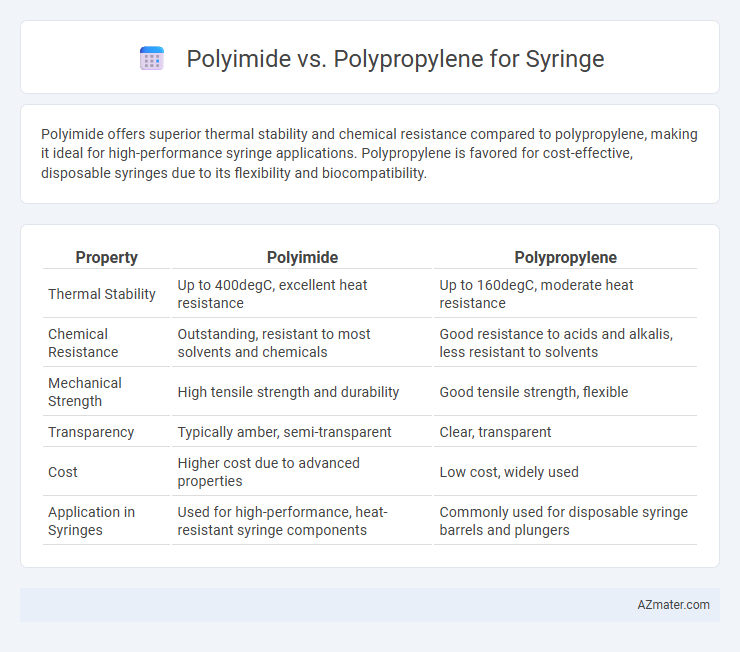
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for high-performance syringe applications. Polypropylene is favored for cost-effective, disposable syringes due to its flexibility and biocompatibility.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide | Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 400degC, excellent heat resistance | Up to 160degC, moderate heat resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding, resistant to most solvents and chemicals | Good resistance to acids and alkalis, less resistant to solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Good tensile strength, flexible |
| Transparency | Typically amber, semi-transparent | Clear, transparent |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Low cost, widely used |
| Application in Syringes | Used for high-performance, heat-resistant syringe components | Commonly used for disposable syringe barrels and plungers |
Introduction to Syringe Materials: Polyimide and Polypropylene
Polyimide and polypropylene are critical materials used in syringe manufacturing due to their unique chemical and physical properties. Polyimide offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance syringe components like thin films and coatings. Polypropylene is favored for its cost-effectiveness, excellent flexibility, and biocompatibility, commonly used for syringe barrels and plungers where durability and safety are essential.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polyimide features aromatic imide linkages providing exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature applications in syringes. Polypropylene, a semi-crystalline polymer composed of repeating propylene units, offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility but lower thermal resistance compared to polyimide. The rigid, aromatic backbone of polyimide contrasts with the aliphatic hydrocarbon chain of polypropylene, resulting in distinct mechanical strength and solvent compatibility profiles critical for syringe performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyimide offers superior mechanical strength and exceptional thermal stability compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for syringes requiring high durability under extreme conditions. Polypropylene exhibits good chemical resistance and flexibility but has lower tensile strength and may degrade faster with repeated sterilization cycles. For applications demanding long-term mechanical integrity and resistance to high temperatures, polyimide is the preferred choice over polypropylene in syringe manufacturing.
Resistance to Chemicals and Temperature
Polyimide syringes exhibit superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for applications requiring sterilization and exposure to harsh solvents. Polypropylene syringes offer good chemical resistance to acids, bases, and alcohols, but they degrade at elevated temperatures above 100degC, limiting their use in high-temperature environments. The exceptional thermal stability of polyimide allows it to maintain structural integrity in autoclaving and gamma sterilization, whereas polypropylene may warp or lose strength under similar conditions.
Biocompatibility and Safety in Medical Use
Polyimide exhibits superior biocompatibility and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene, making it highly suitable for syringe components in medical use. Its high thermal stability and inertness reduce risks of leaching and adverse reactions, enhancing patient safety during injections and fluid administration. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and widely used, may pose higher risks of chemical interaction and lower temperature tolerance in critical medical applications.
Flexibility and Ease of Manufacturing
Polyimide offers superior flexibility due to its high thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for intricate syringe components requiring precision. Polypropylene excels in ease of manufacturing because of its low melting point and excellent moldability, enabling efficient mass production of syringe barrels and plungers. While polyimide's flexibility supports complex designs, polypropylene provides cost-effective and rapid fabrication for standard syringe applications.
Applications in Syringe Components
Polyimide is widely used in syringe components requiring high thermal stability and chemical resistance, such as the needle hub and barrel lining, due to its excellent mechanical strength and ability to withstand sterilization processes. Polypropylene is preferred for syringe barrels and plungers because of its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and ease of molding, making it suitable for disposable syringes with high volume production. The choice between polyimide and polypropylene in syringe manufacturing depends on the specific application needs, including durability, chemical compatibility, and sterilization requirements.
Cost Analysis: Polyimide vs Polypropylene
Polypropylene syringes offer a significantly lower manufacturing cost compared to polyimide due to their widely available raw materials and simpler processing techniques. Polyimide syringes, while providing superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, involve higher synthesis expenses and specialized fabrication, resulting in increased overall production costs. Cost analysis reveals polypropylene as the more economical choice for mass-produced syringes, whereas polyimide is justified in high-performance applications requiring enhanced durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyimide syringes offer high thermal stability and chemical resistance but present environmental challenges due to their complex, energy-intensive manufacturing and limited recyclability. Polypropylene syringes are more sustainable, benefiting from widespread recyclability, lower production energy requirements, and greater biodegradability potential. Evaluating lifecycle assessments reveals polypropylene's reduced carbon footprint and environmental impact compared to polyimide alternatives.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Syringes
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for high-performance syringe applications requiring durability and sterilization tolerance. Polypropylene remains the preferred choice for cost-effective, disposable syringes due to its excellent moldability, lower price, and adequate chemical resistance for routine medical use. Selecting the right material depends on application-specific requirements, balancing performance demands of polyimide with the economical advantages of polypropylene.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polypropylene for Syringe
 azmater.com
azmater.com