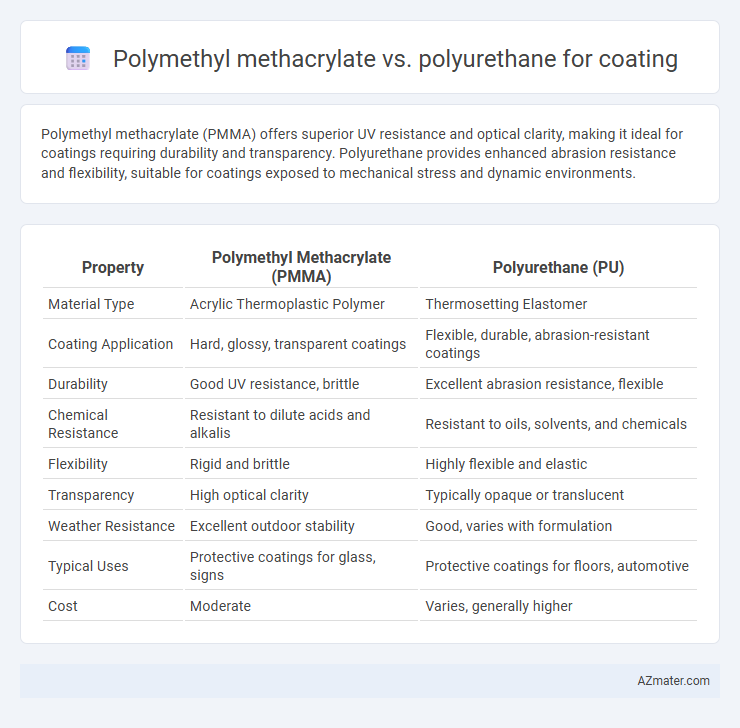
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior UV resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for coatings requiring durability and transparency. Polyurethane provides enhanced abrasion resistance and flexibility, suitable for coatings exposed to mechanical stress and dynamic environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Acrylic Thermoplastic Polymer | Thermosetting Elastomer |
| Coating Application | Hard, glossy, transparent coatings | Flexible, durable, abrasion-resistant coatings |
| Durability | Good UV resistance, brittle | Excellent abrasion resistance, flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to dilute acids and alkalis | Resistant to oils, solvents, and chemicals |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Highly flexible and elastic |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | Typically opaque or translucent |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent outdoor stability | Good, varies with formulation |
| Typical Uses | Protective coatings for glass, signs | Protective coatings for floors, automotive |
| Cost | Moderate | Varies, generally higher |
Introduction to Polymethyl Methacrylate and Polyurethane Coatings
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) coatings are known for their excellent optical clarity, UV resistance, and weather durability, making them ideal for protective and decorative applications. Polyurethane coatings offer superior abrasion resistance, flexibility, and chemical resistance, often used where high-performance and durability are required. Both PMMA and polyurethane coatings serve distinct purposes in industrial and commercial sectors, with PMMA preferred for aesthetic protection and polyurethane for mechanical endurance.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a thermoplastic polymer composed of methyl methacrylate monomers, characterized by a rigid acrylic backbone that provides excellent transparency and UV resistance. Polyurethane, a versatile polymer formed through the reaction of polyols and isocyanates, exhibits a segmented structure with soft and hard segments that contribute to its elasticity and durability. The distinct chemical composition and structural differences between PMMA and polyurethane influence their coating properties, with PMMA offering superior clarity and weather resistance, while polyurethane provides enhanced flexibility and abrasion resistance.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and rigidity. Polyurethane coatings provide superior flexibility and impact resistance, allowing for better performance under mechanical stress and deformation. The choice between PMMA and polyurethane depends on the specific balance needed between mechanical strength and elasticity for the intended coating application.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent weather resistance with strong UV stability, maintaining clarity and color over time, making it ideal for outdoor coatings exposed to sunlight. Polyurethane provides superior durability, featuring high abrasion resistance and flexibility, which helps withstand mechanical wear and temperature fluctuations. While PMMA excels in maintaining surface aesthetics against environmental degradation, polyurethane is better suited for applications requiring robust mechanical protection and resilience under diverse weather conditions.
Application Techniques and Surface Preparation
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) coatings require meticulous surface preparation, including thorough cleaning and priming to ensure optimal adhesion and durability, typically applied using spray or dip techniques for uniform coverage. Polyurethane coatings demand a similarly clean and dry substrate but often benefit from light abrasion to enhance mechanical bonding, with application methods including brushing, rolling, or spraying depending on the project scale. Both materials necessitate controlled environmental conditions during application to prevent defects such as bubbling or incomplete curing, ensuring a high-performance protective finish.
Adhesion to Different Substrates
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits strong adhesion to glass and metal substrates due to its excellent surface energy compatibility and chemical bonding capabilities. Polyurethane coatings demonstrate superior adhesion on flexible and porous substrates such as wood, textiles, and plastics, owing to their elastomeric nature and versatile formulation options. The choice between PMMA and polyurethane depends on substrate type and application requirements, with PMMA favored for rigid, smooth surfaces and polyurethane preferred for dynamic or irregular surfaces.
Optical Clarity and Aesthetic Qualities
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity with over 90% light transmittance, making it ideal for coatings requiring high transparency and brilliance. Polyurethane coatings, while durable and flexible, typically have lower clarity and may exhibit slight yellowing over time, affecting aesthetic qualities. PMMA's resistance to UV degradation preserves its clarity and color stability, enhancing long-term visual appeal compared to polyurethane.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) coatings generally exhibit lower environmental impact due to their recyclability and resistance to UV degradation, leading to longer service life and reduced waste. Polyurethane coatings, while offering excellent durability and flexibility, often rely on isocyanates and solvents, which can contribute to higher VOC emissions and environmental toxicity during manufacture and application. Sustainable considerations favor PMMA for applications emphasizing recyclability and lower pollutant release, whereas advancements in bio-based polyurethanes aim to improve polyurethane's ecological footprint.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) coatings generally offer a lower initial cost compared to polyurethane, making them a budget-friendly choice for short-term applications. Polyurethane coatings provide superior durability and chemical resistance, justifying their higher price point, and dominate markets requiring long-lasting protective finishes. Market availability of PMMA is widespread in decorative and automotive sectors, while polyurethane maintains strong presence in industrial and marine coatings due to its robust performance characteristics.
Suitability for Specific Industries and Applications
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) coatings excel in optical clarity and UV resistance, making them highly suitable for automotive, signage, and display industries where aesthetics and durability against sunlight are critical. Polyurethane coatings offer superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and chemical durability, ideal for industrial equipment, flooring, and marine applications requiring robust protection against mechanical wear and harsh environments. Choosing between PMMA and polyurethane depends on the need for visual clarity and UV stability versus mechanical toughness and chemical resilience in specific industry use-cases.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyurethane for Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com