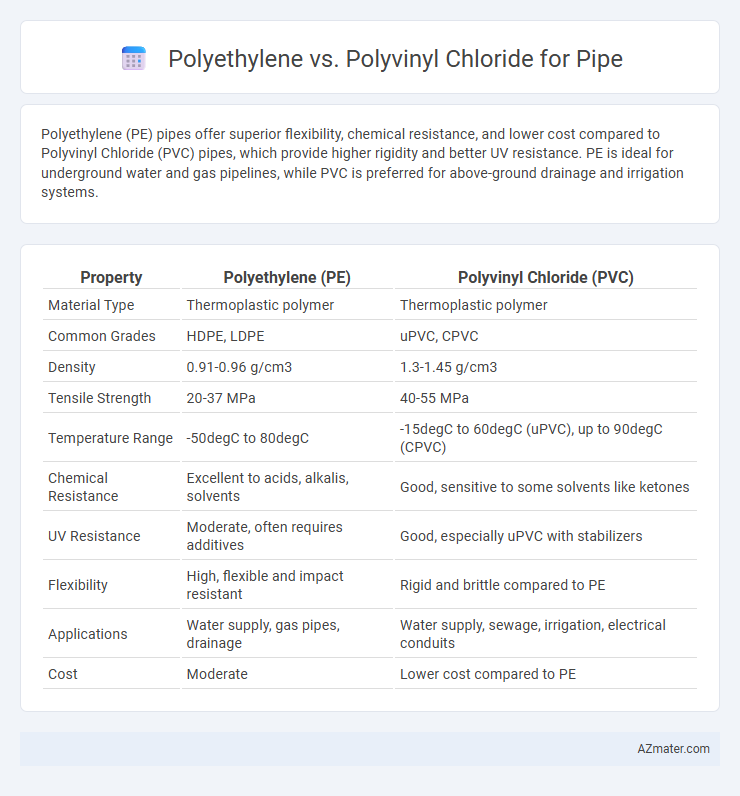
Polyethylene (PE) pipes offer superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and lower cost compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes, which provide higher rigidity and better UV resistance. PE is ideal for underground water and gas pipelines, while PVC is preferred for above-ground drainage and irrigation systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Common Grades | HDPE, LDPE | uPVC, CPVC |
| Density | 0.91-0.96 g/cm3 | 1.3-1.45 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 20-37 MPa | 40-55 MPa |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 80degC | -15degC to 60degC (uPVC), up to 90degC (CPVC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent to acids, alkalis, solvents | Good, sensitive to some solvents like ketones |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, often requires additives | Good, especially uPVC with stabilizers |
| Flexibility | High, flexible and impact resistant | Rigid and brittle compared to PE |
| Applications | Water supply, gas pipes, drainage | Water supply, sewage, irrigation, electrical conduits |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower cost compared to PE |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polyvinyl Chloride Pipes
Polyethylene pipes are known for their flexibility, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties, commonly used in water supply and gas distribution systems. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes offer high durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for drainage, irrigation, and industrial applications. Both materials provide distinct advantages depending on the specific requirements of pipe installation and performance conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure Differences
Polyethylene (PE) is a polymer made of repeating ethylene monomers with a simple hydrocarbon chain, characterized by strong carbon-carbon single bonds that provide flexibility and chemical resistance. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) consists of vinyl chloride monomers, incorporating chlorine atoms in its polymer chain, which results in increased rigidity and enhanced resistance to fire and chemicals. The presence of chlorine in PVC gives it a higher density and different thermal properties compared to the purely hydrocarbon-based polyethylene.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene (PE) pipes exhibit superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes, making PE more suitable for dynamic loading and ground movement conditions. PVC pipes demonstrate higher tensile strength and rigidity, providing excellent dimensional stability under pressure. The elongation at break of PE is significantly greater than PVC, indicating enhanced ductility and resistance to cracking under stress.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Polyethylene (PE) pipes exhibit superior flexibility and resistance to cracking, chemicals, and corrosion, making them highly durable in various environmental conditions. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes, while rigid and resistant to abrasion, can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light and extreme temperatures, potentially reducing lifespan. Typically, PE pipes have a longer service life of 50-100 years compared to PVC pipes, which generally last 25-40 years depending on exposure and application.
Resistance to Chemicals and Corrosion
Polyethylene (PE) pipes exhibit superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals including acids, bases, and salts, making them ideal for corrosive environments and industrial applications. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes offer good chemical resistance mainly to acids and alkalis but can degrade when exposed to certain solvents and strong oxidizing agents over time. Both materials resist corrosion effectively, but polyethylene's flexibility and higher chemical tolerance often provide longer service life in harsh conditions.
Flexibility and Ease of Installation
Polyethylene (PE) pipes offer superior flexibility compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), making them easier to bend and maneuver around obstacles during installation. This flexibility reduces the need for fittings and joints, speeding up the installation process and minimizing potential leak points. PVC pipes, while rigid and durable, often require additional fittings and precise placement, resulting in longer and more labor-intensive installation.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polyethylene (PE) pipes typically offer greater cost efficiency due to lower material and installation expenses compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes. Market availability favors PVC pipes as they dominate a broad range of applications, benefiting from well-established manufacturing and distribution networks worldwide. Both materials are widely accessible, but polyethylene's flexibility and lower overall lifecycle costs provide a competitive advantage in budget-sensitive projects.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene pipes exhibit superior environmental performance due to their lower carbon footprint in production and higher recyclability rates compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes. PVC manufacturing releases hazardous chemicals like dioxins, posing significant environmental and health risks, whereas polyethylene is more energy-efficient to produce and easier to recycle into new products. The biodegradability potential and minimal toxic residue of polyethylene make it a more sustainable piping option in long-term environmental impact assessments.
Typical Applications in Various Industries
Polyethylene (PE) pipes excel in water supply, gas distribution, and irrigation due to their flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability, making them ideal for municipal and agricultural use. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes dominate in construction and sanitation, widely applied in drainage, sewage systems, and electrical conduit because of their rigidity and ease of installation. Both materials are integral in industrial applications, with PE favored for gas and hazardous chemical transport, while PVC is preferred for potable water and wastewater management.
Final Considerations: Choosing the Right Pipe Material
Polyethylene (PE) pipes offer superior flexibility, corrosion resistance, and are ideal for cold water applications, while Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes provide excellent rigidity and perform well in higher pressure systems and hot water supply. Cost efficiency favors polyethylene in long-term projects due to lower maintenance demands, whereas PVC's ease of installation suits budget-conscious, rapid deployment needs. Final considerations should weigh environmental factors, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress to select the optimal pipe material for specific plumbing or industrial applications.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polyvinyl Chloride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com