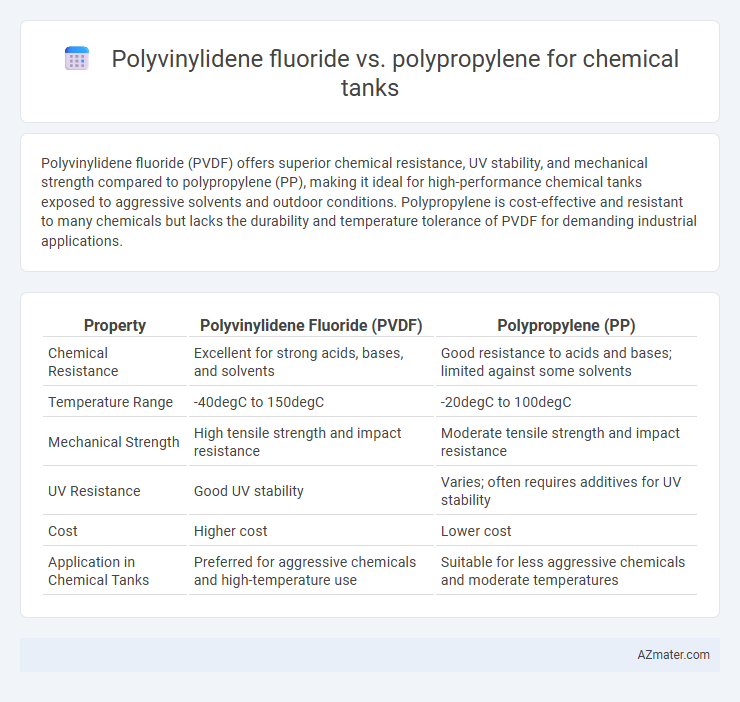
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength compared to polypropylene (PP), making it ideal for high-performance chemical tanks exposed to aggressive solvents and outdoor conditions. Polypropylene is cost-effective and resistant to many chemicals but lacks the durability and temperature tolerance of PVDF for demanding industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent for strong acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance to acids and bases; limited against some solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -20degC to 100degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and impact resistance | Moderate tensile strength and impact resistance |
| UV Resistance | Good UV stability | Varies; often requires additives for UV stability |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Application in Chemical Tanks | Preferred for aggressive chemicals and high-temperature use | Suitable for less aggressive chemicals and moderate temperatures |
Introduction to Chemical Tank Materials
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and polypropylene (PP) are widely used materials in the construction of chemical tanks due to their outstanding chemical resistance and durability. PVDF offers superior resistance to aggressive chemicals and high temperatures, making it ideal for storing highly corrosive substances, while polypropylene is cost-effective and suitable for less demanding chemical storage applications. Material selection depends on the chemical compatibility, temperature range, and mechanical requirements of the intended storage environment.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) is a highly durable fluoropolymer known for exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for chemical tank applications exposed to aggressive solvents and corrosive substances. Its low permeability and excellent thermal stability allow PVDF tanks to maintain integrity under extreme temperature variations, outperforming Polypropylene (PP) in resistance to harsh acids, bases, and organic solvents. PVDF's superior resistance to cracking and abrasion ensures long service life and minimal maintenance in demanding industrial environments compared to the more cost-effective but less chemically resistant polypropylene.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used for chemical tanks due to its excellent chemical resistance to acids, bases, and solvents, making it suitable for harsh environments. Its high impact strength and lightweight nature enhance durability and ease of installation, while its resistance to stress cracking ensures long-term performance. PP also offers good thermal resistance up to approximately 100degC, making it ideal for various industrial chemical storage applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison: PVDF vs PP
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), especially against strong acids, bases, and solvents, making it highly suitable for chemical tanks handling aggressive substances. PVDF's molecular structure provides excellent resistance to chlorinated hydrocarbons and aromatic compounds, which can degrade polypropylene over time. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and resistant to many mild chemicals, tends to swell or degrade under prolonged exposure to concentrated acids and alkalis, limiting its use for highly corrosive environments.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), making it more durable under harsh chemical tank conditions. PVDF exhibits higher tensile strength, impact resistance, and long-term stability, which enhances tank integrity and lifespan. Conversely, polypropylene provides good flexibility and cost-effectiveness but falls short in withstanding aggressive chemicals and mechanical wear over time.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior temperature tolerance compared to polypropylene (PP), maintaining structural integrity up to approximately 150degC, while polypropylene typically withstands temperatures only up to 100degC. PVDF's higher thermal stability ensures better resistance to thermal degradation and consistent performance in high-temperature chemical storage environments. This makes PVDF a preferred material for chemical tanks requiring durability under elevated temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure.
Cost Analysis: PVDF vs Polypropylene
PVDF offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polypropylene, but at a significantly higher material cost, often ranging from 3 to 5 times more expensive per kilogram. Polypropylene provides a cost-effective solution for chemical tanks suitable for less aggressive chemicals, balancing lower upfront investment with moderate lifespan. Total cost of ownership favors polypropylene for low-corrosive environments, whereas PVDF justifies its premium price in highly corrosive or temperature-sensitive applications due to reduced maintenance and replacement frequency.
Ease of Fabrication and Installation
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior ease of fabrication compared to polypropylene due to its excellent weldability and chemical resistance at higher temperatures, which reduces processing time and complexity for chemical tank manufacturing. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and lightweight, tends to have lower thermal stability, making it more challenging to weld and requiring specialized techniques for secure installation. PVDF's enhanced mechanical properties and dimensional stability facilitate smoother installation processes, minimizing downtime and ensuring longer service life in aggressive chemical environments.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability compared to polypropylene, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and extended tank lifespan in harsh chemical environments. Polypropylene may degrade faster when exposed to aggressive chemicals or prolonged sunlight, necessitating more frequent inspections and repairs. Choosing PVDF tanks significantly reduces downtime and replacement costs due to its enhanced durability and resistance to chemical attack.
Best Applications for PVDF and Polypropylene Tanks
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) tanks are ideal for storing highly corrosive chemicals such as acids, hydrocarbons, and solvents due to their superior chemical resistance and temperature stability up to 150degC. Polypropylene tanks are best suited for handling less aggressive chemicals, including dilute acids, alkalis, and aqueous solutions, with excellent impact resistance and cost-effectiveness in applications up to 90degC. PVDF tanks excel in pharmaceuticals, electronics, and chemical processing industries, while polypropylene tanks are favored in water treatment, agriculture, and food processing where moderate chemical resistance is sufficient.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polypropylene for Chemical tank
 azmater.com
azmater.com