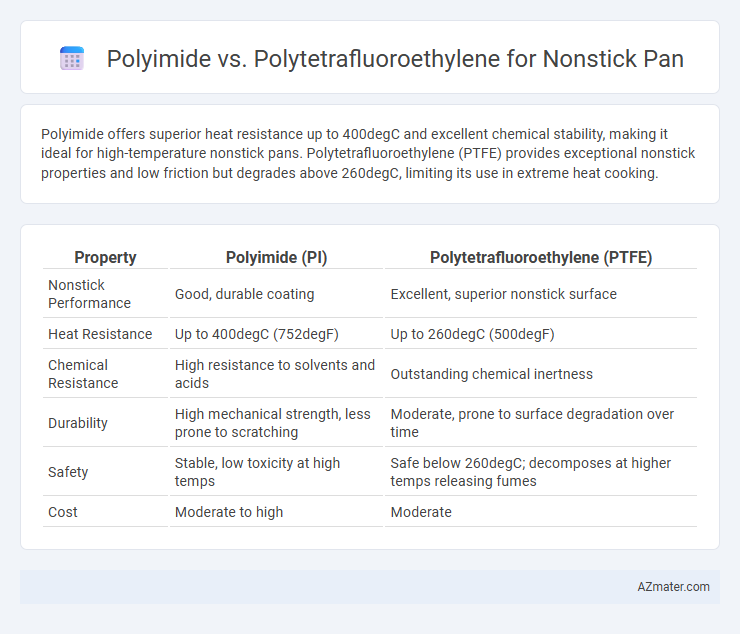
Polyimide offers superior heat resistance up to 400degC and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature nonstick pans. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides exceptional nonstick properties and low friction but degrades above 260degC, limiting its use in extreme heat cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide (PI) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Nonstick Performance | Good, durable coating | Excellent, superior nonstick surface |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 400degC (752degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to solvents and acids | Outstanding chemical inertness |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, less prone to scratching | Moderate, prone to surface degradation over time |
| Safety | Stable, low toxicity at high temps | Safe below 260degC; decomposes at higher temps releasing fumes |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Nonstick Pan Materials
Nonstick pans primarily utilize materials like polyimide and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) due to their excellent heat resistance and low friction properties. Polyimide offers superior thermal stability up to 400degC, making it suitable for high-temperature cooking, while PTFE, widely known as Teflon, provides exceptional nonstick performance and chemical inertness below 260degC. The choice between polyimide and PTFE impacts durability, cooking efficiency, and ease of cleaning in nonstick cookware applications.
Overview of Polyimide and PTFE
Polyimide exhibits exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance nonstick pan coatings that endure extreme cooking temperatures. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is widely favored for its superior nonstick properties, low friction, and resistance to chemicals but has a lower maximum operating temperature compared to polyimide. While PTFE ensures easy food release, polyimide offers enhanced durability and heat tolerance, catering to different cookware performance needs.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyimide features a rigid aromatic backbone with imide linkages, providing excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance essential for nonstick pans. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) consists of a carbon backbone fully fluorinated, yielding exceptional nonreactivity and a low friction surface. The imide groups in polyimide enhance mechanical strength, while PTFE's strong C-F bonds prevent chemical degradation, making each polymer uniquely suited for high-performance cookware coatings.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polyimide offers superior heat resistance with a melting point around 400degC, making it highly suitable for high-temperature nonstick pan applications, while polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has a lower decomposition temperature of approximately 260degC, limiting its thermal stability. The thermal stability of polyimide allows it to maintain structural integrity and nonstick properties under prolonged heat exposure, whereas PTFE can degrade and release harmful fumes when overheated above its threshold. This difference in heat resistance and thermal stability makes polyimide a more durable choice for cookware subjected to extreme cooking conditions.
Nonstick Performance and Food Release
Polyimide offers excellent heat resistance and durability, making it suitable for nonstick pans with high-temperature cooking, but its nonstick performance tends to be less effective than polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). PTFE, commonly known as Teflon, provides superior food release properties due to its low surface energy, which minimizes food adhesion and ensures easy cleaning. Despite PTFE's vulnerability to high temperatures above 260degC, its unmatched nonstick efficiency makes it the preferred choice for everyday nonstick cookware applications.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Polyimide coatings on nonstick pans demonstrate exceptional durability due to their high thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them less prone to degradation over time compared to other materials. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, offers superior scratch resistance and a smooth nonstick surface but may degrade faster under high heat or when exposed to abrasive utensils. While both materials provide strong nonstick performance, polyimide pans excel in long-term durability, whereas PTFE excels in scratch resistance, influencing their suitability based on cooking habits and maintenance.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Polyimide coatings offer high thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them safe for cooking at elevated temperatures without releasing harmful substances. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, is widely used in nonstick pans for its excellent food release properties but can emit toxic fumes if overheated above 260degC (500degF). Both materials are food-compatible when used properly, but polyimide may provide a safer alternative for high-heat cooking applications due to its greater thermal tolerance and reduced risk of toxic degradation.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Polyimide coatings offer excellent scratch resistance and thermal stability, making them easier to clean as food residues do not adhere strongly to the surface. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, provides superior nonstick properties but requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive tools to prevent damage. Both materials benefit from hand washing, but polyimide's enhanced durability reduces the frequency of re-coating or replacement compared to PTFE.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyimide offers a more sustainable alternative to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in nonstick pans due to its higher thermal stability and resistance to degradation, which reduces the need for frequent replacements and waste. PTFE production involves fluorinated compounds that pose significant environmental risks, including persistent pollutants and greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing. Choosing polyimide-coated cookware supports eco-friendly practices by minimizing harmful chemical release and enhancing product lifespan, contributing to lower overall environmental impact.
Conclusion: Which Material is Better for Nonstick Pans?
Polyimide offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking without degradation. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides excellent nonstick properties with low friction but can degrade at temperatures above 260degC, releasing harmful fumes. Considering longevity, safety, and performance, polyimide is generally better suited for nonstick pans used in high-heat and professional cooking environments.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick Pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com