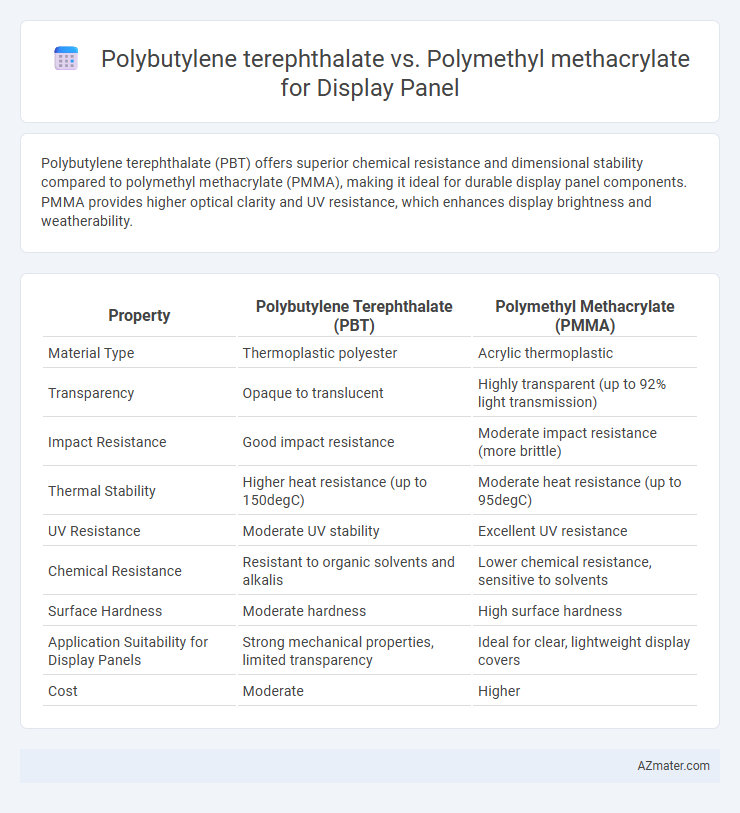
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it ideal for durable display panel components. PMMA provides higher optical clarity and UV resistance, which enhances display brightness and weatherability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Acrylic thermoplastic |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent (up to 92% light transmission) |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance (more brittle) |
| Thermal Stability | Higher heat resistance (up to 150degC) | Moderate heat resistance (up to 95degC) |
| UV Resistance | Moderate UV stability | Excellent UV resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to organic solvents and alkalis | Lower chemical resistance, sensitive to solvents |
| Surface Hardness | Moderate hardness | High surface hardness |
| Application Suitability for Display Panels | Strong mechanical properties, limited transparency | Ideal for clear, lightweight display covers |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Display Panel Materials
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers high dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and good dielectric properties, making it suitable for display panel housings and components requiring mechanical strength and thermal endurance. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) excels in optical clarity, light transmission up to 92%, and weather resistance, ideal for display panel screens and protective covers where transparency and aesthetics are critical. Selecting between PBT and PMMA depends on the application focus: structural durability versus optical performance in display panel materials.
Overview of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its high mechanical strength, excellent electrical insulation properties, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it suitable for electronic display panel components. It offers superior dimensional stability and thermal resistance compared to many polymers, ensuring reliable performance under varying environmental conditions. PBT's low shrinkage rate and ease of injection molding contribute to precise and consistent manufacturing of intricate display parts.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic commonly used in display panels due to its excellent optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability. Compared to Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), PMMA offers superior light transmittance and scratch resistance, making it ideal for high-visibility screens and protective covers. Its mechanical rigidity and ease of fabrication also contribute to enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal in electronic display applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior impact resistance and dimensional stability compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in display panel applications, making it more suitable for environments requiring durability under mechanical stress. PMMA offers higher surface hardness and optical clarity but results in lower tensile strength and flexibility, limiting its performance in impact-prone conditions. The choice between PBT and PMMA depends on balancing mechanical toughness with visual quality demands in display panel manufacturing.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers moderate optical clarity with light transmission typically around 85%, making it suitable for applications requiring durability over transparency. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic, provides superior optical clarity and exceptional light transmission rates exceeding 92%, ideal for display panels demanding high visibility and brightness. PMMA's lower haze and higher refractive index enhance image sharpness, surpassing PBT in applications where optical performance is critical.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly against solvents, oils, and alkalis, making it ideal for display panels exposed to harsh environments. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent clarity but is more susceptible to chemical attack and environmental degradation, especially from UV radiation and certain solvents. PBT's enhanced environmental resistance ensures longer durability and stability in outdoor or industrial display applications compared to PMMA.
Processability and Manufacturing Differences
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior processability in display panel manufacturing due to its high melting point and excellent flow characteristics, enabling precision injection molding and faster cycle times. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) requires careful thermoforming or casting processes, which can be slower and less adaptable to high-volume production. The inherent thermal stability and chemical resistance of PBT support automated, large-scale manufacturing, while PMMA's brittleness and lower thermal tolerance often necessitate additional post-processing treatments to prevent deformation and maintain optical clarity.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers a cost-effective solution for display panels with lower raw material prices and improved manufacturing efficiency compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PMMA commands a higher market price due to superior optical clarity and UV resistance, but these benefits lead to increased production costs, impacting the overall budget of display applications. Economic considerations favor PBT where cost reduction and mechanical strength are prioritized, while PMMA is preferred for premium displays requiring enhanced visual performance despite higher expenditure.
Durability and Lifespan in Display Applications
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it highly durable for display panel components exposed to varying environmental conditions. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provides excellent optical clarity but has lower impact resistance and is more prone to UV-induced degradation, which can reduce its lifespan in outdoor or high-exposure display applications. When prioritizing longevity and durability in display panels, PBT typically outperforms PMMA due to its robustness against mechanical stress and environmental aging factors.
Final Recommendations for Display Panel Selection
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior impact resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for durable display panel housings requiring mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) excels in optical clarity and UV resistance, providing excellent light transmission and scratch resistance for high-visibility display surfaces. Selecting PBT is recommended for structural components exposed to mechanical stress, while PMMA is optimal for transparent display covers prioritizing clarity and surface hardness.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polymethyl methacrylate for Display Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com