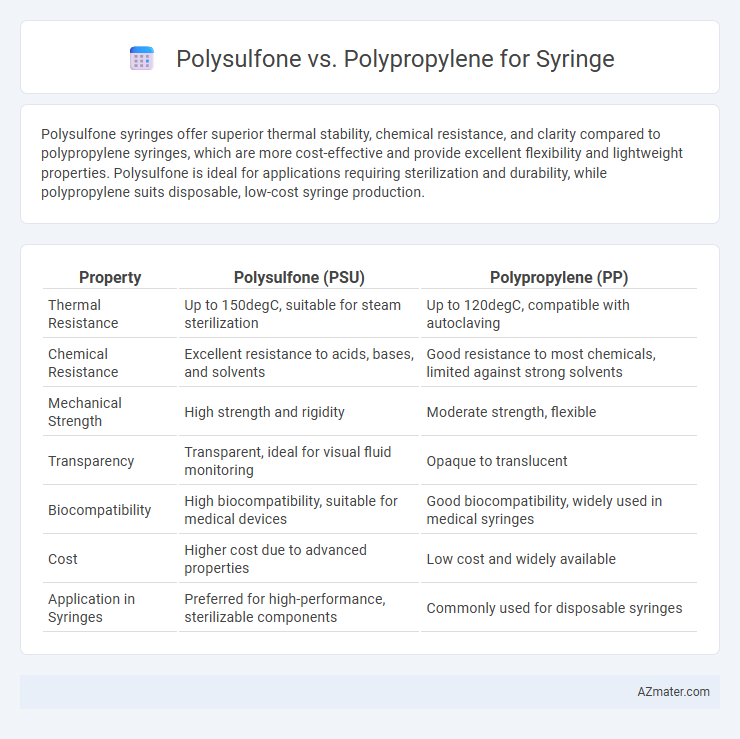
Polysulfone syringes offer superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and clarity compared to polypropylene syringes, which are more cost-effective and provide excellent flexibility and lightweight properties. Polysulfone is ideal for applications requiring sterilization and durability, while polypropylene suits disposable, low-cost syringe production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC, suitable for steam sterilization | Up to 120degC, compatible with autoclaving |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance to most chemicals, limited against strong solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and rigidity | Moderate strength, flexible |
| Transparency | Transparent, ideal for visual fluid monitoring | Opaque to translucent |
| Biocompatibility | High biocompatibility, suitable for medical devices | Good biocompatibility, widely used in medical syringes |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Low cost and widely available |
| Application in Syringes | Preferred for high-performance, sterilizable components | Commonly used for disposable syringes |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polypropylene in Syringes
Polysulfone is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and clarity, making it ideal for syringes requiring sterilization and visibility of fluid levels. Polypropylene is a widely used polymer in syringe manufacturing due to its cost-effectiveness, chemical resistance, and flexibility, suitable for disposable and single-use applications. Both materials offer distinct advantages in syringe production, with polysulfone preferred for high-temperature sterilization processes and polypropylene favored for mass production of lightweight, economical syringes.
Chemical Properties: Polysulfone vs Polypropylene
Polysulfone exhibits exceptional chemical resistance to acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it highly suitable for syringes requiring sterility and durability under harsh conditions. Polypropylene offers good chemical resistance to many solvents and is generally inert but may degrade when exposed to strong oxidizing agents or high-temperature sterilization. The superior thermal stability and resistance to hydrolysis of polysulfone distinguish it from polypropylene in syringe applications where prolonged exposure to aggressive chemicals or elevated temperatures is critical.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polypropylene, making it more resistant to deformation and cracking under stress in syringe applications. Its higher tensile strength and thermal stability enable prolonged use and sterilization without compromising structural integrity. Polypropylene, while more cost-effective and chemically resistant, generally offers lower impact resistance and less resilience to high temperatures, limiting its durability in demanding medical environments.
Temperature Resistance and Sterilization Compatibility
Polysulfone exhibits superior temperature resistance compared to polypropylene, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 150degC, making it highly suitable for autoclave sterilization processes. Polypropylene withstands temperatures up to approximately 135degC but may deform under prolonged high-heat exposure, limiting its use with autoclaving. Polysulfone's compatibility with high-temperature sterilization methods such as steam autoclaving and gamma irradiation ensures enhanced durability and repeated sterilization cycles for syringes, whereas polypropylene is often preferred for chemical resistance and single-use applications due to its lower thermal tolerance.
Chemical Compatibility with Pharmaceuticals
Polysulfone syringes exhibit superior chemical resistance to a broad spectrum of pharmaceuticals, including strong acids, bases, and organic solvents, maintaining integrity without leaching or degradation. In contrast, polypropylene syringes offer moderate chemical compatibility but may swell or degrade when exposed to certain solvents, reducing performance in aggressive pharmaceutical applications. Polysulfone's thermal stability and resistance to hydrolysis make it a preferred choice for syringes requiring prolonged exposure to chemically active drugs.
Clarity and Transparency Considerations
Polysulfone exhibits superior clarity and transparency compared to polypropylene, making it an ideal choice for syringe barrels requiring precise visual monitoring of fluid levels. Its glass-like transparency enhances user confidence in dosing accuracy, while polypropylene's more opaque nature limits clear visibility. In medical applications where clarity is critical, polysulfone ensures better patient safety through enhanced visual inspection.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing Factors
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance for syringe components but comes with higher raw material and processing costs compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene is favored in mass production due to its lower cost, ease of molding, and faster cycle times, enhancing overall manufacturing efficiency. Cost efficiency in syringe production balances the performance benefits of polysulfone with the affordability and scalability of polypropylene during high-volume manufacturing.
Biocompatibility and Safety Aspects
Polysulfone exhibits superior biocompatibility and thermal stability compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for syringes used in sensitive medical applications requiring sterilization. Polypropylene offers cost-effectiveness and chemical resistance but has lower resistance to repeated autoclaving, potentially affecting safety in long-term use. The inherent strength and inertness of polysulfone reduce leachables and ensure patient safety, while polypropylene's lower biocompatibility may limit its use in high-risk or prolonged exposure scenarios.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Polysulfone syringes meet stringent FDA and ISO standards for biocompatibility, ensuring safety in medical applications, while polypropylene syringes comply with USP Class VI and ISO 10993 regulations, emphasizing chemical resistance and sterilization compatibility. Both materials require rigorous testing for extractables and leachables to guarantee patient safety and regulatory approval. Ultimately, the choice depends on specific regulatory requirements related to the intended use, with polysulfone favored for high-temperature sterilization and polypropylene preferred for its cost-effective disposability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Syringe Applications
Polysulfone offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and clarity compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring sterilization and high performance. Polypropylene provides excellent cost-efficiency, impact resistance, and lightweight properties suitable for disposable syringe manufacturing. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance requirements with budget constraints and intended use conditions.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polypropylene for Syringe
 azmater.com
azmater.com