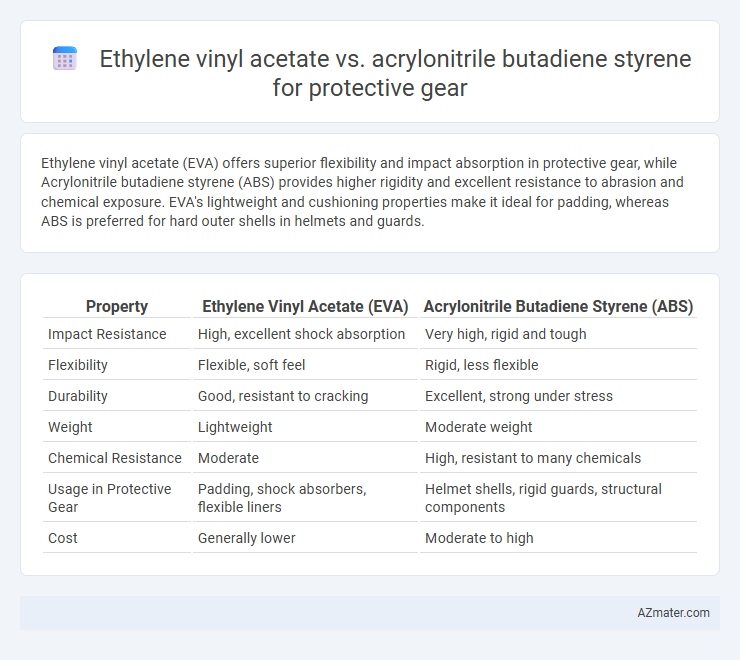
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and impact absorption in protective gear, while Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides higher rigidity and excellent resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure. EVA's lightweight and cushioning properties make it ideal for padding, whereas ABS is preferred for hard outer shells in helmets and guards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High, excellent shock absorption | Very high, rigid and tough |
| Flexibility | Flexible, soft feel | Rigid, less flexible |
| Durability | Good, resistant to cracking | Excellent, strong under stress |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High, resistant to many chemicals |
| Usage in Protective Gear | Padding, shock absorbers, flexible liners | Helmet shells, rigid guards, structural components |
| Cost | Generally lower | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Protective Gear Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility, lightweight properties, and shock absorption, making it ideal for protective gear like padding and insoles. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides superior impact resistance, rigidity, and durability, commonly used in helmets and hard protective shells. Selecting the appropriate material depends on balancing comfort, protection level, and application-specific requirements in safety equipment design.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible polymer commonly used in protective gear for its excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties. It offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it ideal for helmets, padding, and footwear insoles. EVA's chemical resistance and low-temperature tolerance enhance performance in various environmental conditions, ensuring long-lasting protection and comfort.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer renowned for its impact resistance, toughness, and rigidity, making it ideal for protective gear applications. Its chemical composition provides excellent resistance to physical impacts, heat, and various chemicals, ensuring durability and safety in demanding environments. Compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), ABS offers superior structural strength and abrasion resistance, essential for helmets, protective casings, and guards.
Mechanical Properties: EVA vs ABS
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and shock absorption, making it ideal for protective gear requiring cushioning and comfort. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides superior hardness, tensile strength, and rigidity, ensuring robust protection against heavy impacts and abrasion. While EVA excels in flexibility and lightweight performance, ABS is preferred for structural durability and resistance to mechanical stresses in protective equipment.
Impact Resistance and Shock Absorption
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior shock absorption due to its soft, flexible nature, making it ideal for protective gear requiring cushioning and impact dispersion. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides higher impact resistance with its rigid, durable structure, enhancing protection against high-force collisions in hard-shell applications. Selecting EVA enhances comfort and energy absorption, while ABS ensures robust impact resistance and structural integrity in protective equipment.
Flexibility and Comfort in Protective Gear
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and cushioning, making it an ideal material for protective gear requiring enhanced comfort and shock absorption. In contrast, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides rigid impact resistance but lacks the pliability that enables prolonged wear comfort. EVA's lightweight and soft texture allow greater freedom of movement, whereas ABS prioritizes durability and structural integrity over flexibility.
Weight and Ergonomics Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior lightweight properties compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making it ideal for protective gear that requires enhanced comfort and reduced fatigue during prolonged use. EVA's flexible and cushioning characteristics contribute to better ergonomics by providing improved impact absorption and conforming more naturally to body contours. In contrast, ABS, while more rigid and durable, tends to be heavier and less adaptable, which can compromise wearability and user comfort in extended protection scenarios.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility and shock absorption, making it highly durable for protective gear that requires cushioning and impact resistance. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides superior rigidity and toughness, ensuring long-lasting performance under mechanical stress and resistance to physical impacts. Both materials excel in durability, but ABS typically outperforms EVA in longevity due to its higher resistance to wear, chemicals, and environmental degradation.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and shock absorption for protective gear, making it cost-effective due to lower material and processing expenses compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). ABS provides higher impact resistance and structural rigidity but involves higher manufacturing costs due to complex molding and longer cycle times. Choosing EVA reduces production costs and enhances comfort, while ABS supports durability and strength, influencing long-term investment and application-specific manufacturing decisions.
Application Suitability: EVA vs ABS
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, cushioning, and shock absorption, making it ideal for protective gear such as padding and impact-resistant linings. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides enhanced rigidity, impact resistance, and durability, commonly used in hard-shell protective equipment like helmets and guards. Selecting EVA or ABS depends on the need for either comfort and flexibility (EVA) or structural strength and toughness (ABS) in protective gear applications.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Protective gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com