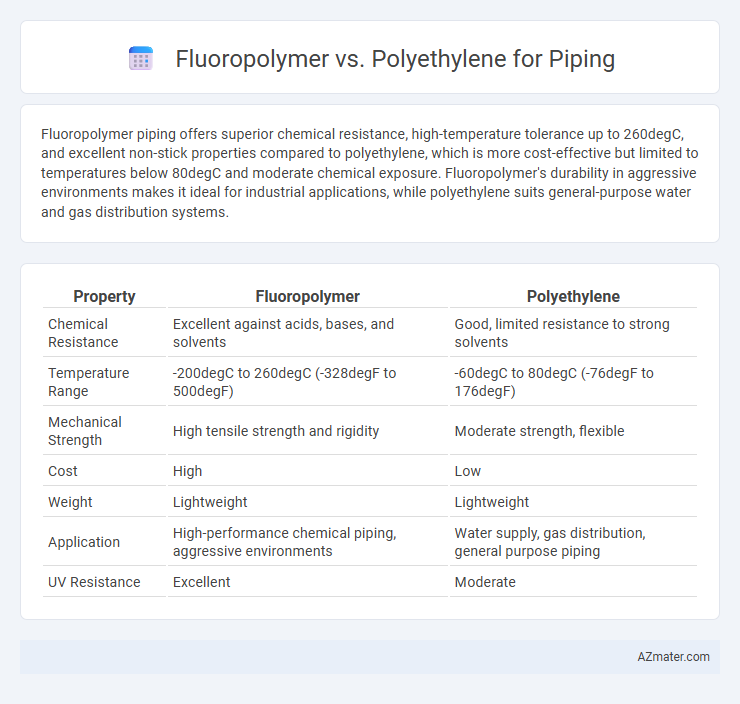
Fluoropolymer piping offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and excellent non-stick properties compared to polyethylene, which is more cost-effective but limited to temperatures below 80degC and moderate chemical exposure. Fluoropolymer's durability in aggressive environments makes it ideal for industrial applications, while polyethylene suits general-purpose water and gas distribution systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, bases, and solvents | Good, limited resistance to strong solvents |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 260degC (-328degF to 500degF) | -60degC to 80degC (-76degF to 176degF) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Moderate strength, flexible |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Application | High-performance chemical piping, aggressive environments | Water supply, gas distribution, general purpose piping |
| UV Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
Introduction to Fluoropolymer and Polyethylene Piping
Fluoropolymer piping, known for its exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, is widely used in industries requiring durability under aggressive conditions. Polyethylene piping offers excellent flexibility, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for water supply and gas distribution systems. Comparing these materials involves assessing factors such as temperature limits, chemical compatibility, and mechanical strength to determine the most suitable piping solution.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Fluoropolymer piping offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and excellent non-stick properties, making it ideal for aggressive fluids and corrosive environments compared to polyethylene. Polyethylene pipes provide excellent impact resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, with temperature limits typically around 60degC, suitable for water distribution and general utility applications. Both materials demonstrate low permeability, but fluoropolymers exhibit higher durability in extreme conditions, while polyethylene excels in ease of installation and environmental stress resistance.
Chemical Resistance and Corrosion Protection
Fluoropolymer piping exhibits exceptional chemical resistance due to its strong carbon-fluorine bonds, making it highly effective against aggressive chemicals, acids, and solvents where polyethylene may degrade. Polyethylene offers good chemical resistance to many non-polar substances but lacks the superior corrosion protection of fluoropolymers in highly corrosive environments. For industrial applications involving harsh chemicals or extreme conditions, fluoropolymer pipes provide enhanced durability and longevity compared to polyethylene piping.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Fluoropolymer piping exhibits superior temperature tolerance, maintaining structural integrity in extreme conditions ranging from -200degC to 260degC, compared to polyethylene, which typically withstands temperatures between -50degC and 80degC. The exceptional thermal stability of fluoropolymers allows for minimal thermal expansion and resistance to thermal degradation, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Polyethylene, while cost-effective and chemically resistant, experiences significant deformation and reduced mechanical performance under elevated thermal conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Fluoropolymer piping offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for high-pressure and corrosive environments. Polyethylene pipes exhibit greater flexibility and impact resistance, allowing for easier installation and bending in complex layouts. The choice between fluoropolymer and polyethylene depends on application-specific requirements such as temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Fluoropolymer piping offers superior chemical resistance and durability, reducing maintenance frequency and operational downtimes compared to polyethylene pipes, which may require more frequent inspections due to susceptibility to stress cracking. Installation of fluoropolymer pipes demands specialized equipment and skilled labor to handle their rigidity and fusion techniques, whereas polyethylene pipes provide easier handling and flexibility, allowing quicker and less complex installation processes. Maintenance costs for fluoropolymer systems tend to be lower over time due to their resistance to corrosion and UV degradation, while polyethylene piping may necessitate more frequent replacements in harsh environments.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Fluoropolymer piping typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced material properties such as superior chemical resistance and temperature tolerance, making it ideal for specialized industrial applications. Polyethylene piping offers a more cost-effective solution for general use, with lower material and installation expenses, benefiting large-scale projects with budget constraints. Long-term economic factors favor polyethylene in standard environments, while fluoropolymers justify their premium in applications requiring durability against aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures.
Typical Applications in Industry
Fluoropolymer piping excels in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing due to its superior chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance, and low friction properties. Polyethylene piping dominates water distribution, gas conveyance, and agricultural irrigation applications because of its cost-effectiveness, chemical resistance, and flexibility. Industries requiring extreme corrosion resistance and purity, such as aerospace and food processing, prefer fluoropolymer systems, while polyethylene is widely adopted in municipal infrastructure and residential plumbing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fluoropolymer piping offers superior chemical resistance and longevity, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing waste generation compared to polyethylene. Polyethylene pipes are more commonly recyclable and derived from less energy-intensive processes, contributing to a lower carbon footprint during production. Evaluating the environmental impact, polyethylene often presents a more sustainable option for piping in applications where extreme chemical resistance is not critical.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Piping System
Fluoropolymer piping offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, making it ideal for corrosive or industrial environments, while polyethylene excels in cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and impact resistance for water and gas distribution. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as temperature range, chemical exposure, pressure requirements, and installation conditions within your piping system. Evaluating these parameters ensures optimal performance, longevity, and safety tailored to specific application needs.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polyethylene for Piping
 azmater.com
azmater.com