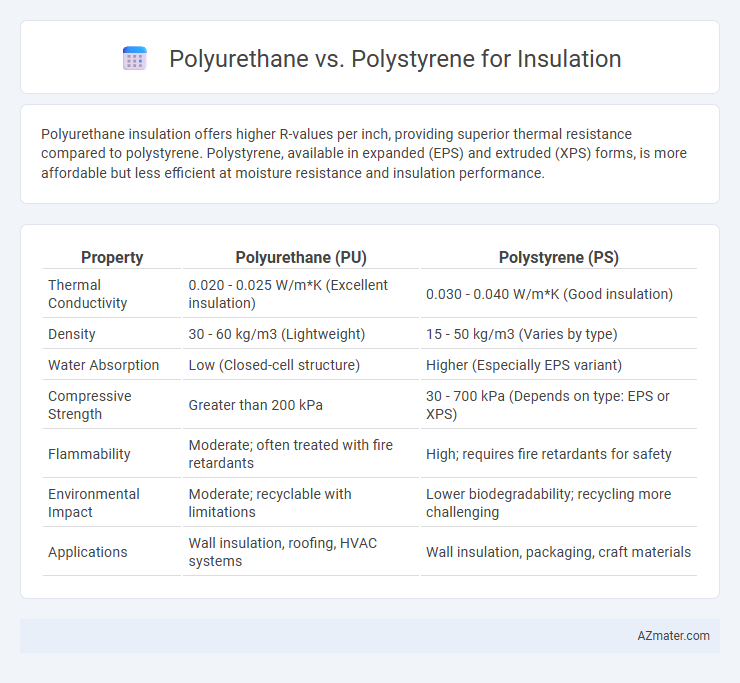
Polyurethane insulation offers higher R-values per inch, providing superior thermal resistance compared to polystyrene. Polystyrene, available in expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) forms, is more affordable but less efficient at moisture resistance and insulation performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.020 - 0.025 W/m*K (Excellent insulation) | 0.030 - 0.040 W/m*K (Good insulation) |
| Density | 30 - 60 kg/m3 (Lightweight) | 15 - 50 kg/m3 (Varies by type) |
| Water Absorption | Low (Closed-cell structure) | Higher (Especially EPS variant) |
| Compressive Strength | Greater than 200 kPa | 30 - 700 kPa (Depends on type: EPS or XPS) |
| Flammability | Moderate; often treated with fire retardants | High; requires fire retardants for safety |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate; recyclable with limitations | Lower biodegradability; recycling more challenging |
| Applications | Wall insulation, roofing, HVAC systems | Wall insulation, packaging, craft materials |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polystyrene Insulation
Polyurethane insulation is a rigid foam known for its high thermal resistance (R-value) and excellent air-sealing properties, making it ideal for reducing energy loss in buildings. Polystyrene insulation comes in two main types, expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS), offering good moisture resistance and moderate thermal performance commonly used in walls, roofs, and foundations. Both materials provide effective insulation, but polyurethane generally offers superior insulation efficiency and versatility in application.
Key Differences Between Polyurethane and Polystyrene
Polyurethane insulation offers a higher R-value per inch, typically around 6 to 7, compared to polystyrene's R-value of about 4 to 5, making polyurethane more effective for thermal resistance. Polyurethane is also more versatile, available as spray foam that seals gaps, whereas polystyrene commonly comes in rigid foam board forms with good moisture resistance but less air-sealing capability. While polyurethane tends to be more expensive, it provides superior adhesion and durability, whereas polystyrene is cost-effective and widely used in applications requiring moisture resistance and lightweight properties.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polyurethane insulation offers superior thermal performance with an R-value ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, significantly higher than polystyrene's R-value, which typically falls between 3.6 and 5 per inch depending on the type (EPS or XPS). The closed-cell structure of polyurethane provides better air and moisture resistance, enhancing its overall insulation efficiency in various applications. Polystyrene insulation, while cost-effective, often requires thicker layers to match the thermal resistance provided by thinner polyurethane panels, impacting space and installation flexibility.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Polyurethane insulation offers superior moisture resistance compared to polystyrene, effectively preventing water absorption and reducing the risk of mold growth. This closed-cell foam structure ensures long-term durability by maintaining its thermal performance even in high-humidity environments. Polystyrene, while also resistant to moisture, tends to be less durable under prolonged exposure to water, making polyurethane a preferred choice for insulation in moisture-prone areas.
Fire Safety and Flammability Ratings
Polyurethane insulation offers superior fire resistance compared to polystyrene, with a higher ignition temperature and enhanced flame-retardant additives that reduce combustion risks. Polystyrene, particularly expanded polystyrene (EPS), has lower fire safety ratings due to its propensity to melt and emit toxic smoke when exposed to flames. Building codes often mandate the use of fire barriers with polystyrene insulation to meet safety standards, while polyurethane typically requires less extensive protective measures.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane insulation offers superior thermal performance with a higher R-value per inch compared to polystyrene, which results in reduced energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions over a building's lifecycle. Polystyrene, particularly expanded polystyrene (EPS), is more widely recyclable and often contains less toxic blowing agents than some polyurethane foams, enhancing its sustainability profile. Considering environmental impact, choosing insulation with low global warming potential (GWP) blowing agents and recyclability is crucial for sustainable building practices.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Polyurethane insulation offers superior flexibility and can be sprayed into irregular spaces, creating a seamless barrier that minimizes air leaks during installation. Polystyrene insulation, available in rigid foam boards, requires precise cutting and fitting, which may lead to gaps or compromised sealing if not installed carefully. The ease of application and adaptability of polyurethane make it preferable for complex or uneven surfaces, whereas polystyrene suits straightforward, flat installations.
Cost Analysis: Polyurethane vs Polystyrene
Polyurethane insulation generally costs more per board foot compared to polystyrene due to its higher R-value and superior thermal performance. Polystyrene, available in both expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) forms, typically offers a lower upfront cost but may require thicker layers to achieve similar insulation levels. Long-term energy savings from polyurethane's efficiency often offset the initial price difference, making it a cost-effective choice in many insulation projects.
Common Applications in Construction
Polyurethane foam is widely used in wall panels, roofing, and floor insulation due to its superior thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings. Polystyrene, available as expanded (EPS) or extruded (XPS), is commonly applied in foundation walls, under slabs, and exterior insulation finishing systems (EIFS) for its compressive strength and water resistance. Both materials contribute to reducing heat transfer, but polyurethane excels in areas requiring higher insulation values and moisture control.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Project
Polyurethane offers higher R-values per inch compared to polystyrene, making it more efficient for tight spaces requiring superior thermal performance. Polystyrene, available as expanded (EPS) or extruded (XPS), provides moisture resistance and is often more cost-effective for large-scale applications. Selecting the right insulation depends on budget, moisture exposure, and required thermal resistance, with polyurethane favored for premium insulation and polystyrene suited for budget-conscious or moisture-prone environments.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polystyrene for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com