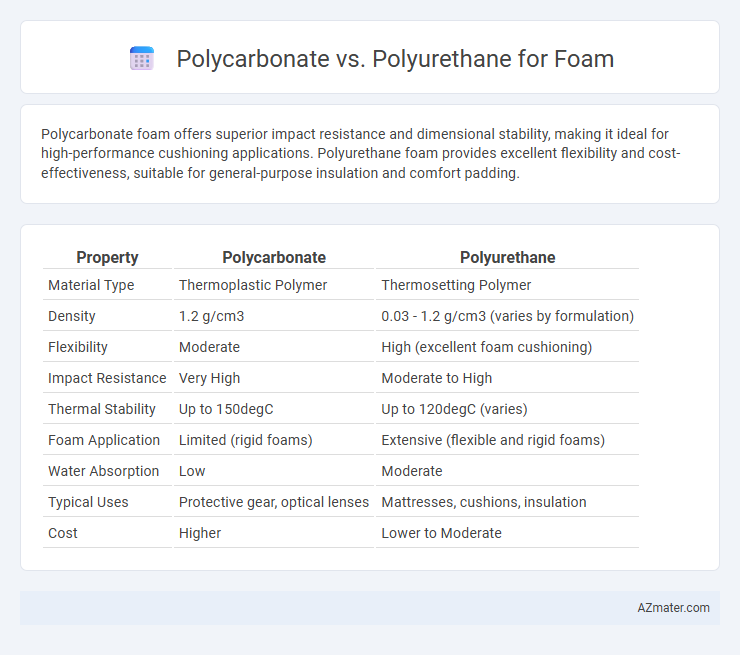
Polycarbonate foam offers superior impact resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for high-performance cushioning applications. Polyurethane foam provides excellent flexibility and cost-effectiveness, suitable for general-purpose insulation and comfort padding.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate | Polyurethane |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Thermosetting Polymer |
| Density | 1.2 g/cm3 | 0.03 - 1.2 g/cm3 (varies by formulation) |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High (excellent foam cushioning) |
| Impact Resistance | Very High | Moderate to High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 150degC | Up to 120degC (varies) |
| Foam Application | Limited (rigid foams) | Extensive (flexible and rigid foams) |
| Water Absorption | Low | Moderate |
| Typical Uses | Protective gear, optical lenses | Mattresses, cushions, insulation |
| Cost | Higher | Lower to Moderate |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Polyurethane Foams
Polycarbonate foam is a lightweight, durable material known for its excellent impact resistance and thermal insulation properties, commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and protective equipment applications. Polyurethane foam offers exceptional flexibility, cushioning, and sound absorption, making it ideal for furniture, bedding, and automotive seating. Both foams differ significantly in chemical structure and performance characteristics, influencing their suitability for specific industrial uses.
Chemical Composition and Structural Properties
Polycarbonate foam is derived from polycarbonate polymers featuring carbonate groups in its backbone, resulting in high-impact resistance, thermal stability, and excellent dimensional stability. Polyurethane foam originates from the reaction of polyols and isocyanates, producing a versatile polymer with customizable density, elasticity, and superior cushioning properties. Chemically, polycarbonate's rigid aromatic carbonate links provide structural robustness, while polyurethane's segmented copolymer structure imparts flexibility and varied mechanical performance.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Polycarbonate foams are produced through a chemical foaming process that involves gas injection into molten polymer, resulting in a rigid, high-strength cellular structure ideal for impact-resistant applications. Polyurethane foams, manufactured by reacting polyols with isocyanates in the presence of blowing agents, allow for greater versatility in density and flexibility, making them suitable for cushioning and insulation. The polycarbonate foam manufacturing process demands higher processing temperatures and precise control of foaming agents, whereas polyurethane foams benefit from faster reaction times and easier moldability during production.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polycarbonate foam exhibits higher mechanical strength with superior impact resistance and rigidity, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting structural support. Polyurethane foam offers excellent flexibility and cushioning properties but tends to degrade faster under mechanical stress and environmental factors. Durability of polycarbonate foam is enhanced due to its resistance to wear, UV exposure, and chemicals compared to polyurethane, which is more susceptible to abrasion and hydrolysis.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Polyurethane foam exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity compared to polycarbonate foam, allowing it to return to its original shape after compression with minimal deformation. Polycarbonate foam, while durable and impact-resistant, tends to be more rigid and less capable of significant elongation without permanent damage. These differences make polyurethane ideal for cushioning applications requiring enhanced comfort and resilience, whereas polycarbonate suits structural uses demanding stiffness and durability.
Thermal Resistance and Insulation Performance
Polycarbonate foam exhibits superior thermal resistance due to its high melting point and ability to withstand temperatures up to 150degC without degradation, making it ideal for high-heat insulation applications. Polyurethane foam offers excellent insulation performance with low thermal conductivity values, typically around 0.02 W/m*K, providing efficient energy conservation in building and refrigeration uses. While polyurethane excels in thermal insulation efficiency, polycarbonate's durability and thermal stability make it preferable for environments requiring both insulation and heat resistance.
Applications Across Industries
Polycarbonate foam excels in high-impact protection and thermal insulation, making it ideal for automotive components, aerospace structures, and electronics housings. Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and cushioning properties, widely used in furniture manufacturing, medical cushions, and soundproofing applications. Both materials support diverse industrial needs, but polycarbonate suits environments demanding rigidity and durability, while polyurethane adapts to comfort and shock absorption requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polycarbonate foam offers high durability and recyclability, contributing to environmental sustainability by reducing waste and extending product lifecycle. Polyurethane foam, while versatile and widely used, often involves toxic chemicals and less eco-friendly manufacturing processes, leading to greater environmental concerns. Choosing polycarbonate foam supports greener practices due to its lower greenhouse gas emissions during production and improved potential for recycling.
Cost Efficiency and Value Analysis
Polycarbonate foam typically offers higher durability and thermal stability but comes at a premium cost, making it suitable for applications where long-term resilience justifies the investment. Polyurethane foam provides a more cost-efficient option with flexible cushioning and ease of manufacturing, ideal for budget-conscious projects requiring moderate performance. Analyzing overall value, polyurethane's lower upfront expense often outweighs polycarbonate's benefits unless demanding environmental conditions necessitate enhanced material performance.
Choosing the Right Foam Material
Polycarbonate foam offers superior thermal insulation and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring high impact resistance and long-term stability. Polyurethane foam excels in flexibility and cushioning properties, with better cost-efficiency for padding, soundproofing, and lightweight structural support. Selecting between polycarbonate and polyurethane foam depends on the specific performance needs such as load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polyurethane for Foam
 azmater.com
azmater.com