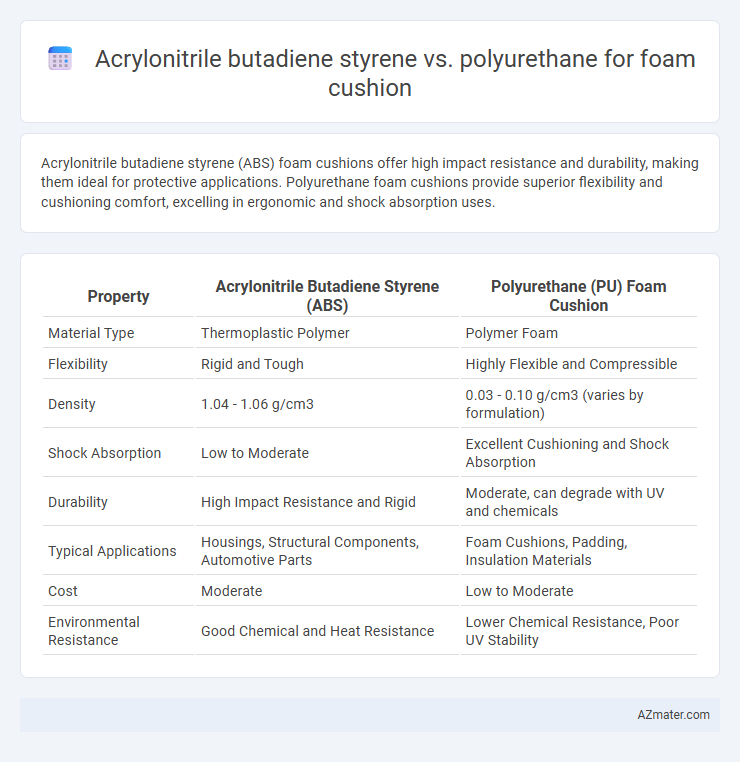
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) foam cushions offer high impact resistance and durability, making them ideal for protective applications. Polyurethane foam cushions provide superior flexibility and cushioning comfort, excelling in ergonomic and shock absorption uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyurethane (PU) Foam Cushion |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Polymer Foam |
| Flexibility | Rigid and Tough | Highly Flexible and Compressible |
| Density | 1.04 - 1.06 g/cm3 | 0.03 - 0.10 g/cm3 (varies by formulation) |
| Shock Absorption | Low to Moderate | Excellent Cushioning and Shock Absorption |
| Durability | High Impact Resistance and Rigid | Moderate, can degrade with UV and chemicals |
| Typical Applications | Housings, Structural Components, Automotive Parts | Foam Cushions, Padding, Insulation Materials |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Environmental Resistance | Good Chemical and Heat Resistance | Lower Chemical Resistance, Poor UV Stability |
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) and Polyurethane
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, rigidity, and toughness, making it suitable for structural foam cushion applications requiring durability. Polyurethane foam, a versatile elastomer, offers superior cushioning properties with excellent flexibility, shock absorption, and comfort, ideal for ergonomic seating and padding. ABS provides structural support and hardness, while polyurethane excels in softness and resilience, reflecting their distinct material characteristics in foam cushion design.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene monomers, offering rigidity and impact resistance due to its styrene-acrylonitrile matrix reinforced with rubbery butadiene particles. Polyurethane foam consists of a polymer formed by reacting polyols with diisocyanates, creating a network of urethane linkages that provide flexibility, shock absorption, and varying densities depending on the foam formulation. The chemical structure of ABS results in a hard, durable material suited for structural components, while polyurethane's cross-linked, cellular structure enables cushioning with superior energy dissipation and comfort.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Density
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits high strength and moderate flexibility with a density around 1.04 g/cm3, making it durable but relatively rigid for foam cushions. Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and cushioning due to its low density, typically between 0.02 and 0.08 g/cm3, combined with excellent resilience and energy absorption properties. The choice between ABS and polyurethane depends on the required balance of structural strength and pliability, with polyurethane favored for comfort and ABS for structural support in foam cushions.
Cushioning Performance and Comfort
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate cushioning performance with a rigid structure that limits flexibility and comfort, making it less ideal for foam cushions. Polyurethane foam excels in cushioning performance due to its superior resilience, elasticity, and ability to conform to body contours, resulting in enhanced comfort and pressure distribution. The choice of polyurethane foam is preferred in applications requiring prolonged use and superior ergonomic support, highlighting its dominance over ABS in comfort-centric cushioning solutions.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior durability and wear resistance due to its high impact strength and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for foam cushion components subject to frequent stress. Polyurethane foam cushions excel in flexibility and cushioning but tend to wear down faster under continuous compression and friction, showing reduced longevity in high-use environments. ABS's robust polymer structure ensures better retention of shape and resistance to surface degradation compared to the softer, more compressible polyurethane foam.
Manufacturing Processes and Versatility
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) manufacturing involves injection molding, enabling high precision and consistent foam cushion shapes with rigid properties ideal for structural support. Polyurethane foam cushions are typically produced through a chemical foaming process allowing customization of density and flexibility, making them highly versatile for various comfort and ergonomic applications. The versatility of polyurethane in adjusting firmness and resilience contrasts with ABS's strength and durability, influencing their suitability based on performance requirements in cushion manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) foam cushions exhibit lower biodegradability and higher environmental persistence compared to polyurethane foams, contributing to long-term ecological pollution. Polyurethane foam cushions offer enhanced sustainability potential through advancements in bio-based polyols and recycling technologies that reduce carbon footprint and waste generation. Life cycle assessments highlight polyurethane's evolving eco-friendly profile, whereas ABS foam's dependence on fossil fuel-derived components limits its environmental viability.
Cost-Effectiveness and Value Analysis
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and durability at a moderate cost, making it a cost-effective choice for foam cushion components requiring structural integrity. Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning, flexibility, and comfort at a lower price point but may degrade faster under heavy use, affecting long-term value. Evaluating specific application needs and lifespan requirements is essential to determine the optimal balance between upfront cost and overall performance value.
Common Applications in Foam Cushions
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) foam cushions are commonly used in automotive interiors and protective packaging due to their impact resistance and structural rigidity. Polyurethane foam cushions dominate in furniture upholstery, bedding, and orthopedic supports because of their excellent cushioning, flexibility, and durability. Both materials serve distinct purposes where ABS provides more structural support and polyurethane offers superior comfort and resilience.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers rigid, impact-resistant foam cushions ideal for applications requiring durability and structural integrity, while polyurethane provides flexible, soft, and highly resilient foam cushioning suited for comfort and shock absorption. When choosing the right material, prioritize ABS for high-load support and abrasion resistance, and opt for polyurethane foam where cushioning, elasticity, and pressure distribution are critical. Consider factors such as load-bearing capacity, comfort requirements, environmental exposure, and cost to determine the best fit for your specific foam cushion needs.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyurethane for Foam Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com