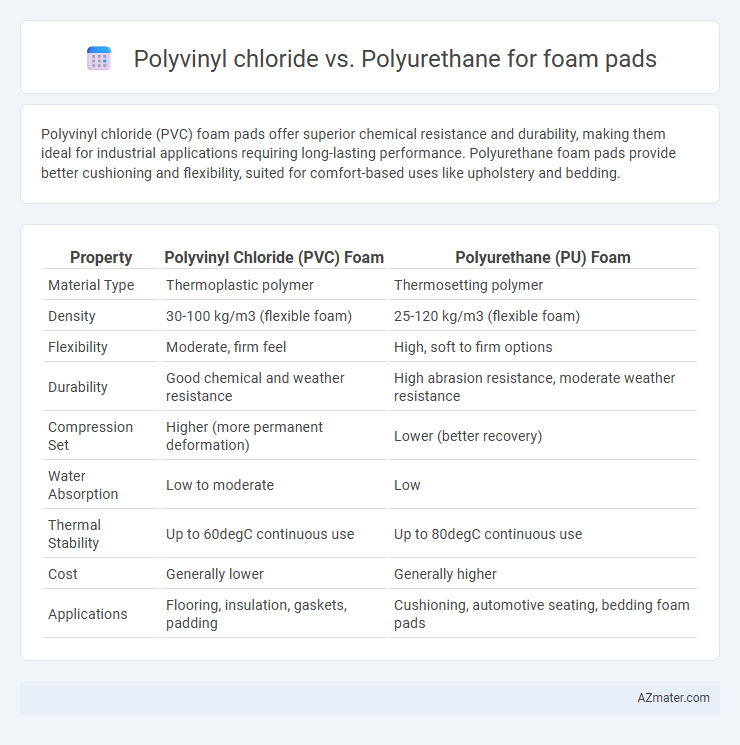
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam pads offer superior chemical resistance and durability, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring long-lasting performance. Polyurethane foam pads provide better cushioning and flexibility, suited for comfort-based uses like upholstery and bedding.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Polyurethane (PU) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermosetting polymer |
| Density | 30-100 kg/m3 (flexible foam) | 25-120 kg/m3 (flexible foam) |
| Flexibility | Moderate, firm feel | High, soft to firm options |
| Durability | Good chemical and weather resistance | High abrasion resistance, moderate weather resistance |
| Compression Set | Higher (more permanent deformation) | Lower (better recovery) |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate | Low |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 60degC continuous use | Up to 80degC continuous use |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Applications | Flooring, insulation, gaskets, padding | Cushioning, automotive seating, bedding foam pads |
Introduction to Foam Pad Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyurethane (PU) are widely used materials for foam pads, each offering distinct properties suited for various applications. PVC foam pads provide excellent durability, resistance to moisture, and ease of cleaning, making them ideal for outdoor and marine environments. In contrast, polyurethane foam pads deliver superior cushioning, flexibility, and breathability, favored in comfort-focused uses such as mattresses and seating.
Composition of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam pads are composed primarily of vinyl chloride monomers polymerized into a rigid plastic matrix that often incorporates plasticizers to enhance flexibility and durability. The chemical structure of PVC features chlorine atoms bound to a carbon chain, which provides high resistance to chemicals, weathering, and fire, making it suitable for various industrial and consumer applications. Compared to polyurethane, PVC's composition results in a denser, more rigid foam with superior resistance to oils and solvents but less inherent elasticity.
Structure of Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane (PU) foam pads feature a versatile polymer structure composed of flexible urethane links formed by the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a three-dimensional network that provides superior elasticity and durability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foams. The microcellular structure of PU enhances its cushioning properties, breathability, and resistance to compression set, making it ideal for high-performance foam applications. Unlike PVC, PU's molecular architecture allows for greater customization in density and firmness, optimizing comfort and support in foam pads.
Key Differences Between PVC and PU Foam Pads
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam pads are rigid, dense, and resistant to moisture and chemicals, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and water resistance. Polyurethane (PU) foam pads offer superior cushioning, flexibility, and breathability, which provides enhanced comfort and shock absorption in seating and bedding products. The key differences lie in PVC's structural rigidity and waterproof properties versus PU's softness, elasticity, and better air permeability.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Polyurethane foam pads exhibit superior durability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to their enhanced resistance to wear, tear, and environmental factors such as UV exposure and moisture. PVC foam pads tend to degrade faster under prolonged use, becoming brittle and prone to cracking, which significantly shortens their lifespan. Polyurethane pads typically last 3 to 5 times longer than PVC counterparts, making them a more reliable choice for long-term cushioning applications.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Polyurethane foam pads offer superior cushioning and enhanced comfort due to their high elasticity and breathability, making them ideal for prolonged use and pressure distribution. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam pads tend to be firmer with less resilience, providing basic support but often resulting in lower comfort levels over time. The open-cell structure of polyurethane foam allows better air circulation, reducing heat buildup compared to the denser, closed-cell PVC foam, which can lead to a less comfortable experience.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam pads pose significant environmental challenges due to their production involving toxic chlorine-based chemicals and difficulties in recycling, which contribute to long-term pollution. Polyurethane (PU) foam pads offer a more sustainable option, as they can be produced with bio-based polyols and have better recyclability, reducing their carbon footprint and waste impact. Choosing polyurethane foam for pads supports lower environmental harm and aligns more closely with circular economy principles.
Cost Analysis: PVC vs Polyurethane
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam pads typically offer lower upfront costs compared to polyurethane foam due to cheaper raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. Polyurethane foam pads, while more expensive initially, provide superior durability and comfort, potentially reducing replacement frequency and long-term expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including longevity and performance, is essential when choosing between PVC and polyurethane foam pads.
Common Applications in Foam Pads
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam pads are widely used in construction, packaging, and automotive industries due to their durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Polyurethane (PU) foam pads are preferred in furniture, bedding, and soundproofing applications because of their superior cushioning, flexibility, and excellent energy absorption properties. Both materials serve distinct roles in foam pad manufacturing, with PVC favored for sturdy, weather-resistant pads and polyurethane chosen for comfort and impact mitigation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam Pad Material
Polyurethane foam pads offer superior flexibility, durability, and comfort, making them ideal for applications requiring cushioning and resilience. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam pads provide excellent chemical resistance and water impermeability, suitable for outdoor or moisture-prone environments. Selecting the right foam pad depends on specific use cases, with polyurethane preferred for ergonomic support and PVC favored for durability in harsh conditions.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polyurethane for Foam pad
 azmater.com
azmater.com